(Based on Visual Paradigm’s tool + best practices & comparative insights)
🎯 Overview
The Visual Paradigm’s AI-Assisted UML Class Diagram Generator is a guided, browser-based tool that transforms a vague idea into a rigorously analyzed, professional-quality UML class diagram—without requiring syntax expertise or deep UML mastery [source].
Unlike raw LLM prompts (e.g., “Draw me a class diagram for an e-commerce app”), this tool embeds domain-specific intelligence: AI checks for correctness, suggests improvements, validates against best practices, and even generates PlantUML code and SVG exports.
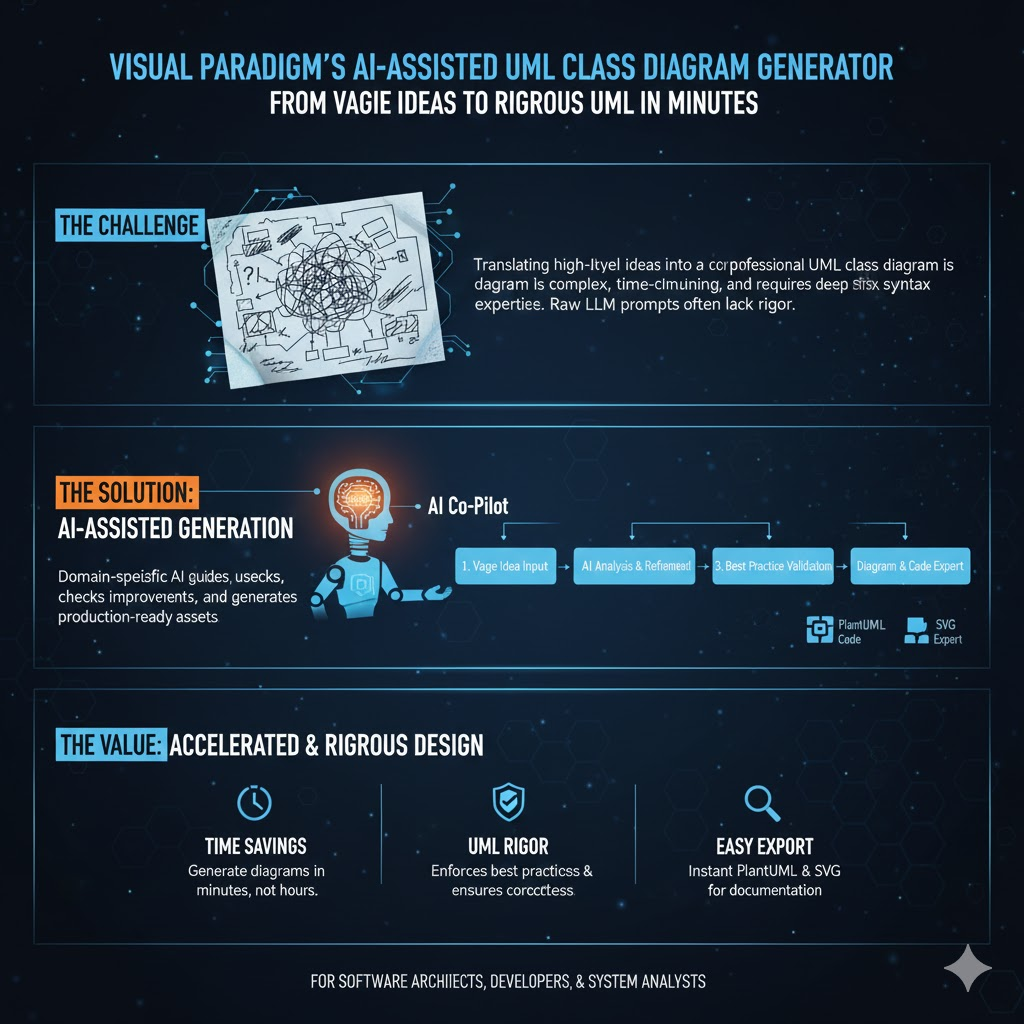
🧠 Why Use This Instead of a General LLM?
| Feature | General LLM (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude) | AI-Assisted UML Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Syntax Safety | May hallucinate invalid PlantUML or UML semantics | Generates validated PlantUML code (e.g., class Order { -id: UUID }) |
| Structural Consistency | No automated checks for circular dependencies/incomplete relationships | Built-in Validation Checklist (Step 7) enforces modeling best practices |
| Progressive Refinement | All-at-once generation; hard to iterate | 10-step guided wizard supports incremental design |
| Educational Feedback | Limited domain-specific critique | AI Analysis Report (Step 10) gives architecture-level suggestions |
| Export & Collaboration | Text-only (unless manually formatted) | Exports in PUML, JSON, SVG—ideal for docs, PRDs, and versioning |
In short:
🧠 LLMs are great for brainstorming; this tool is built for production-grade modeling—with guardrails.
Recent research confirms that while LLMs show promise in supporting architecture decisions, they still require scaffolding and validation to ensure correctness and traceability , .
🏗️ Core Concepts & Best Practices
1. Classes
Represent nouns in your system (e.g., User, Order, PaymentGateway).
✅ Best Practice: Use singular, camel-case or PascalCase names (ShoppingCart, not shopping_cart or carts) .
❌ Common Mistake: Overloading classes with too many responsibilities—break into smaller, cohesive units .
2. Attributes
Data members of a class: -email: String, +isActive: Boolean
- Prefix:
-= private,+= public,#= protected (UML visibility) - Type annotations are strongly recommended for clarity and tooling support .
3. Operations (Methods)
Behaviors: +placeOrder(): Order, -validate(): Boolean
✅ Keep them focused; avoid “god methods” that do too much .
4. Relationships
| Type | Symbol | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Association | → or line |
“Uses” or “knows about” | User → Order |
| Aggregation | ◇—— | “Has-a” (weak ownership) | Department ◇—— Employee |
| Composition | ◆—— | “Owns” (strong lifecycle) | Order ◆—— OrderLine |
| Inheritance | ▷—— | “Is-a” | PremiumUser ▷—— User |
| Dependency | ⤳ | Temporary use (e.g., param) | ReportGenerator ⤳ PDFRenderer |
✅ Best Practice: Avoid crossing lines; keep parents above children (“Parents Up” rule) .
❌ Mistake: Using composition when aggregation suffices (e.g., a Car composes Engine, but aggregates Driver) .
🛠️ Step-by-Step Tutorial with Example: Online Bookstore
Let’s walk through the 10-Step Wizard, applying best practices at each stage.
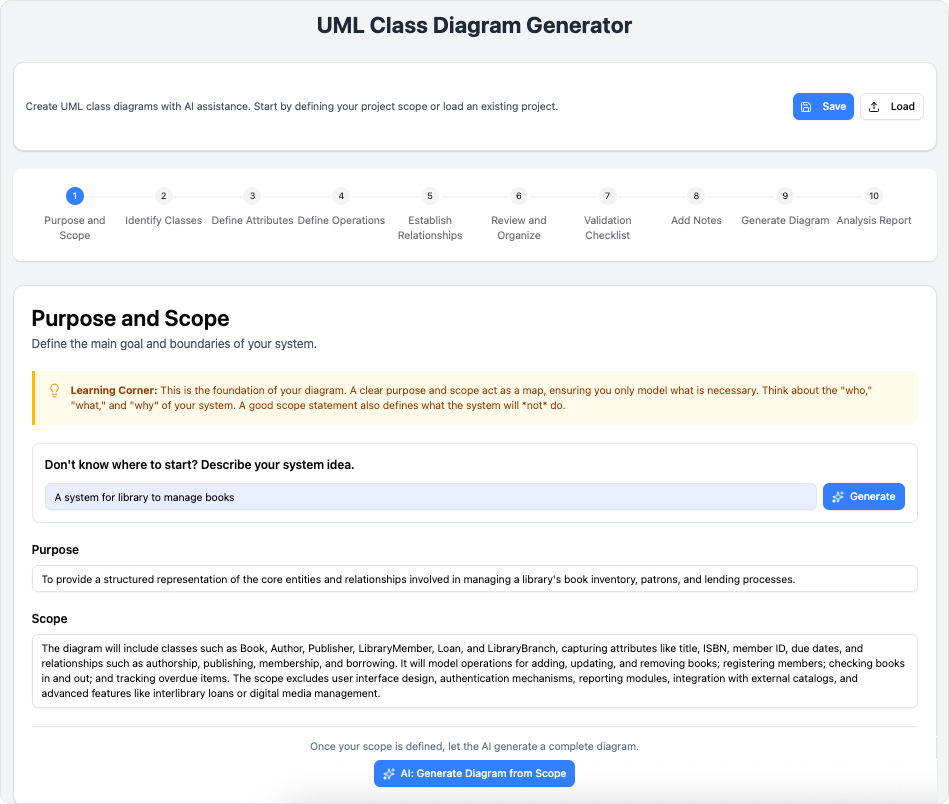
🔹 Step 1: Purpose & Scope
Input:
“Design a backend for an online bookstore where users browse books, add to cart, place orders, and admins manage inventory.”
👉 Click AI Generate → gets refined scope:
“Support CRUD for Books, Users, Orders; enforce stock constraints; track order status; separate Customer vs Admin roles.”
💡 Why AI helps: Turns vague scope into actionable boundaries, reducing scope creep .
🔹 Step 2: Identify Classes
List core entities:
User,Book,ShoppingCart,Order,OrderLine,Inventory,Admin
✅ Tip: Start broad, then refactor (e.g., later split User → Customer, Admin via inheritance).
🔹 Step 3: Define Attributes
| Class | Attributes |
|---|---|
Book |
-isbn: String, -title: String, -price: BigDecimal, -stock: int |
Order |
-id: UUID, -status: OrderStatus, -createdAt: LocalDateTime |
ShoppingCart |
-items: List<OrderLine> |
⚠️ Avoid clutter—omit trivial getters/setters unless behaviorally significant , .
🔹 Step 4: Define Operations
| Class | Operations |
|---|---|
ShoppingCart |
+addItem(book: Book, qty: int), +removeItem(isbn: String), +checkout(): Order |
Order |
+cancel(): Boolean, +getStatus(): OrderStatus |
Inventory |
+deductStock(isbn: String, qty: int): Boolean, +restock(...) |
✅ Name methods using verbs + nouns for clarity .
🔹 Step 5: Establish Relationships
@startuml
class User
class Customer
class Admin
class Book
class ShoppingCart
class Order
class OrderLine
class Inventory
Customer --|> User
Admin --|> User
Customer "1" *-- "1" ShoppingCart
ShoppingCart "1" *-- "many" OrderLine
OrderLine "1" -- "1" Book
Customer "1" --> "many" Order
Order "1" *-- "many" OrderLine
Inventory --> Book : manages
@enduml
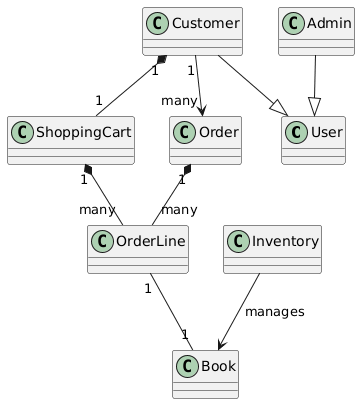
(This is real PlantUML—valid syntax generated/exportable from Step 9) ,
🔑 Notes:
*--= composition (cart owns its lines; destroy cart → destroy lines)-->= association (customer places orders, but orders persist after user deletion)
🔹 Step 6: Review & Organize
Check for:
- Duplicate classes?
- Missing relationships (e.g., how does
OrdergetBookprice at checkout?) - Ambiguous multiplicities?
🛠 Use drag-and-drop to reorganize visually.
🔹 Step 7: Validation Checklist
The tool auto-checks for:
- Classes without attributes/operations
- Orphaned classes
- Cyclic inheritance
- Redundant relationships
✅ Pass all checks before proceeding—this is where general LLMs fail silently .
🔹 Step 8: Add Notes (AI-Assisted)
Click AI Generate Notes → gets:
“
OrderLinestores snapshot ofBookprice/title at checkout time to ensure invoice accuracy—even if book details change later.”
💡 This captures design rationale—critical for onboarding and audits .
🔹 Step 9: Generate Diagram
Export options:
- 🖼️ SVG: Embed in Confluence/docs
- 📄 PUML: Version in Git, regenerate anytime
- 💾 JSON: Save/load project state
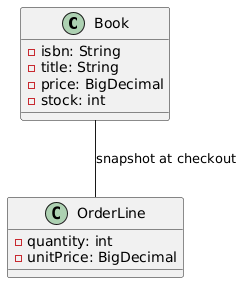
Example exported PlantUML (simplified):
@startuml
class Book {
-isbn: String
-title: String
-price: BigDecimal
-stock: int
}
class OrderLine {
-quantity: int
-unitPrice: BigDecimal
}
Book -- OrderLine : "snapshot at checkout"
@enduml
🔹 Step 10: AI Analysis Report
Sample critique:
⚠️ Warning:
ShoppingCart.checkout()creates anOrder, but no validation for stock availability.
✅ Suggestion: InjectInventoryservice intoShoppingCartor delegate toOrderService.
🎓 Learning Tip: Prefer service classes for cross-aggregate operations to preserve encapsulation.
This mirrors expert peer review—impossible with raw LLM alone .
🚀 Real-World Use Cases
| Role | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Students | Learn UML in context with instant feedback |
| Product Managers (e.g., Alex, with CS + HCI background) | Visualize requirements before sprint planning; align eng/design on domain model |
| Tech Leads | Onboard new hires faster with AI-annotated diagrams |
| Architects | Audit legacy systems via AI-suggested refactorings |
💡 Pro Tip for PMs: Use Step 1 (Scope) + Step 8 (AI Notes) to auto-generate PRD appendix sections—saving hours in documentation.
📌 Summary: Advantages Over Raw LLMs
| Dimension | General LLM | AI-Assisted Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Correctness | May violate UML semantics | Enforces ISO/OMG UML standards |
| Iterability | Start-from-scratch each time | Save/load, incremental edits |
| Traceability | Prompt → output (black box) | 10 transparent steps + rationale logging |
| Team Use | Personal assistant | Export/share/version (JSON/SVG) |
| Learning | Explain-on-demand | Embedded tips at decision points |
As research notes:
“Generative AI can assist architects in addressing cross-functional requirements by providing insights and recommendations—but domain-specific tooling ensures those insights are actionable and safe.”
✅ Final Checklist Before Exporting
- All classes named consistently (PascalCase, singular)
- Attributes typed (even
String,int) - Relationships labeled with multiplicity (
1,0..1,*) - Composition ≠ aggregation (lifecycle matters!)
- Passed Validation Checklist
- Reviewed AI Analysis Report
- Saved as
.jsonand exported.svgfor docs
Ready to try?
➡️ Launch the AI-Assisted UML Class Diagram Generator
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













