A Use Case describes a task that is performed by an actor yielding a result of business value for a business. A use case may be visualized as a use case diagram or/and in structured textual specification format:
Continue reading
Learning one new thing everyday

A Use Case describes a task that is performed by an actor yielding a result of business value for a business. A use case may be visualized as a use case diagram or/and in structured textual specification format:
Continue reading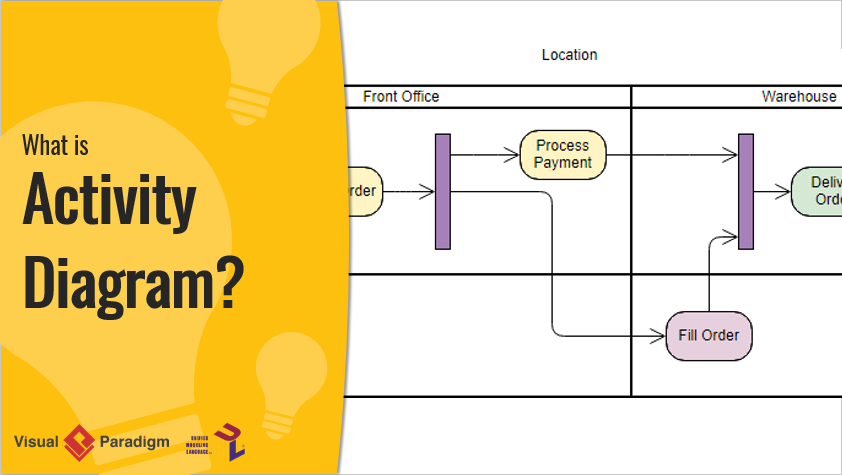
UML activity diagram is another common tool used by UML to model the dynamic behavior of the system. It describes the sequence of activities and shows the flow of control from one activity to another. UML activity diagram is essentially a flow chart.
Continue reading
A use case approach is a kind of technique for identifying the business goals of a system. The identification of use cases helps define system scope, ensuring that the requirements to be found will all be aligned with the business values, needs and strategy.
Continue reading
A use case is a requirements capture and documentation technique that can be written in plain text to describe in a narrative manner the actions and interactions of participants using the system. Finally, the functionality of the system should satisfy the purpose for which stakeholders use the system.
Continue reading
Use cases are often graphical, and use case diagrams are supported by text descriptions, including use case and participant descriptions, as well as scenarios associated with use case templates that make use case methods simple and intuitive and ideal tools for discussing and clarifying developers’ understanding of user needs.
Continue reading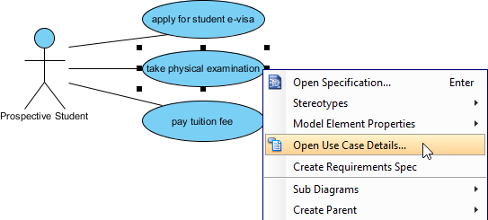
Use case modeling is a technique for capturing, modeling, and specifying system requirements that correspond to a set of behaviors that the system may perform when interacting with actors. These behaviors produce observable results and help achieve their goals. Use cases are named for the specific user goals of the principal actors, which in turn describe or explain the general order of activities and events, as well as variations in special conditions, exceptions, or error conditions, through textual description.
Continue reading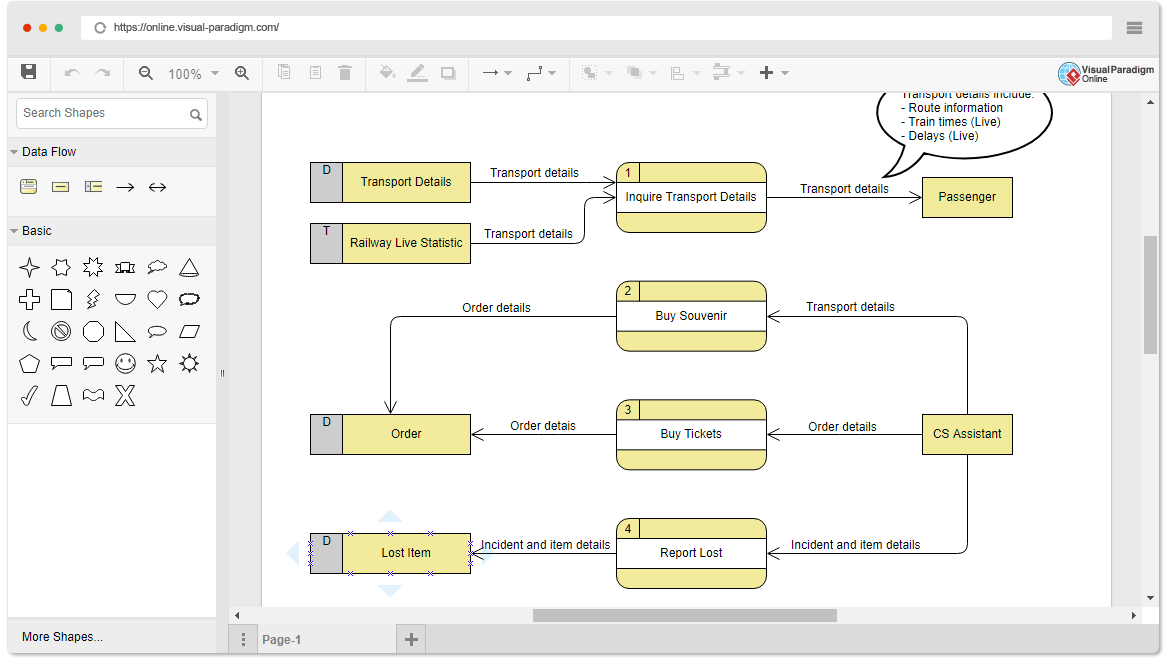
Although data flow oriented modeling is considered as an outdated technology by some software engineers, it is still one of the most widely used requirements analysis symbols. Although data flow diagrams (DFDs) are not formal parts of UML, they can be used to supplement UML diagrams and provide additional insight into system requirements and processes.
Continue reading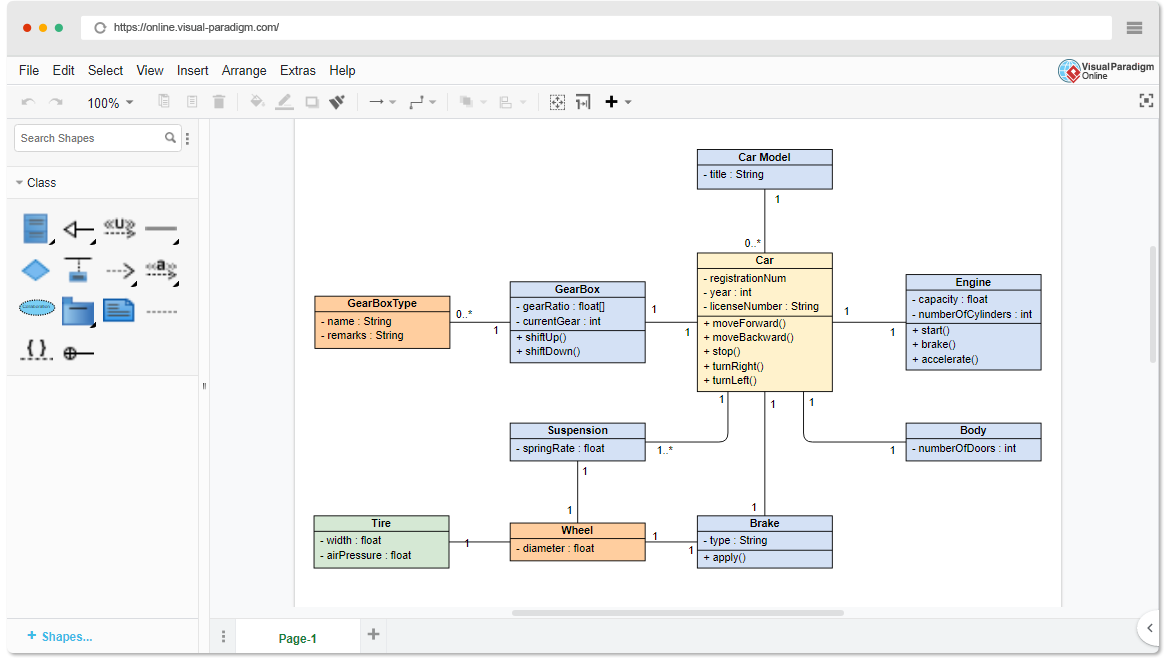
The Unified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language and nowadays is managed as a de facto industry standard by the Object Management Group (OMG). UML includes a set of graphic notation techniques to create visual models for software-intensive systems. In UML 2.2 there are 14 types of UML diagrams, which are divided into two categories
Continue reading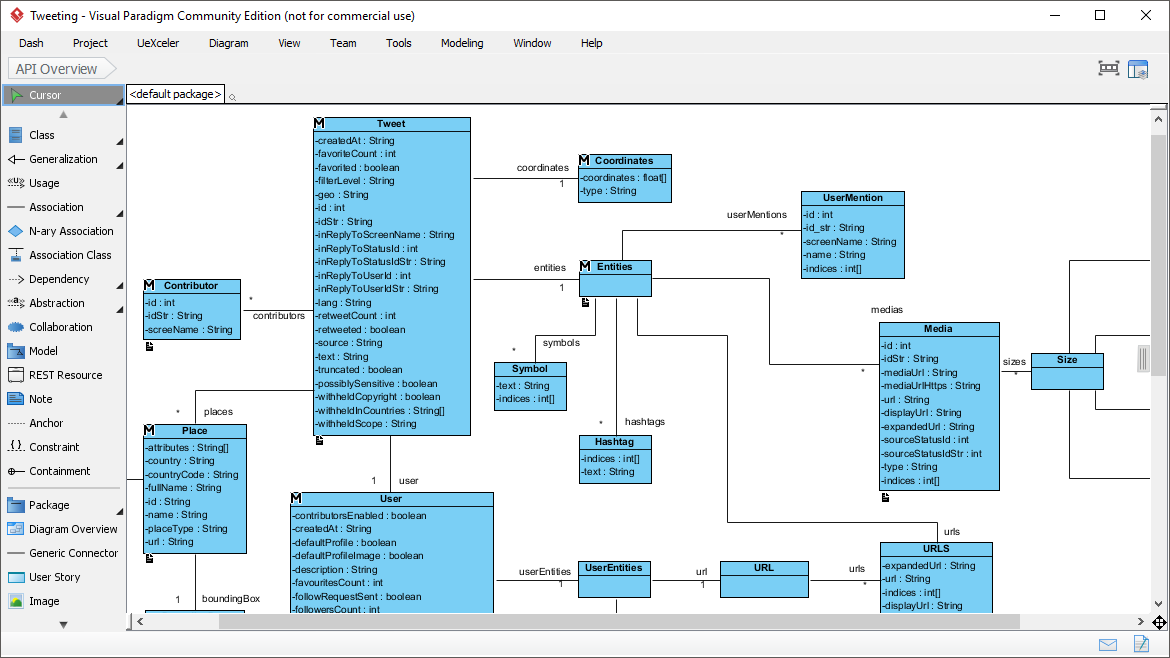
This Article will show you how to effectively apply UML modeling in both agile and just-in-time manner with the powerful Model ETL feature. A UML model or diagram is a specific view into what you are trying to understand in a specific context.
Continue reading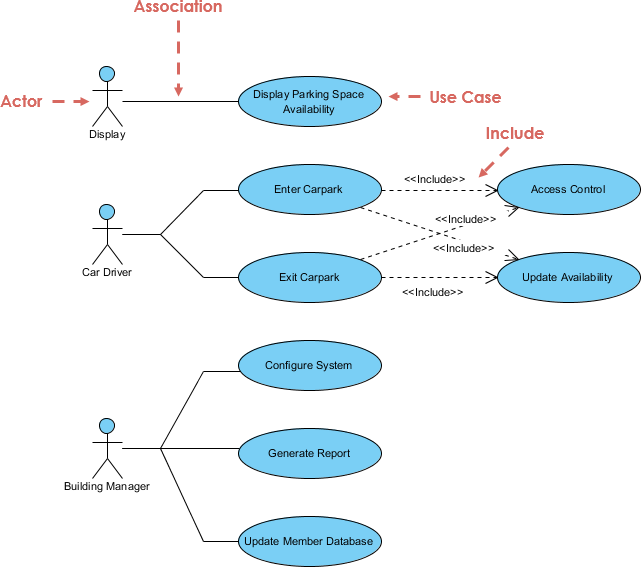
A UML use case diagram is the primary form of system/software requirements for a new software program under developed. Use cases specify the expected behavior (what) of a system, and not the exact method of making it happen (how). A complete set of use cases specifies all the different ways to use the system and therefore defines all behavior required of the system bounding the scope of the system.
Continue reading