Here is a comprehensive guide on how to write effective descriptions (prompts) for Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot to quickly and simply produce high-quality UML use case diagrams.
What is a Use Case Diagram? Key Concepts
A use case diagram is a UML behavioral diagram that captures the functional requirements of a system from the user’s perspective. It shows:
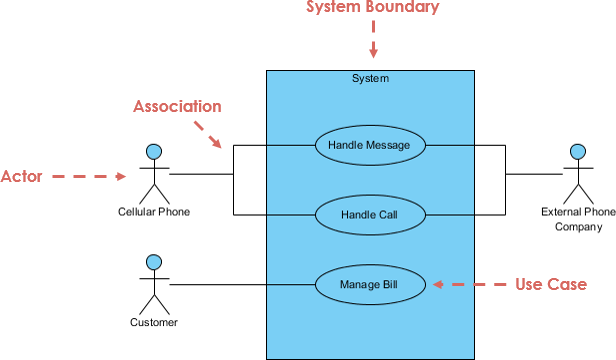
- Actors — people, roles, external systems, or devices that interact with the system (represented as stick figures).
- Use cases — the main goals or functionalities the system provides (represented as ovals).
- Relationships — associations (lines connecting actors to use cases), «include» (mandatory sub-behavior, solid arrow), «extend» (optional/conditional behavior, dashed arrow), generalization (inheritance between actors or use cases), and system boundary (rectangle enclosing use cases).
The primary purpose is to provide a high-level overview of what the system does, who uses it, and how those interactions relate — without detailing internal implementation (the “how”).
Traditional Development of Use Case Diagrams
Traditionally, creating use case diagrams is a manual, iterative process:
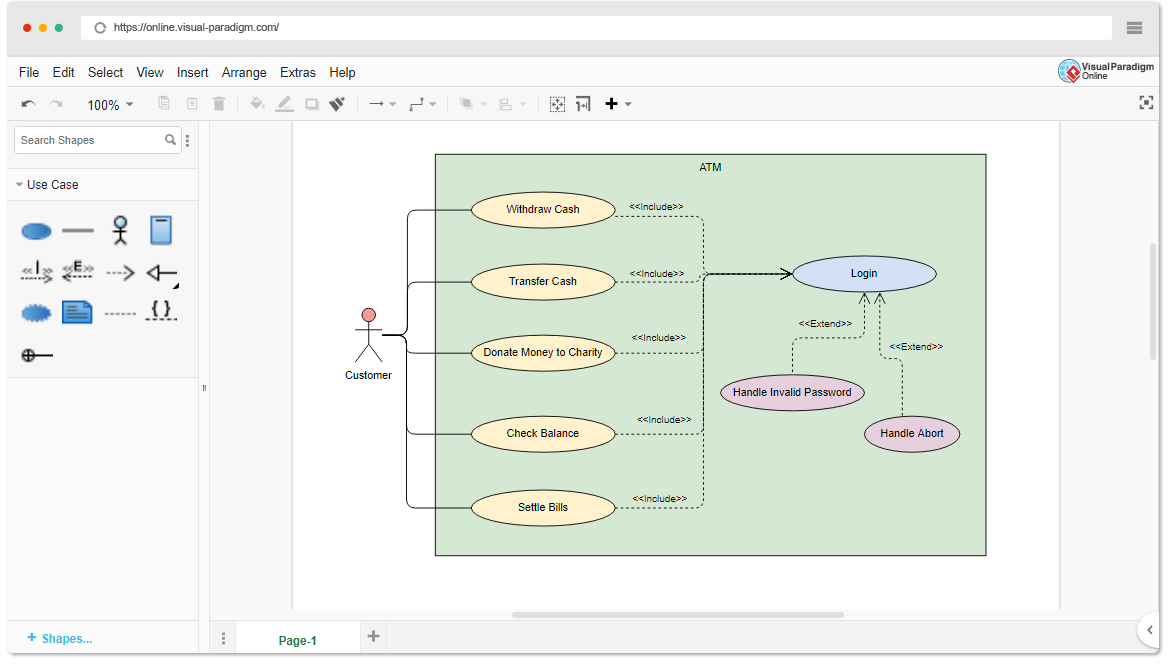
- Requirements gathering — Conduct interviews, workshops, or analyze documents to identify users (actors) and their goals.
- Identify actors — List primary, secondary, and external actors.
- Identify use cases — Name each goal as a verb-noun phrase (e.g., “Place Order”, “Withdraw Cash”).
- Define relationships — Decide inclusions (always happens), extensions (conditional), generalizations, and multiplicities if needed.
- Draw manually — Use tools like Visual Paradigm desktop, Lucidchart, draw.io, or even paper/whiteboard; drag shapes, connect lines, label relationships.
- Review & refine — Validate with stakeholders, add details (e.g., flow of events, scenarios), iterate.
Why do people use it? It bridges business stakeholders and technical teams, clarifies scope early, helps identify gaps/missing requirements, supports testing (use cases → test cases), and serves as a foundation for detailed design (sequence/activity diagrams).
Challenges — Time-consuming layout, ensuring UML compliance, handling complexity in large systems, manual iteration for changes, learning curve for notation.
The AI Approach with Visual Paradigm Chatbot
Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot (accessible at chat.visual-paradigm.com) revolutionizes this by turning natural language descriptions into fully rendered, editable UML use case diagrams in seconds. It handles layout, notation, relationships, and basic UML semantics automatically.
Comparison: Traditional vs. AI Approach
- Speed — Traditional: minutes to hours (drawing + layout). AI: seconds to first version.
- Skill required — Traditional: needs UML knowledge + tool proficiency. AI: almost none — plain English works.
- Iteration — Traditional: manual redraws. AI: conversational (“add X”, “rename Y”, “make Payment included”).
- Accuracy & standards — Traditional: human error possible. AI: enforces UML rules (OMG-compliant), reduces syntax mistakes.
- Accessibility — Traditional: steeper for non-modelers. AI: democratizes modeling for business analysts, product owners, students.
- Limitations — AI may generalize or miss very niche/edge cases → still needs human review/refinement. Traditional gives full control but slower.
AI excels for rapid prototyping, learning, early requirements visualization, and exploration — then refine manually in Visual Paradigm desktop if needed.
Quick & Simple Guide: How to Write Prompts for Fast, Effective Use Case Diagrams
-
Start simple and direct — Begin with a clear command + system description. Examples:
- “Create a use case diagram for an online shopping system”
- “Generate UML use case diagram for a library management system”
- “Draw use case diagram for ATM cash withdrawal”
-
Add key details for better results (recommended for accuracy):
- List main actors
- List primary use cases
- Mention relationships (include/extend)
- Specify external systems/services if relevant
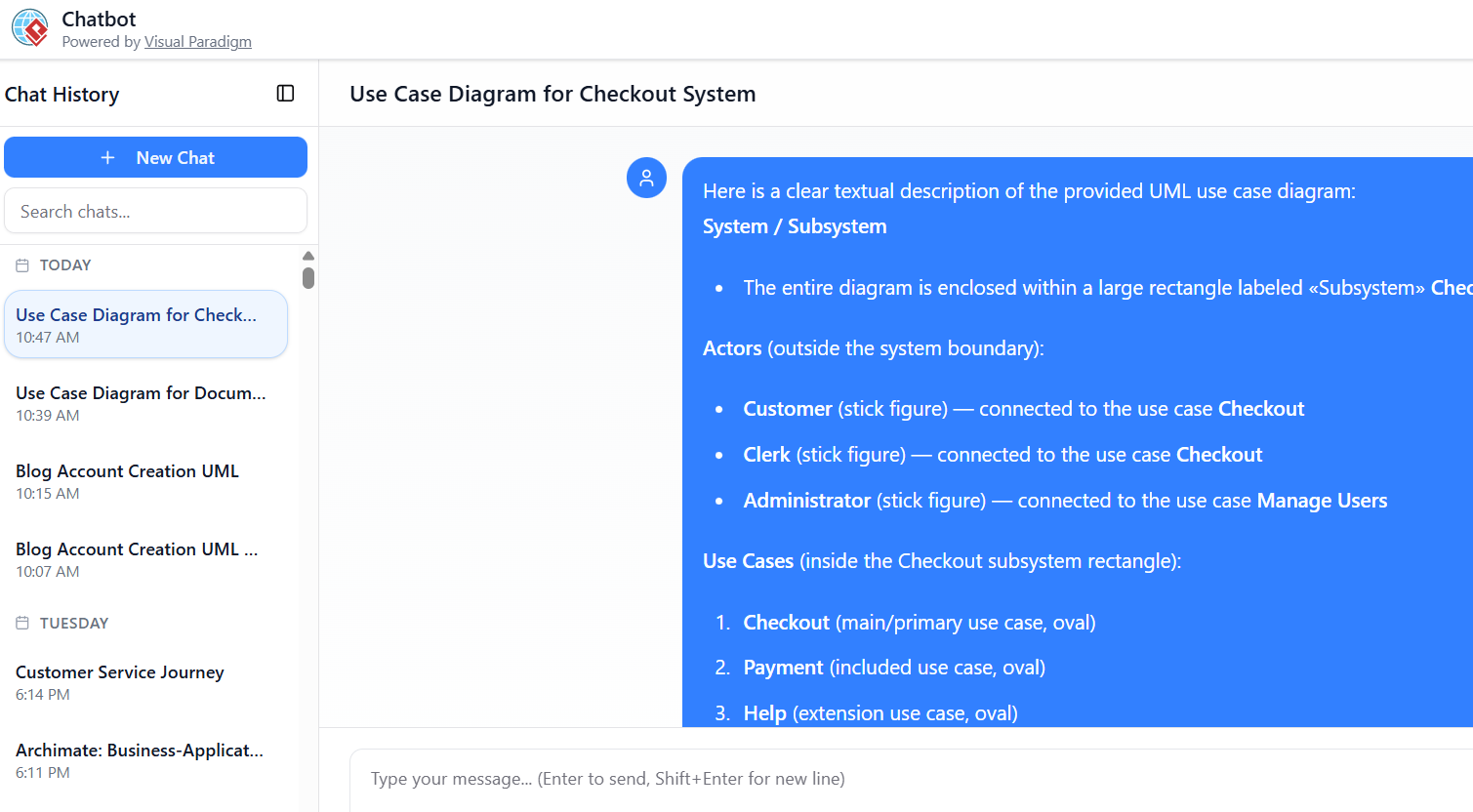
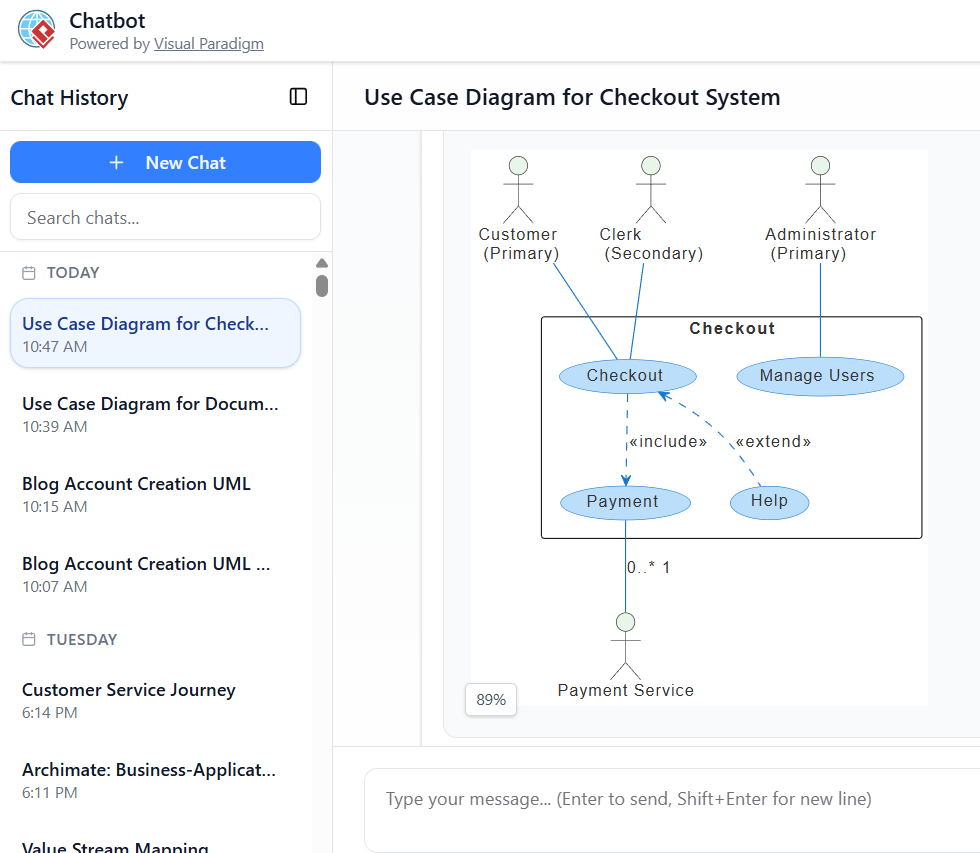
Strong prompt example (produces detailed diagram quickly): “Create a use case diagram for an e-commerce checkout system with actors Customer, Clerk, and Administrator. Main use case is Checkout, which includes Payment (interacting with external Payment Service) and can extend to Help. Administrator can Manage Users.”
-
Iterate conversationally — Treat it like chatting:
- “Add an actor Guest who can only Browse Products”
- “Make Login an include of Checkout”
- “Add extend relationship from Checkout to Apply Discount when promo code is entered”
- “Rename Customer to Buyer”
- “Show multiplicities on associations”
- “Explain this diagram” or “Generate documentation for these use cases”
-
Best practices for prompts
- Be specific but concise — more context = better inference (actors, goals, optionals).
- Use natural language — no need for UML jargon unless you want precision.
- Specify diagram type early — “Generate a UML use case diagram for…” avoids confusion.
- Start broad → refine → avoid overloading first prompt.
- For complex systems — break into parts (e.g., first core, then extensions).
- Request refinements — “Make it more detailed”, “Add exception handling use case”, “Improve layout”.
-
Tips for quickest results
- Name your chat session meaningfully (e.g., “Checkout System Use Cases”) for easy reference.
- Use trial/free mode to experiment.
- After generation — export as PNG/SVG, copy to Visual Paradigm desktop for advanced editing, or ask AI to “Write explanations of each use case”.
- If result is off — reply with corrections instead of restarting.
Example full prompt sequence (produces something close to your checkout example):
- “Create a use case diagram for a retail Checkout subsystem with actors Customer (primary), Clerk (secondary), Administrator (primary). Include use cases Checkout, Payment (included), Help (extended), Manage Users. Payment interacts with external Payment Service.”
- (If needed) “Add association multiplicities: Customer to Checkout 1.., Payment to Payment Service 0.. to 1.”
- “Generate a textual description of this diagram.”
This approach typically yields a professional diagram in under 30 seconds, with refinements taking just a few messages — far faster than traditional drawing while maintaining UML integrity.
Articles and resources Visual Paradigm AI
-
AI-Powered Visual Modeling and Design Solutions by Visual Paradigm: This portal allows users to explore cutting-edge AI-driven tools for visual modeling, diagramming, and software design to enable faster, smarter development workflows.
-
Visual Paradigm – All-in-One Visual Development Platform: This is a comprehensive platform for visual modeling, software design, and business process modeling that integrates various AI-powered development tools.
-
AI Chatbot Feature – Intelligent Assistance for Visual Paradigm Users: Users can leverage this AI-powered chatbot functionality to get instant guidance, automate tasks, and enhance productivity within the modeling environment.
-
Visual Paradigm Chat – AI-Powered Interactive Design Assistant: This interactive AI chat interface helps users generate diagrams, write code, and solve complex design challenges in real time.
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: This tool uses AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate diagrams such as UML, BPMN, and ERD for faster modeling and documentation.
-
AI Brainstorming Features – Visual Paradigm: These features enhance the idea generation process by providing intelligent suggestions and supporting collaborative workflows.
-
AI-Powered Use Case Diagram Refinement Tool – Smart Diagram Enhancement: This tool leverages AI to automatically refine and optimize use case diagrams for improved clarity, consistency, and completeness.
-
AI Fishbone Diagram Generator: This AI-powered tool identifies the root causes of complex problems by automatically generating Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagrams.
-
AI Development Plan Generator – Visual Paradigm: This tool is designed to revolutionize project planning by empowering users to quickly transform ideas into actionable roadmaps and visualized timelines.
-
AI-Powered 3-Aspect Infographic Designer Tool: This AI-driven designer tool enables the instant generation of professional infographics based on user input.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













