In the high-stakes world of election technology and corporate governance, the integrity of a digital voting platform is paramount. A single bottleneck, security loop, or compliance oversight can compromise an entire election. Traditionally, system architects rely on manual reviews of state machine diagrams to catch these issues. However, the integration of Artificial Intelligence into modeling tools has revolutionized this process.
This comprehensive guide explores how to take a digital voting system from a conceptual workflow to a robust, AI-analyzed model using PlantUML and Visual Paradigm (VP) AI. We will demonstrate how to move beyond static diagrams to proactive, data-driven system optimization.
Step 1: Understanding the Digital Voting Workflow
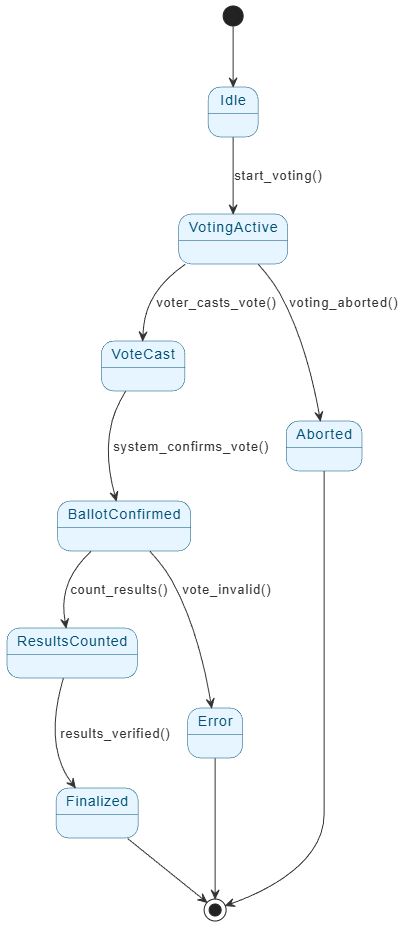
Before writing code or drawing diagrams, it is essential to map the lifecycle of a vote. A robust digital voting system enables secure, transparent, and auditable interactions. The core state machine typically follows this progression:
- Idle: The system initializes and waits for the voting period to begin.
- Voting Active: The window opens, and authenticated users are permitted to cast votes.
- Vote Cast: A user submits a vote, triggering validation protocols.
- Ballot Confirmed: The system validates the authenticity of the vote and confirms receipt.
- Results Counted: All valid confirmed ballots are tallied.
- Finalized: Results are cryptographically sealed and made publicly available.
- Error or Aborted: The system handles invalid votes, connection failures, or user-initiated cancellations.
The Goal: Our objective is to model this process using a clear state machine diagram and then leverage VP AI to detect risks, identify performance bottlenecks, and suggest architectural improvements.
Step 2: Creating the Baseline Model with PlantUML
The foundation of our analysis is a syntactically correct PlantUML state diagram. PlantUML allows architects to define systems using code, which renders into clean, professional visual documentation.
How to Implement the Diagram
Once you have your PlantUML source code defining the states mentioned above (Idle through Finalized), the process is straightforward:
- Draft the Code: Write the state transitions in any PlantUML editor (e.g., VS Code, PlantText).
- Import to Visual Paradigm: Paste the code into Visual Paradigm’s editor to render the visual model.
- Baseline Creation: This establishes the standard behavior of your system, ready for AI analysis.
Step 3: Transforming Static Diagrams with Visual Paradigm AI
This is where the process shifts from traditional documentation to intelligent engineering. Visual Paradigm (VP) AI analyzes the diagram to uncover issues that human review might miss.
Manual vs. AI-Powered Modeling
Traditional modeling relies on manual inspection, which is time-consuming and prone to error. VP AI transforms this by offering:
- Bottleneck Detection: Instead of manual guessing, AI auto-identifies high-risk transitions where data might clog.
- Risk Scoring: AI assigns quantitative risk levels (High/Medium/Low) to specific states.
- Performance Suggestions: The system recommends optimizations like rate limiting or parallel processing.
- Security Scanning: It flags potential attack vectors such as vote flooding.
- Compliance Checks: It ensures alignment with regulations like GDPR or EAC (Election Assistance Commission) standards.
Step 4: How VP AI Enhances the Digital Voting Use Case
Let’s analyze how specific VP AI features directly improve the reliability and security of a digital voting platform.

1. Automated Risk & Bottleneck Detection
The Challenge: In a real-world election, a slight delay in vote validation can be exploited by attackers via timing attacks or vote flooding.
VP AI Insight: Upon scanning the VoteCast → BallotConfirmed transition, VP AI identifies a High-Risk state. It recognizes that without explicit rate limiting, the system is vulnerable to flooding.
Actionable Suggestion: The AI recommends adding a “rate limit” guard at the VoteCast stage and requiring a cryptographic voter ID to throttle inputs effectively.
2. Security Vulnerability Scanning
The Challenge: Digital systems must resist spoofing, duplication, and external manipulation.
VP AI Insight: The AI detects critical logic gaps, such as duplicate vote paths (e.g., a user triggering multiple VoteCast events) or a lack of audit logging in the BallotConfirmed state.
Actionable Suggestion: Implement strict voter identity checks (biometric or digital ID) and ensure every state transition logs a timestamp, IP address, and device hash. Furthermore, automated alerting should be attached to the Error state to flag suspicious spikes in invalid votes.
3. Performance & Scalability Recommendations
The Challenge: Elections involve massive concurrency. A poorly designed aggregation phase can crash under the load of thousands of simultaneous voters.
VP AI Insight: The analysis flags the ResultsCounted state as a throughput bottleneck, noting that linear counting will fail at scale.
Actionable Suggestion: Adopt a microservice architecture with asynchronous vote processing. The AI suggests splitting vote counting into batches or utilizing a distributed ledger (blockchain) for parallel counting.
4. Compliance & Audit Alignment
The Challenge: Voting systems operate under strict legal frameworks ensuring secrecy and immutability.
VP AI Insight: The AI checks if the Finalized state is truly immutable. It flags missing audit trails or potential breaches in voter anonymity.
Actionable Suggestion: Finalize results using a cryptographic hash (e.g., SHA-256) and store logs in a tamper-evident format. Ensure the architecture decouples the vote from the user identity to satisfy privacy laws.
5. Automated Reports & Visual Insights
The Challenge: Communicating technical risks to non-technical stakeholders (auditors, project managers) is difficult with raw code.
VP AI Solution: The tool generates structured reports including:
- Risk Heatmaps: Visual overlays showing high-risk transitions.
- Performance Scorecards: Clear metrics on system health.
- Compliance Summaries: A checklist of regulatory adherence.
Summary: The Business Value of AI-Driven Modeling
Integrating AI-powered modeling into your design workflow shifts your team from reactive bug-fixing to proactive system hardening. By automating risk detection, you prevent vote manipulation and fraud before a single line of production code is written. You ensure scalability for large elections and guarantee compliance with international standards.
Final Steps for Your Team
- Design: Create your state diagram using PlantUML.
- Analyze: Upload the diagram to Visual Paradigm and run the AI Analysis.
- Refine: Review the AI-generated recommendations regarding risks, bottlenecks, and compliance.
- Report: Export the comprehensive report to share with stakeholders.
Pro Tip: Use VP’s AI-powered requirement generation to instantly turn risk insights into formal project requirements (e.g., “System must validate votes within 500ms”).
Conclusion
The state machine diagram for a digital voting platform is a foundational model, but its true power lies in how it is analyzed. With Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered features, you do not just draw a diagram; you mathematically validate it. This approach transforms the design process, ensuring your digital voting system is secure, reliable, scalable, and fully compliant.
Resources
- A plug-in to convert VP UML models to/from PlantUML
- The Ultimate Guide to C4-PlantUML Studio: Revolutionizing …
- C4-PlantUML Studio | AI-Powered C4 Diagram Generator
- Why PlantUML Is a Smart Choice for Architecture Documentation
- Software Architecture & Diagramming Articles | PlantUML …
- Does email marketing still make sense? – Visual Paradigm Blog
- VOTING SYSTEM.vpd | Visual Paradigm User-Contributed Diagrams / Designs
- Voting Registration Data Flow Diagram | Visual Paradigm User-Contributed Diagrams / Designs
- How AI Chatbot Can Help You Learn UML Faster – Visual Paradigm Blog
- Database Design Software & ERD Tool | Visual Paradigm
- Electronic voting system | Visual Paradigm User-Contributed Diagrams / Designs
- Voting Activity Diagram | Visual Paradigm User-Contributed Diagrams / Designs
- Case Study: Enhancing System Modeling Efficiency with Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered Chatbot – Visual Paradigm Blog
- Visual Paradigm Online Shop
- Visual Paradigm AI: Advanced Software & Intelligent Apps
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский and Việt Nam.









