In the evolving landscape of software development and database architecture, bridging the gap between abstract requirements and production-ready schemas is a critical challenge. The journey typically involves three distinct stages of architectural maturity: Class Diagrams, Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs), and Normalization. While these concepts have traditionally functioned in silos, modern tools like Visual Paradigm’s AI DB Modeler act as a unified bridge, automating the transition from ideas to optimized technical implementation.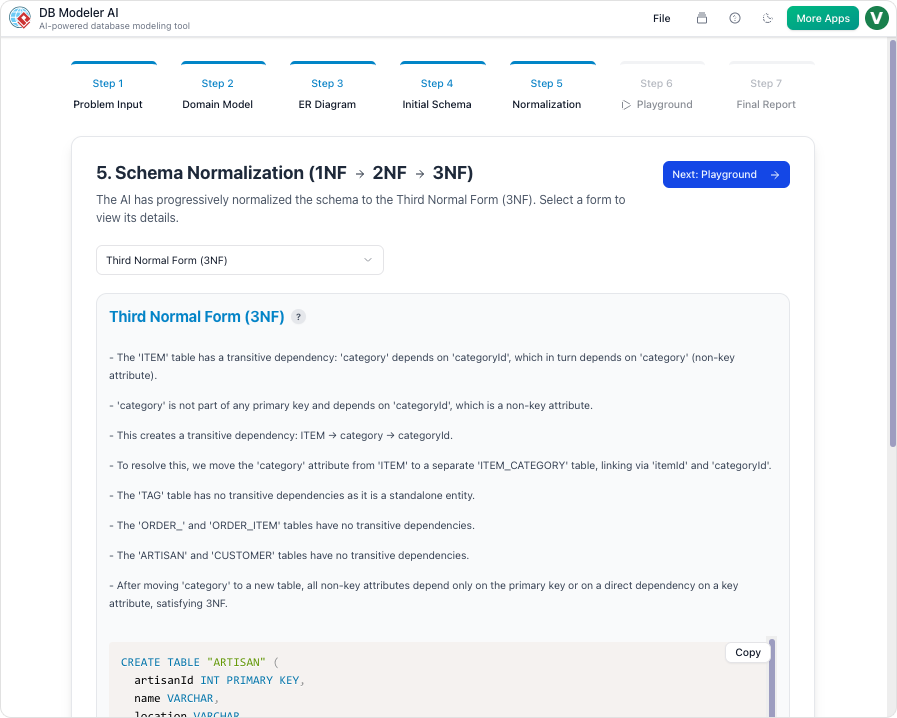
The Core Pillars of Database Architecture
To build scalable and robust software, developers must understand the specific roles of the three main architectural views. Each serves a distinct purpose in the lifecycle of data management.
1. Class Diagram: The Conceptual View
The Class Diagram is a fundamental component of the Unified Modeling Language (UML). It focuses primarily on a system’s objects and behaviors. In the specific context of database design, a Domain Class Diagram allows architects to visualize high-level entities and their attributes without being immediately constrained by technical database rules. It answers the question: What are the things in this system and how do they interact conceptually?
2. ER Diagram: The Database View
Moving from concept to structure, the Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) serves as the graphical representation of the actual database. This view is strictly technical, defining tables, columns, and the relationships between them. The ERD is essential for defining primary keys, foreign keys, and constraints. It typically spans three phases of development: conceptual, logical, and physical design.
3. Normalization: The Optimization View
Once the structure is defined, it must be refined. Normalization is the process of organizing data to ensure data integrity and eliminate redundancy. This involves restructuring tables through various forms—typically First (1NF), Second (2NF), and Third (3NF) Normal Forms—to prevent data anomalies that could corrupt the system later.
Streamlining Design with Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler
Visual Paradigm has introduced a platform that integrates these concepts into a cohesive 7-step guided workflow. By leveraging artificial intelligence, the tool ensures consistency between the initial conceptual classes and the final physical database.
From Text to Class Diagram
The process begins with natural language. Users can describe their requirements in plain English—for example, “Design a Hospital Management System.” The AI interprets this intent and instantly generates a Domain Class Diagram, identifying the necessary objects and attributes automatically.
Automated ERD Conversion
Transitioning from a class diagram to a database schema is often a manual, error-prone task. The AI DB Modeler automates this by converting the conceptual domain model into a database-specific ERD. It handles complex technical requirements by automatically defining relationships and foreign key constraints, effectively bridging the gap between object-oriented analysis and relational design.
Intelligent Normalization
One of the most powerful features of the platform is its approach to optimization. Once the ERD is established, the AI guides the design toward 3NF. Unlike traditional automated tools that simply separate tables, this system provides educational rationales for every change. It explains why specific architectural shifts are necessary to reduce redundancy, serving as both a production tool and a learning resource.
Advanced AI Features for Refinement
Beyond generating initial models, the AI DB Modeler offers a suite of tools designed to refine, validate, and test database architectures.
- Natural Language Chatbot: Users can interact with their diagrams using conversational commands. Requests such as “Add a payment gateway” or “Rename Customer to Buyer” are executed immediately, eliminating the need to manually drag and drop shapes.
- Live SQL Playground: The platform supports instant testing. After generating PostgreSQL-compatible SQL DDL statements, users can access an in-browser playground seeded with realistic, AI-generated sample data. This allows for immediate query testing against the normalized schema.
- Global Multi-Language Support: To cater to a global audience, the AI processes prompts and generates content in over 40 languages, including Spanish, Chinese, Japanese, and German.
- Model Traceability: Using the Model Transitor, the system maintains strict synchronization between conceptual, logical, and physical models, allowing developers to trace the evolution of their design seamlessly.
Analogy: The Automotive Factory
To better understand how these components fit together, consider the process of building a custom sports car:
- The Class Diagram is the initial artistic sketch, outlining the sleek look and general concept of the car.
- The ERD represents the detailed mechanical blueprints, specifying how the engine, transmission, and wheels connect.
- Normalization is the tuning process, ensuring there are no loose bolts or unnecessary weight that would hamper fuel efficiency.
- The AI DB Modeler acts as an automated factory. You simply request a sports car, and the factory instantly draws the sketch, drafts the blueprints, and tunes the engine for maximum performance, handling the transition from art to engineering automatically.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.












