In the evolving landscape of digital design and system architecture, the ability to rapidly generate accurate, standard-compliant diagrams is invaluable. The Visual Paradigm AI chatbot distinguishes itself by adhering strictly to formal modeling standards rather than merely producing generic visualizations. With support for over 20 distinct diagram types across multiple professional domains, it serves as a robust tool for engineers, architects, and business strategists.
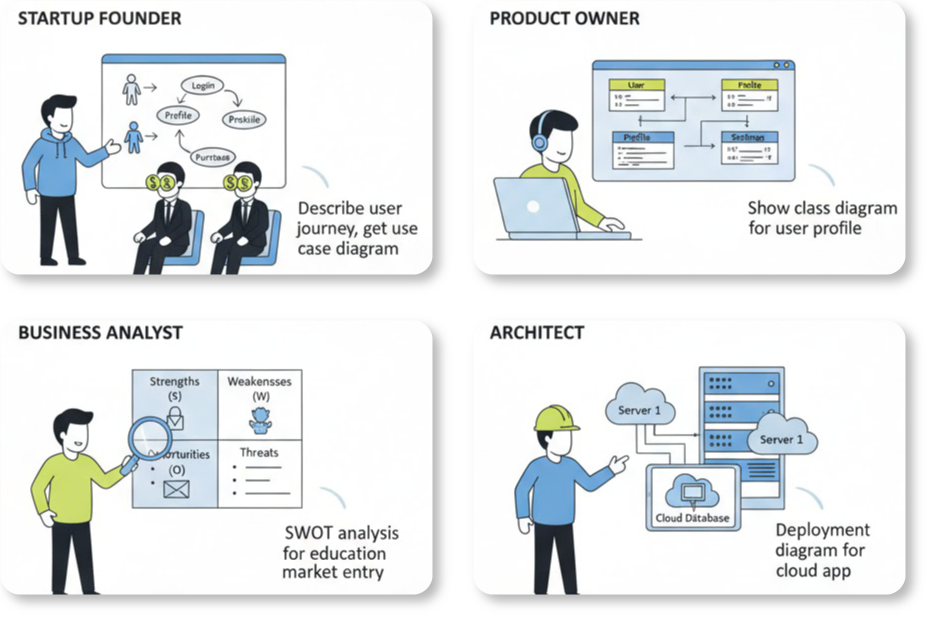
This guide explores the extensive range of frameworks and standards supported by the AI, detailing how it bridges the gap between natural language requirements and technical diagramming.
1. Software and Systems Engineering Standards
For software developers and systems engineers, precision is paramount. The Visual Paradigm AI chatbot is engineered to understand the specific semantics and syntax required by major engineering frameworks.
Unified Modeling Language (UML)
The AI supports the full spectrum of UML diagrams, ensuring that the structural and behavioral aspects of software systems are represented accurately. It goes beyond simple drawing by understanding complex relationships, such as the distinction between aggregation and composition in class structures or the management of branching logic in interaction flows. Supported diagram types include:

- Class Diagrams: For modeling static system structure.
- Sequence Diagrams: For visualizing object interactions over time.
- Use Case Diagrams: For capturing functional requirements.
- Activity and State Machine Diagrams: For modeling workflow and object states.
- Component, Package, Deployment, Object, and Composite Structure Diagrams: For detailed architectural views.
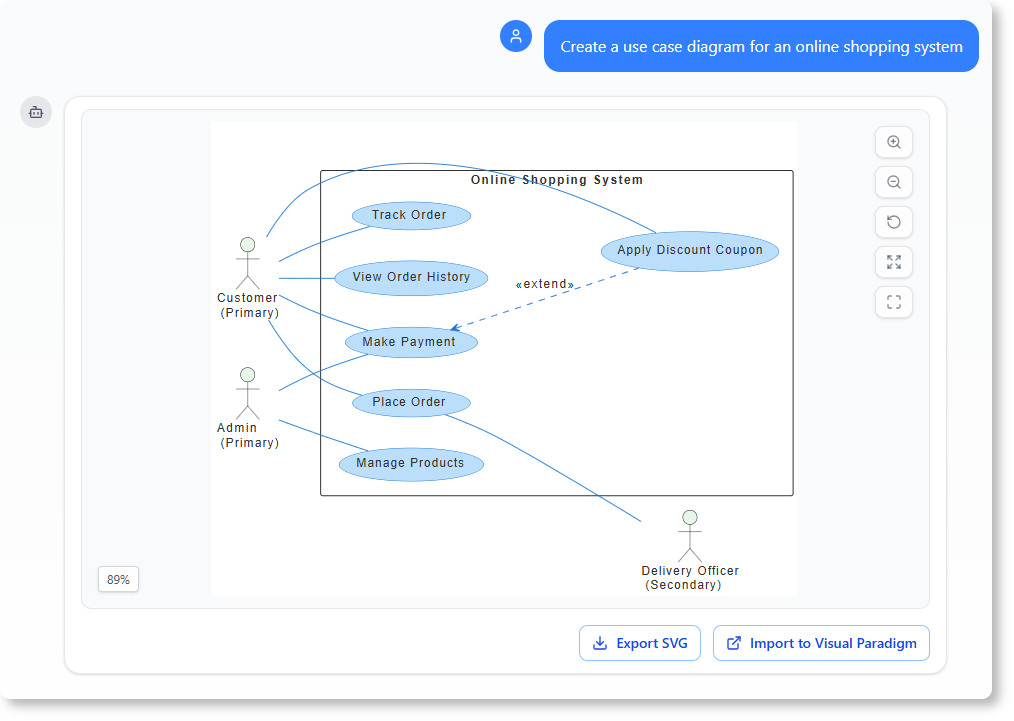
The C4 Model
To visualize software architecture at various levels of abstraction, the AI implements the C4 model. This allows teams to generate diagrams that map hierarchies effectively, including: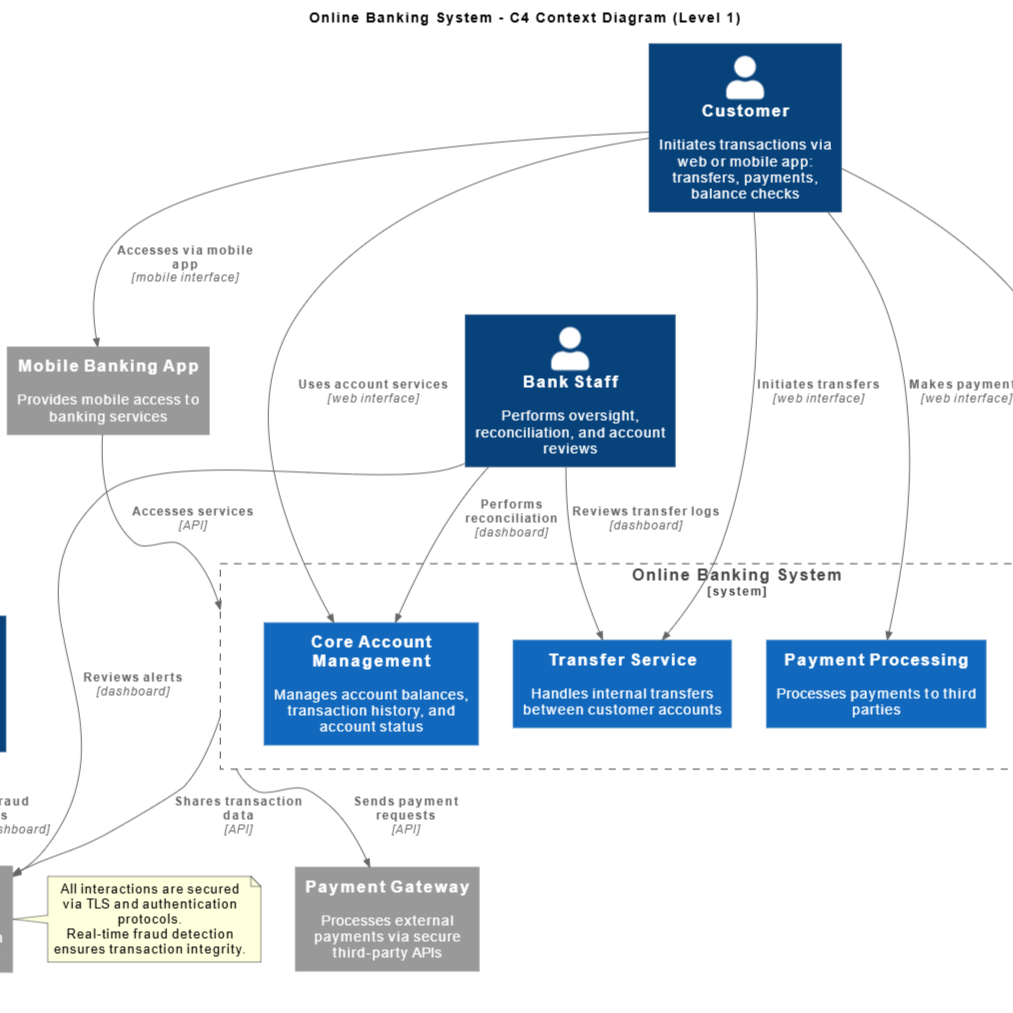
- System Context Diagrams: High-level interactions with external systems and users.
- Container Diagrams: Applications and data stores within the system.
- Component and Deployment Diagrams: Detailed structural and infrastructure views.
Systems Modeling Language (SysML)
For systems engineering applications, the AI generates diagrams essential for defining complex physical and digital systems. Key capabilities include:
- Requirement Diagrams: To trace and manage system requirements.
- Block Definition and Internal Block Diagrams: To define the structural elements and internal connections of a system.
2. Enterprise Architecture with ArchiMate
Enterprise Architects utilize the ArchiMate language to describe, analyze, and visualize the relationships across business domains. The Visual Paradigm AI provides deep support for this standard, covering over 20 different viewpoints. This extensive coverage allows for holistic modeling across several layers:
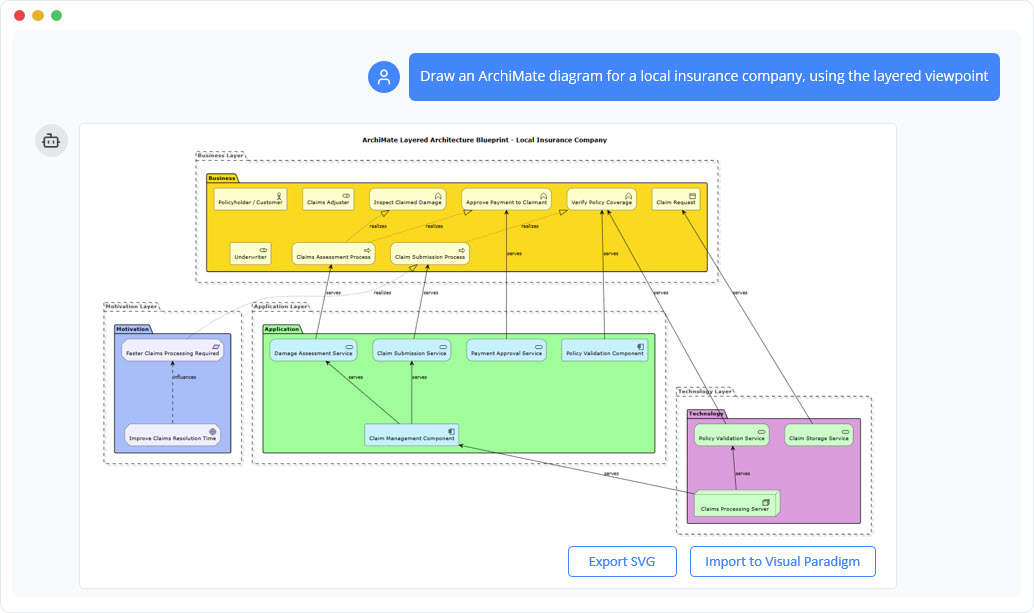
- Motivation and Strategy: Aligning IT with business goals.
- Business Layer: Mapping processes and organizational services.
- Application and Technology Layers: defining software and infrastructure landscapes.
- Implementation and Migration: Planning the transition from current to future states.
3. Business Process and Strategy Frameworks
Beyond technical architecture, the AI is equipped to handle high-level business strategy and process visualization, making it a versatile tool for management consultants and business analysts.
Strategic Analysis Tools
The AI facilitates environmental scanning and competitive analysis through standard frameworks:
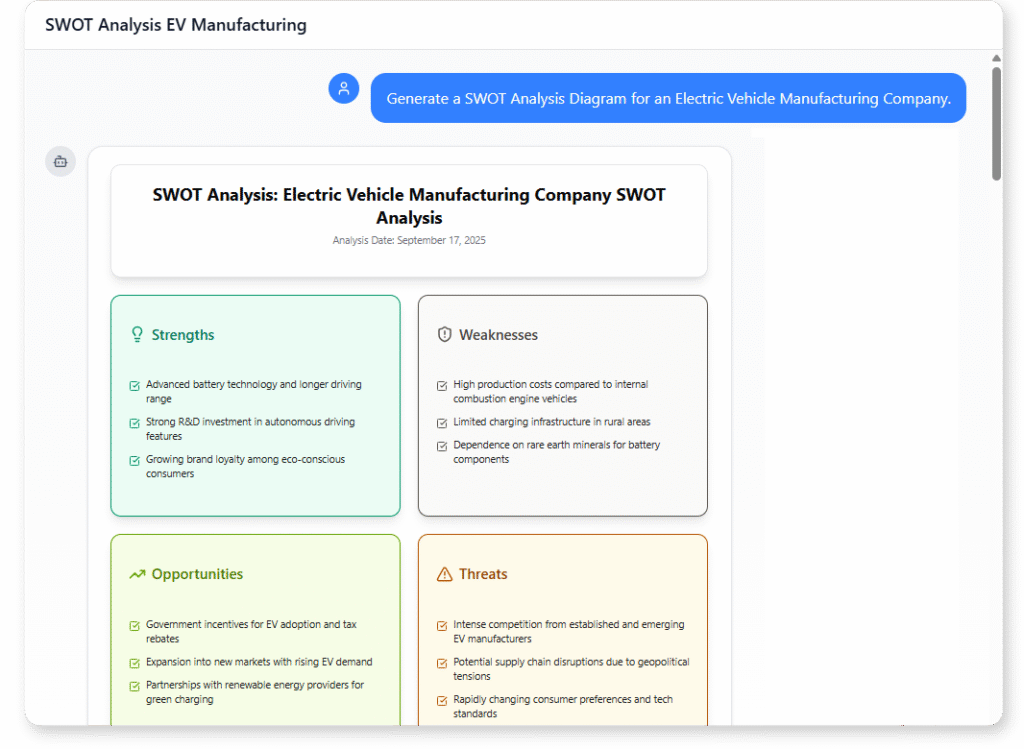
- SWOT Analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- PEST/PESTLE Analysis: Macro-environmental factors (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental).
- SOAR Analysis: Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, and Results.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Analyzing industry competitive intensity.
Management Frameworks
Decision-making and organizational planning are supported through specific matrix generations:
- Ansoff Matrix: For analyzing product-market growth strategies.
- Eisenhower Matrix: For time management and prioritization.
- McKinsey 7S Model: For organizational effectiveness.
- Blue Ocean Four Actions Framework: For value innovation.
- Marketing Mix 4Cs: A consumer-oriented alternative to the 4Ps.
Process Modeling
To visualize workflows and operational efficiency, the AI supports:
- BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation): The industry standard for business process diagrams.
- Flowcharts: For general process mapping.
- PERT Charts: For project management and scheduling.
4. Information and Data Design
Data integrity lies at the core of application design. The AI simplifies database modeling by generating Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD), allowing developers to visualize entities, attributes, and relationships clearly.
Additionally, for general information visualization and brainstorming, the tool supports:
- Mind Maps: For brainstorming and organizing ideas.
- Organization Charts: For structural hierarchy.
- Analytical Charts: Including Radar Charts, Bar Charts, and Pie Charts for data representation.
Understanding the “Translator” Capability
To understand how Visual Paradigm AI operates, it is helpful to view it as a multilingual translator at a global technology summit. In this analogy, the user provides a narrative or a set of requirements in plain English—this is the “story.”
Just as a human translator must grasp the grammar, syntax, and cultural nuances of languages like French or Mandarin to convey a message accurately, this AI understands the rigid “grammars” of UML, ArchiMate, and BPMN. It translates the user’s plain text description into the precise technical language required by the specific framework, ensuring that the resulting visual is not just an image, but a formally valid diagram.

