In the fast-paced world of software development, business analysis, and enterprise architecture, clear visual communication is essential. UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagrams remain one of the most powerful ways to capture and share system requirements and design decisions. Among them, use case diagrams stand out as the go-to tool for illustrating how users (or external systems) interact with a solution, focusing on “what” the system does rather than “how” it does it.
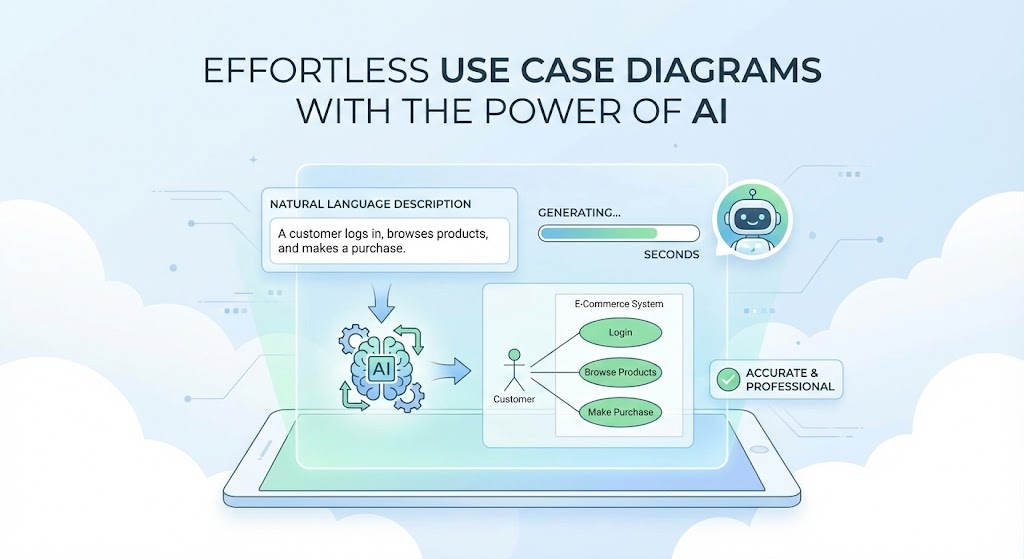
Traditionally, creating these diagrams has been a labor-intensive process—hours spent in tools like Microsoft Visio or Visual Paradigm, dragging shapes, aligning connectors, and manually enforcing UML standards. This manual effort often excludes non-technical stakeholders and slows down agile teams.
Today, AI-powered tools are changing everything. By describing your system in plain English, you can instantly generate professional, standards-compliant use case diagrams. Two standout platforms leading this revolution are Visual Paradigm AI (with its dedicated AI Diagram Generator and Chatbot) and the emerging generation of “text-to-diagram” tools. This article explains the fundamentals of use case diagrams, how AI is reshaping the process, and why Visual Paradigm AI is becoming an essential platform for modern visual modeling in 2025.
What Are UML Use Case Diagrams and Why Do They Matter?
A use case diagram is a behavioral UML diagram that shows the relationships between actors (users or external systems) and use cases (functional goals the system provides). It is ideal for requirements gathering, stakeholder alignment, and high-level design.
Core Elements of a Use Case Diagram
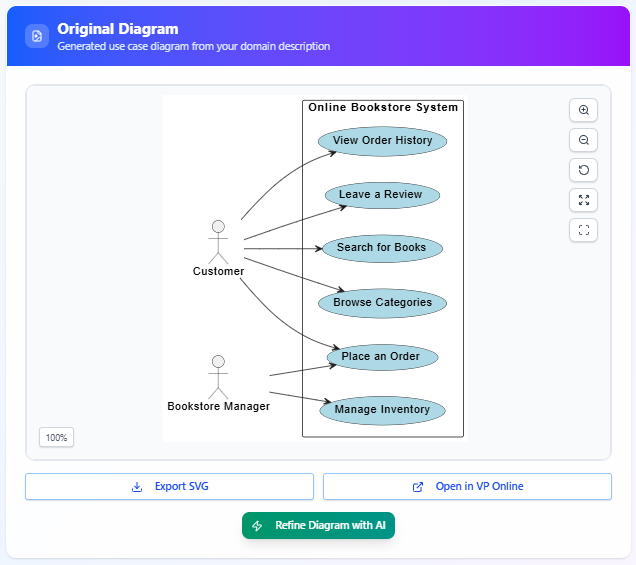
- Actors – Stick-figure symbols representing people or systems that interact with your solution (e.g., Customer, Administrator, Payment Gateway).
- Use Cases – Ovals inside a system boundary that represent specific functionalities (e.g., Place Order, View Balance, Generate Report).
- System Boundary – A rectangle that separates what’s inside the system from the outside world.
- Associations – Lines connecting actors to the use cases they can perform.
- Relationships:
- Include – Mandatory reuse: one use case always incorporates another (e.g., “Login” is included in “Place Order”).
- Extend – Optional or conditional behavior: an extending use case adds functionality under certain conditions (e.g., “Apply Discount” extends “Checkout”).
- Generalization – Inheritance between use cases (less common).
When diagrams follow these rules correctly, they promote clarity, modularity, and reusability—reducing misunderstandings, scope creep, and costly rework.
The AI Revolution: From Manual Drawing to Instant Intelligence
AI tools now leverage natural language processing (NLP), large language models, and UML-specific training data to interpret text descriptions and produce accurate diagrams in seconds. The result is a dramatic shift from tedious drag-and-drop to descriptive, iterative modeling.
How AI-Powered Tools Work (in Three Simple Steps)
- Describe Your System in Natural Language Write a clear description, including stakeholders, goals, and key functionalities. Example: “An e-commerce platform where customers browse products, add items to a cart, checkout with credit card or PayPal, and track orders. Guests can register. Administrators manage inventory and process refunds. Optional gift wrapping is available during checkout.”
- Generate the Diagram Instantly The AI identifies actors, use cases, associations, and the system boundary, then produces a clean, well-organized diagram with live preview.
- Refine and Explore with AI One-click refinement automatically adds include/extend relationships, suggests generalizations, and detects missing elements. Repeated refinements cycle through alternative structures, revealing hidden scenarios and edge cases you might have overlooked.
Why Visual Paradigm AI Stands Out in 2025
While many AI diagramming tools are emerging, Visual Paradigm AI (available at visual-paradigm.com and chat.visual-paradigm.com) is the most mature and comprehensive solution. Here’s why it’s becoming indispensable:
1. Broad Diagram Support Beyond Use Cases
Supports dozens of diagram types:
- All 14 UML diagram types
- SysML
- ArchiMate
- C4 models
- Business frameworks (SWOT, PESTLE, Business Model Canvas, etc.)
2. Enterprise-Grade Standards Compliance
Trained on official OMG specifications, the AI enforces UML 2.5+ best practices, automatically applying correct notation, relationship usage, and layout rules.
3. Seamless Integration with the Full Visual Paradigm Ecosystem
- Export generated diagrams directly to Visual Paradigm Desktop or Online for advanced editing, version control, and team collaboration.
- Real-time cloud co-editing.
- Generate documentation, code stubs, or reports from your models.
4. Conversational AI Chatbot for Refinement
Ask questions like “Add a payment gateway actor,” “Explain why you chose an extend relationship here,” or “Show me an alternative structure.” The AI responds with updated diagrams and explanations—perfect for learning and iteration.
5. Democratizes Modeling for All Skill Levels
- Non-technical stakeholders can describe ideas and receive professional visuals.
- Beginners learn UML faster with built-in explanations.
- Experts save hours on repetitive tasks and focus on high-value design decisions.
6. Proven Productivity Gains
Users report 5–10× faster diagram creation, consistent styling across teams, and faster exploration of alternatives—leading to better requirements, fewer defects, and accelerated delivery.
Real-World Examples
Example 1: E-Commerce Platform
Input description → Instant diagram with actors (Customer, Guest, Administrator, Payment Gateway), use cases (Browse Products, Add to Cart, Checkout, Track Order, etc.), and refinements such as:
- Include “Authenticate User” in Checkout
- Extend “Checkout” with “Apply Gift Wrapping”
- Generalize “Payment Method” into Credit Card and PayPal
Example 2: Hospital Management System
Input description → Actors (Patient, Doctor, Nurse, Insurance Provider), use cases (Book Appointment, View Records, Process Billing, etc.), and AI-suggested refinements:
- Include “Verify Insurance” in Process Billing
- Extend “Book Appointment” with “Emergency Booking”
- Include “Notify Patient” across multiple use cases
These examples show how AI not only saves time but also uncovers insights and compliance considerations that manual modeling might miss.
The Future of Visual Modeling
As AI continues to evolve, expect even deeper integration—automatic code generation, full UML suite support, collaborative VR editing, and real-time model synchronization across tools. The trend is clear: “descriptive design,” where humans articulate ideas in natural language and AI handles the visuals and standards compliance.
Conclusion: Stop Drawing, Start Describing
In 2025, manual diagramming is quickly becoming obsolete. Tools like Visual Paradigm AI empower teams to create accurate, professional UML use case diagrams—and many other diagram types—in seconds, while maintaining enterprise rigor and collaboration features.
Whether you’re a software architect, business analyst, developer, or product owner, Visual Paradigm AI eliminates the biggest barriers to effective visual modeling: time, expertise, and consistency. It doesn’t replace your judgment—it amplifies it, letting you focus on innovation rather than drawing lines.
Ready to experience the future of visual modeling? Visit visual-paradigm.com or try the AI Chatbot at chat.visual-paradigm.com today. Your next diagram is just a description away.
