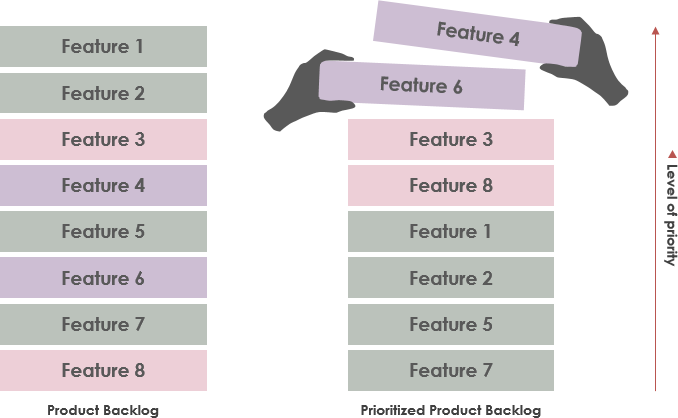
It’s important to prioritize your product backlog to make sure it doesn’t become an open-ended list where everyone has random ideas about your product. Your to-do list needs to be structured, organized, and prioritized to identify the most strategically important things for your team to do. In this article, I introduce the 100 Points method for product backlog refinement activities.
What is the percentage method?
The 100 point method (also known as $100 dollar, fixed sum or fixed allocation) was proposed by Dean Leffingwell and Don Widrig in 2003. The goal is to give more weight to higher priority pending items than other available user stories. It includes giving participants 100 points. They can vote for items in the product to-do list, such as epic or user stories that add the most value to the business. Ballots do not need to be evenly distributed; Instead, the higher priority of some projects can be reflected by weighted allocation. After the voting process is completed, the priority is determined by calculating the total number of points allocated to each user story.
How does the 100-point method work?
As mentioned above, the 100-point method allows participants to assign 100 points to determine the priority of different projects. Ratings are expressed as a percentage, with the most popular choices ranked higher.
Here is an example of a 100/100 point approach to developing new e-commerce sites:
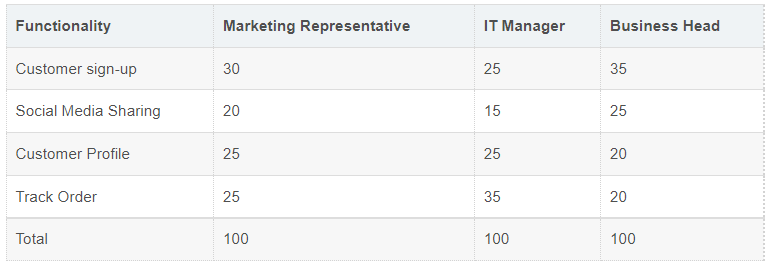
Imagine a group of people trying to prioritize five items.
- 100 points per person.
- One person can decide that each project is equally important and assign 20 items to each project.
- Or, they consider project 1 more important than project 2, project 2 is more important than project 3, and so on. As a result, their votes were allocated on a weighted basis, with 40 votes obtained in case 1, 30 votes in case 2, 15 votes in case 3, and so on, until all votes had been allocated.
- All ballot papers are then added together to determine the final vote for each item, resulting in a priority list.
Conclusion
Sometimes this approach is also called the fixed and or fixed allocation method, because when we give participants the same set of items and ask them to assign 100 points of product backlog items based on their relative importance.
We must weigh the pros and cons in making priority decisions. The more points one gets, the less points the other gets. Does this democratic voting process guarantee quality decisions? It really depends on the quality and intelligence of the team.
Because the 100-point method provides a fixed sum, it needs the correct precedence order to be considered valid. Otherwise, some validation procedures will be necessary, but this may be worth the effort and can also be done with some software tools.
- What is Product Backlog in Scrum? Who Responsible for It?
- How to Refine Product Backlog?
- What is Sprint Backlog in Scrum?
- How to Prioritize Product Backlog Using MoSCoW Method
- How to Prioritize Product Backlog Using 100 Points Methods?
- What is a Sprint Goal in Scrum?
- What is Burndown Chart in Scrum?
- What is the Role-Feature-Reason Template?
- Sprint Increment vs Potential Shippable Product vs MVP vs MMP
- Write SMART Goals & INVEST for User Stories





