Database design has traditionally been a complex task requiring deep technical expertise in SQL, normalization rules, and architectural patterns. However, modern tools like DB Modeler AI are revolutionizing this landscape by enabling users to transform natural language descriptions into production-ready schemas. This comprehensive guide details the seven-step workflow of DB Modeler AI, offering key concepts, detailed guidelines, and practical tips to maximize your database engineering efficiency.
 Key Concepts
Key Concepts
Before diving into the workflow, it is essential to understand the foundational terminologies and technologies that power the DB Modeler AI engine.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The technology used to interpret plain English descriptions and convert them into structured technical requirements.
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD): A graphical representation that depicts relationships among people, objects, places, concepts, or events within an information system.
- PlantUML: An open-source tool used to create diagrams from a plain text language, utilized here for initial domain visualization.
- Normalization (1NF – 3NF): The process of organizing data in a database. This involves creating tables and establishing relationships between those tables according to rules designed both to protect the data and to make the database more flexible by eliminating redundancy and inconsistent dependency.
- DDL (Data Definition Language): A syntax similar to a computer programming language for defining data structures, especially database schemas (e.g., CREATE TABLE statements).
Guidelines: The 7-Step Workflow
The DB Modeler AI workflow is a structured journey from a vague idea to a polished technical asset. Follow these guidelines to navigate each stage effectively.
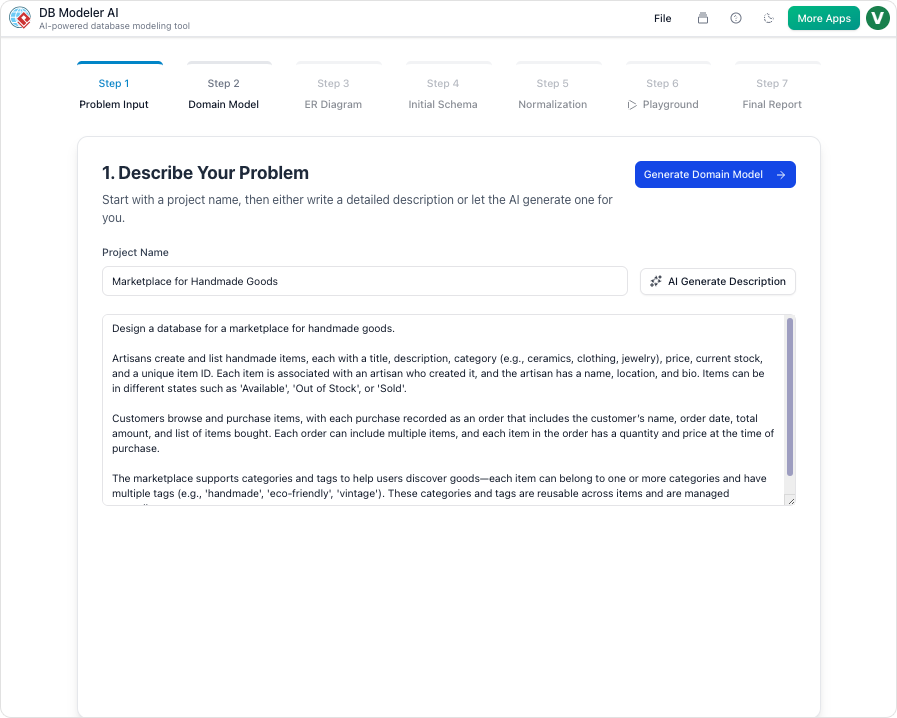
Step 1: Problem Input and Requirement Analysis
The process begins with the user articulating their business needs. Unlike traditional tools that require code immediately, this step accepts plain English. The AI analyzes this input to extract entities, attributes, and logic, expanding them into a set of comprehensive technical requirements.
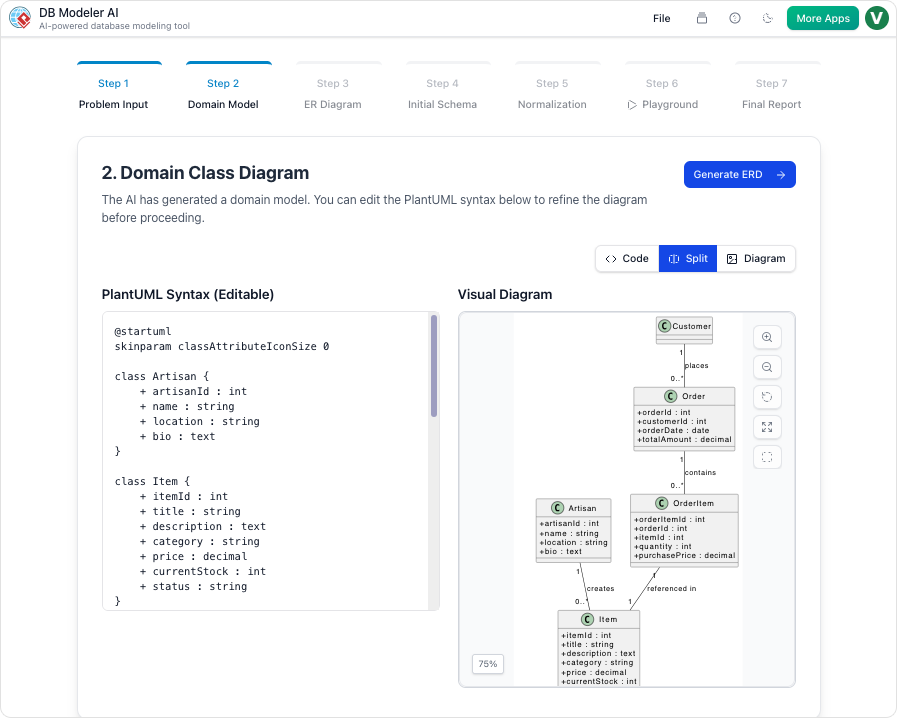
Step 2: Domain Class Diagram Visualization
Once the requirements are set, the system generates a conceptual view using an editable PlantUML diagram. This visualizes high-level objects and their attributes without getting bogged down in database specificities yet. It serves as a structural blueprint.
Step 3: Conversion to ER Diagram
The conceptual model is then transformed into a rigorous Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD). At this stage, the logic becomes database-specific. The system defines primary keys, foreign keys, and the cardinality of relationships (e.g., one-to-many, many-to-many) between tables.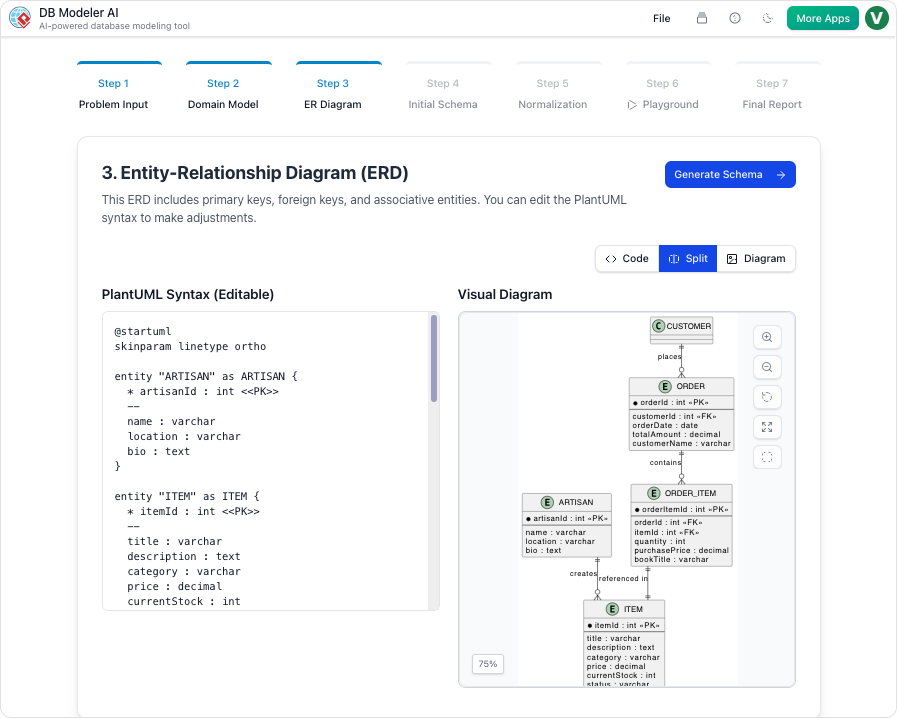
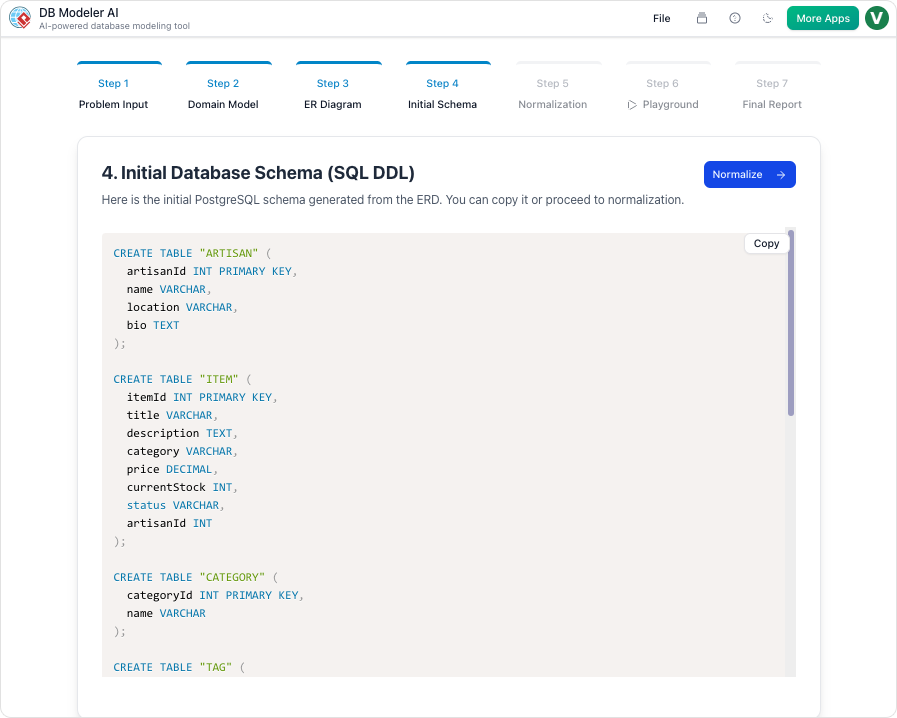
Step 4: Initial Schema Generation
With the relationship map finalized, the platform translates the diagram into executable code. It generates technical PostgreSQL-compatible SQL DDL statements. This code creates the actual tables and constraints that act as the foundation for the database.
 tep 5: Intelligent Normalization
tep 5: Intelligent Normalization
One of the most critical steps is the progressive optimization of the schema. The AI moves the design from the First Normal Form (1NF) up to the Third Normal Form (3NF). Uniquely, the tool provides educational rationales for every structural change, explaining why data redundancy was removed or how data integrity was improved.
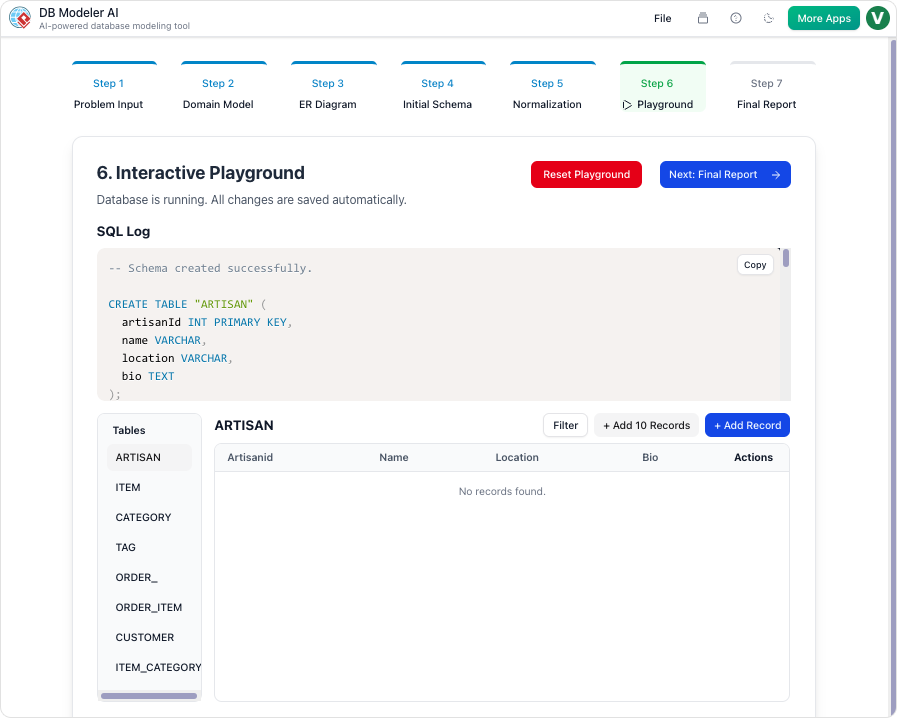
Step 6: The Interactive Playground
Theory meets practice in the in-browser SQL client. The system automatically seeds the new schema with realistic AI-generated sample data. This allows users to write queries and test the database logic immediately without needing to manually populate tables.
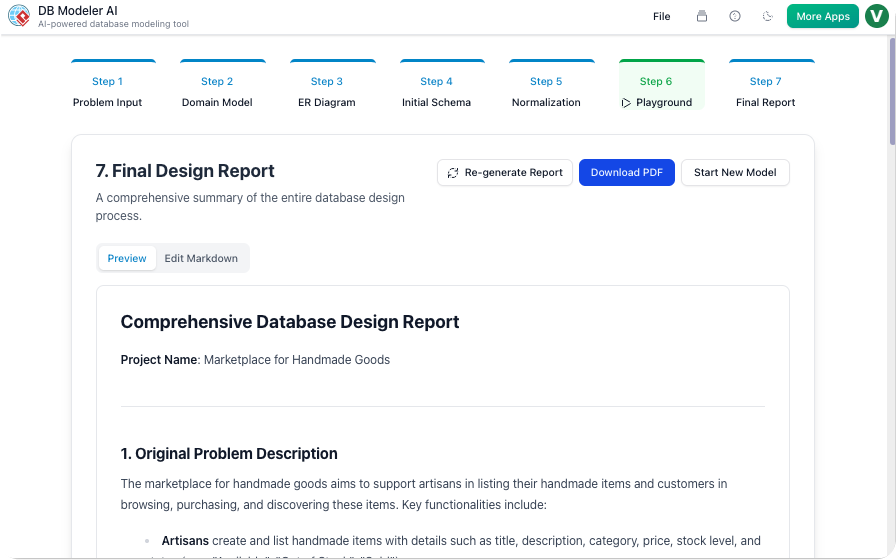
Step 7: Final Report and Export
Upon completion, the design is packaged for deployment. The platform compiles all diagrams, technical documentation, and SQL scripts into a polished PDF or JSON format. This ensures that the documentation matches the code implementation perfectly.
Tips and Tricks
To get the most out of DB Modeler AI, consider the following optimization strategies:
- Be Descriptive in Step 1: The quality of the output depends heavily on the input. Include specific business rules (e.g., “A user can have multiple addresses, but only one primary address”) in your plain English description to ensure the initial requirements are accurate.
- Review the Normalization Rationales: Do not skip the educational notes provided in Step 5. Understanding why the AI split a table will help you maintain the database in the future and make you a better database architect.
- Stress Test in the Playground: Use the generated sample data to run complex JOIN queries. This helps verify that the relationships defined in Step 3 support the analytical questions you intend to ask of your data.
- Iterate on Diagrams: Since the PlantUML diagrams in Step 2 are editable, use this phase to catch structural errors before they become SQL code. It is much easier to fix a diagram than to refactor a populated database.
This is the primary product landing page for DBModeler AI, offering a clear overview of its AI-driven features, including domain modeling, ER diagrams, schema generation, and live SQL testing—making it a top match.
This release notes page highlights the most recent updates and improvements to DBModeler AI, ideal for users looking to stay current with the tool’s evolving functionality.
This guide offers a thorough exploration of DBModeler AI’s integration of expert guidance, visual diagramming, and live SQL testing—key aspects for users evaluating its real-world application.
While not focused solely on AI, this tutorial demonstrates practical database design workflows in Visual Paradigm, the platform hosting DBModeler AI, providing valuable context for users adopting the tool.
This free tool page highlights Visual Paradigm’s ERD capabilities, which are foundational to DBModeler AI’s functionality—making it a relevant resource for users interested in database modeling fundamentals.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













