The Evolution of Database Architecture
In the process of database design, the progression from a Class Diagram to an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) and finally to Third Normal Form (3NF) represents increasing levels of architectural maturity. This evolution is critical for building robust, scalable software systems. However, moving between these stages often involves significant manual effort and a high risk of technical error. Visual Paradigm’s AI DB Modeler acts as a technological bridge, automating these transitions to streamline development and ensure precision.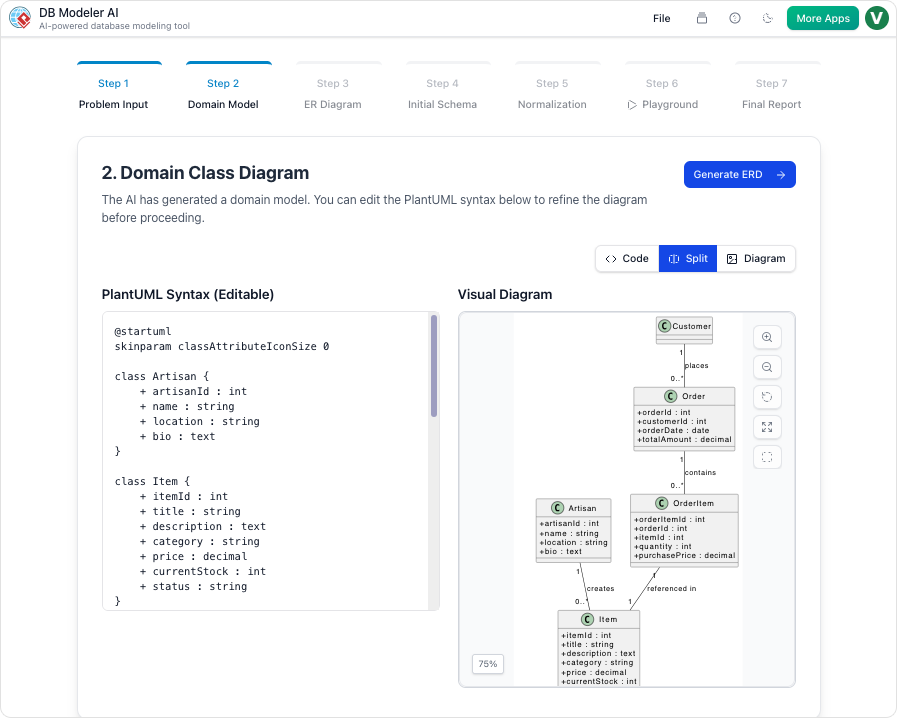
The Two Critical Gaps in Database Design
The transition is rarely seamless because each stage serves a fundamentally different purpose in the development lifecycle. Understanding these “gaps” is the first step toward overcoming them.
The Conceptual Gap: Class Diagram to ERD
A Class Diagram is a conceptual, high-level view that describes a system’s objects and behaviors using Unified Modeling Language (UML). At this stage, the design is not constrained by strict database rules. The “Conceptual Gap” occurs when shifting this abstract view into the technical realm. An ERD requires defining physical constraints such as primary keys, foreign keys, and specific column types, necessitating a translation from object-oriented thinking to relational logic.
The Optimization Gap: ERD to 3NF
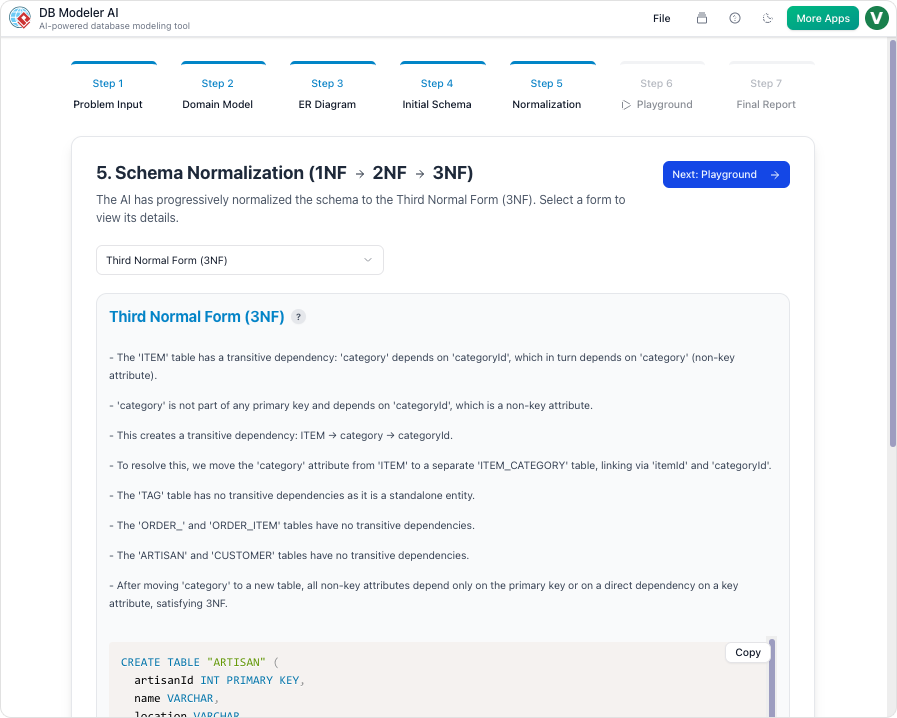
Once an ERD is established, it defines the initial structure, but it is rarely optimized immediately. The “Optimization Gap” refers to the distance between a raw table structure and a normalized database. An initial ERD often contains data redundancy or is prone to data anomalies—errors that occur during updates or deletions. Normalization is the rigorous process of refining these structures to ensure data integrity. Manually achieving Third Normal Form (3NF)—where all attributes depend only on the primary key—is time-consuming and requires deep architectural expertise.
Comparing Design Stages
To better visualize the differences between these stages, consider the following comparison of their primary functions:
| Design Stage | Primary Focus | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Class Diagram | Conceptual Objects | Describes behaviors and high-level attributes without database constraints. |
| ER Diagram (ERD) | Relational Structure | Defines tables, foreign keys, and physical data types. |
| 3rd Normal Form (3NF) | Data Integrity | Eliminates redundancy and ensures dependencies are logical. |
Bridging the Gap with AI DB Modeler
Visual Paradigm’s platform utilizes a comprehensive 7-step guided workflow to automate this entire evolution, effectively closing the gaps between concept and implementation.
- Step 1: Problem Input – Users describe their requirements in plain English. The AI interprets this intent and expands it into detailed technical requirements.
- Step 2: Domain Class Diagram – The system generates a conceptual view using PlantUML, defining high-level objects and attributes without the need for manual drawing.
- Step 3: ER Diagram Generation – The AI automatically converts the class model into a database-specific ERD, intelligently defining relationships and foreign key constraints.
- Step 4: Initial Schema Creation – The logical ERD is translated into executable, PostgreSQL-compatible SQL DDL statements.
- Step 5: Intelligent Normalization – This is a critical differentiator where the AI optimizes the schema from 1NF through to 3NF. Unlike traditional tools, it provides educational rationales for every change, helping developers understand how redundancy is eliminated.
- Step 6: Interactive Playground – Users can validate the normalized design in an in-browser SQL client seeded with realistic, AI-generated sample data for immediate testing.
- Step 7: Final Report and Export – The optimized design is exported as a professional PDF or JSON package, ready for implementation.
Key AI Features for Enhanced Productivity
Beyond the core workflow, specific features are designed to enhance the speed and accuracy of the design process.
Conversational Refinement
The AI Chatbot allows for iterative design changes through natural language commands. Instead of manually dragging and dropping columns, a user can simply instruct the system to “Add a payment gateway” or “Split the address field,” and the model updates instantly.
Model Traceability
The Model Transitor maintains strict synchronization between conceptual, logical, and physical models. This ensures that as the design evolves, the original intent captured in the Class Diagram remains consistent with the final SQL schema.
Live Analysis
Users can query the AI regarding their specific diagrams to receive best-practice suggestions, effectively having an expert consultant review the architecture in real-time.
A Real-World Analogy
To understand the magnitude of this automation, think of building a database like manufacturing a car:
- The Class Diagram is the initial sketch of what the car looks like.
- The ERD is the detailed mechanical blueprint showing how the engine parts connect.
- Normalization is the process of streamlining those parts to ensure there is no unnecessary weight or loose bolts.
The AI DB Modeler acts as an automated factory. You simply describe the car you want, and the factory instantly draws the sketch, drafts the blueprints, and tunes the engine for maximum efficiency, removing the manual labor from the process.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.












