This guide outlines the systematic process of transforming a problem statement into a fully realized database model. The workflow begins with analyzing requirements (problem statement), progresses to object-oriented design via a UML class diagram, transitions to a conceptual data model using an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD), and culminates in physical database modeling.
Visual Paradigm, as an all-in-one modeling platform, streamlines this entire process by integrating UML tools, ERD editors, database engineering features, and synchronization capabilities within a single environment. It supports over 100 diagram types, including UML 2.x, ERD in standard or Chen notation, and database schema generation. Features like textual analysis, AI-powered diagram generation, model transformation, and round-trip engineering (for code and database) ensure seamless transitions between steps, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency. The platform’s drag-and-drop interface, cloud collaboration, and bidirectional synchronization between models make it ideal for this workflow.
We’ll use a simple example throughout: designing a system for an online bookstore that manages books, customers, and orders.
Step 1: From Problem Statement to Class Diagram
General Process
The problem statement describes the system’s requirements in natural language. To model this, identify key entities (nouns), attributes (properties), operations (behaviors), and relationships.
- Analyze the Problem Statement: Extract domain concepts. For the bookstore: “Customers place orders for books, which have authors and prices. Orders include multiple items and track status.”
- Entities: Customer, Book, Order, Author.
- Attributes: Customer (name, address), Book (title, price, ISBN), Order (date, status).
- Relationships: Customer places Order; Order contains Book.
- Behaviors: Calculate total, update stock.
- Create UML Class Diagram: Represent entities as classes, attributes as properties, operations as methods, and relationships as associations, aggregations, or inheritances.
- Use multiplicity (e.g., 1..* for one-to-many).
- Apply stereotypes or visibility modifiers (public/private).
This step focuses on object-oriented design, ensuring the model aligns with software implementation.
How Visual Paradigm Helps
Visual Paradigm’s UML tools accelerate this phase:
- Textual Analysis: Input the problem statement into the Textual Analysis tool. It automatically identifies candidate classes, attributes, and relationships from keywords, generating a preliminary class diagram.
- AI-Powered Generation: Describe the system (e.g., “Online bookstore with customers, books, and orders”), and the AI engine creates a class diagram instantly, including elements like generalizations and aggregations.
- Drag-and-Drop Editor: Use the intuitive interface to refine the diagram. Add classes from the toolbar, connect with associations, and validate syntax in real-time.
- Use Case Integration: If the problem statement includes scenarios, generate use case diagrams first, then derive classes via traceability links.
- Round-Trip Engineering: Synchronize with code; generate Java/C++ classes from the diagram or reverse-engineer existing code.
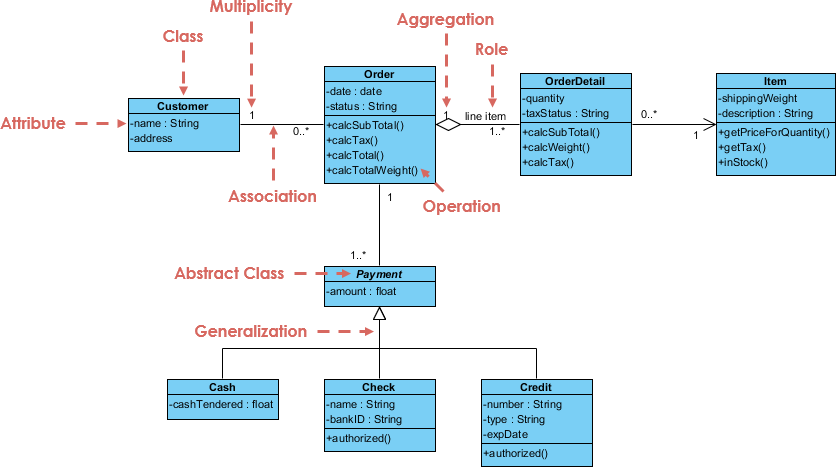
Example Class Diagram for Bookstore:
This visual (from Visual Paradigm’s gallery) shows classes like Order and Customer with associations, similar to our bookstore model.
Step 2: From Class Diagram to ERD
General Process
Transition from object-oriented to data-centric modeling. Class diagrams emphasize behavior, while ERDs focus on data structure and relationships for database design.
- Map Elements:
- Classes → Entities.
- Attributes → Columns (with data types).
- Associations → Relationships (one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many).
- Inheritances → Supertype/subtype relationships or merged entities.
- Resolve many-to-many by introducing junction entities.
- Refine for Data Integrity: Add keys (primary/foreign), constraints (unique, not null), and cardinalities. Ensure normalization (e.g., to 3NF) to avoid redundancy.
For the bookstore: Map Customer class to Customer entity, Order to Order entity, with a one-to-many relationship (Customer places multiple Orders).
How Visual Paradigm Helps
Visual Paradigm’s integration shines here with automated synchronization:
- Synchronize to ERD: Right-click the class diagram and select “Synchronize to Entity Relationship Diagram” (or use Tools > Hibernate > Synchronize to ERD). This transforms classes to entities, associations to relationships, preserving descriptions and types.
- Bidirectional Mapping: Changes in the class diagram update the ERD and vice versa, maintaining consistency. Supports ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) for Hibernate integration.
- Conceptual/Logical/Physical Models: Start with a conceptual ERD (high-level), transition to logical (with keys), and prepare for physical (DB-specific).
- Diagram Transformation: Use model transiter to convert elements; e.g., generate ERD relationships from UML associations.
- Validation and Views: Built-in checks for ERD validity; create database views for complex queries.
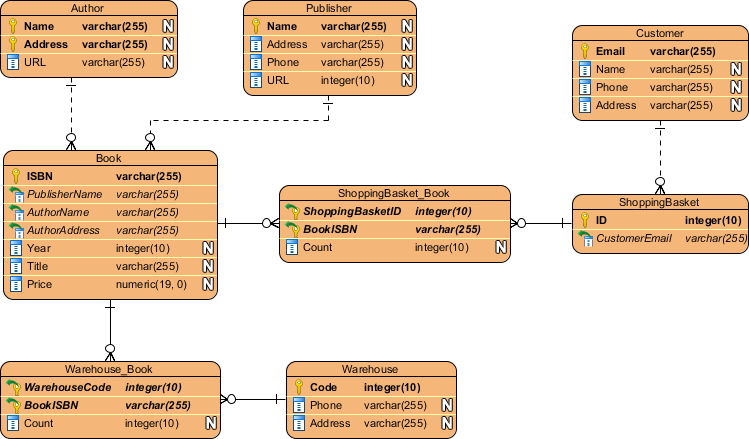
Example ERD for Bookstore:
This ERD (created in Visual Paradigm) illustrates entities like Book and Customer with relationships, mirroring the transition from our class diagram.
Step 3: From ERD to Database Modeling
General Process
Convert the conceptual ERD into a physical database schema ready for implementation.
- Physical Model Refinement: Assign database-specific data types (e.g., VARCHAR(255) for strings), indexes, triggers, and stored procedures.
- Generate Schema: Produce DDL (Data Definition Language) scripts for tables, constraints, and relationships.
- Normalization and Optimization: Ensure the model is normalized; add partitions or views for performance.
- Implementation: Export to a DBMS (e.g., MySQL, Oracle) or generate sample data.
For the bookstore: Generate tables like CUSTOMER (ID PK, NAME VARCHAR), ORDER (ID PK, CUSTOMER_ID FK, DATE DATE), with indexes on frequent queries.
How Visual Paradigm Helps
Visual Paradigm’s database engineering tools enable direct generation and management:
- Generate DDL from ERD: Use the Database Engineering tools to export DDL scripts or generate/update the database directly. Supports over 50 DBMS like PostgreSQL, SQL Server.
- Reverse Engineering: Import existing databases to ERD for modifications, then regenerate.
- Conceptual to Physical Transition: Switch between model types; add DB-specific details in the physical ERD.
- Advanced Features: Model views, triggers, and stored procedures visually. Use ID generators for auto-increment keys. Synchronize with class models for ORM.
- Testing and Documentation: Generate sample data, ERD from DDL, or full reports with Doc. Composer.
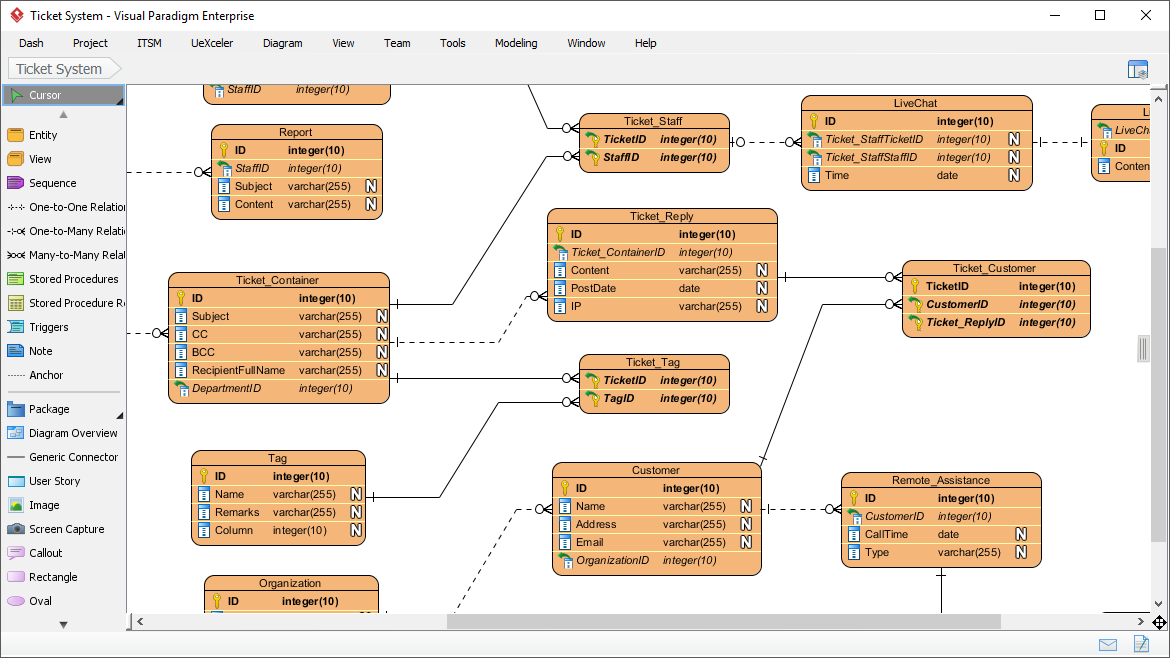
Example Database Schema in Visual Paradigm:
This screenshot shows a physical ERD in the tool, with tables, keys, and relationships, demonstrating the final modeling stage.
Conclusion: Benefits of Visual Paradigm’s All-in-One Platform
Visual Paradigm unifies the entire workflow in one tool, eliminating the need for multiple software packages. Key advantages include:
- Seamless Integration: Automatic synchronization between UML, ERD, and database models reduces manual rework.
- Efficiency Tools: AI assistance, textual analysis, and round-trip engineering speed up development.
- Collaboration and Scalability: Cloud-based sharing, version control, and enterprise features support teams.
- Comprehensive Support: From requirements gathering to deployment, including code generation and database synchronization.
By leveraging Visual Paradigm, developers and database designers can iterate quickly, maintain model consistency, and produce production-ready artifacts. For hands-on experience, refer to Visual Paradigm’s official tutorials on their website for detailed steps with your specific project.
AI Tooling
Visual Paradigm’s AI capabilities significantly accelerate and enhance the process of moving from a problem statement → class diagram → ERD → database modeling, making it faster, more accurate, and accessible even for users with limited modeling experience. By 2026, Visual Paradigm has matured into one of the most comprehensive AI-powered visual modeling platforms, integrating generative AI across desktop, online, and chatbot interfaces.
The core AI features relevant to this workflow include:
- AI Diagram Generator (Tools > AI Diagram Generation): Text-to-diagram creation for dozens of types, including Class Diagram, ERD (Chen notation, Crow’s Foot), and others.
- AI Visual Modeling Chatbot (chat.visual-paradigm.com or integrated in tools): Conversational interface for generating, refining, and analyzing diagrams iteratively via natural language.
- AI-Assisted UML Class Diagram Generator: Guided wizard + AI suggestions for structured class diagram creation with analysis.
- DB Modeler AI and related tools: Specialized for database/ERD generation from descriptions.
- AI Textual Analysis: Enhanced extraction of domain elements from problem statements.
These tools reduce manual work, suggest intelligent relationships/attributes, auto-layout diagrams professionally, and maintain consistency across model layers.
How AI Helps at Each Step (with Examples for the Online Bookstore System)
1. From Problem Statement to Class Diagram — AI Jumpstarts Object-Oriented Design
Traditional Challenge: Manually identifying classes, attributes, operations, and relationships from requirements text is time-consuming and error-prone.
AI Acceleration:
- Paste or describe the problem statement (e.g., “Build an online bookstore system where customers browse and order books. Books have titles, authors, ISBN, price. Orders include multiple books, total price, shipping address, and status. Customers have accounts with email and history.”) into the AI Diagram Generator or AI Chatbot.
- Select Class Diagram as the type → AI instantly generates a preliminary UML class diagram with:
- Classes (Customer, Book, Order, OrderItem, Author)
- Attributes (e.g., Book: title:String, price:double, isbn:String)
- Associations (Customer 1 — places * — Order)
- Multiplicities, potential generalizations, and even basic operations
- Use the AI-Assisted UML Class Diagram Generator for a guided, step-by-step wizard: AI suggests scopes, relationships, notes, and provides design analysis/critique (e.g., “Consider adding encapsulation for price calculation”).
- AI Textual Analysis tool scans the problem text to auto-extract candidate classes/attributes/operations, feeding directly into model elements.
- Iterative Refinement: In the Chatbot, say “Add Author class with many-to-many relationship to Book” or “Make Order calculate total price” — AI updates the diagram in real-time.
Result: From minutes/hours of manual work → seconds for a solid starting class diagram, beautifully laid out with perfect alignment.
2. From Class Diagram to ERD — AI Bridges OO to Data Modeling Seamlessly
Traditional Challenge: Manual mapping of classes → entities, associations → relationships, handling inheritance vs. normalization.
AI Acceleration:
- After generating/refining the class diagram, use the AI Diagram Generator or Chatbot to request: “Generate ERD (Chen notation) from this bookstore class model” or “Convert to conceptual data model for database.”
- AI infers:
- Entities from classes
- Attributes with smart data type suggestions
- Relationships (1:*, M:N resolved with junction entities if needed)
- Primary/foreign keys
- Specialized DB Modeler AI excels here: Describe or reference the domain (“online bookstore data model”) → AI produces domain class diagram first (as conceptual foundation), then automatically derives ERD + suggests normalized structure.
- Conversational refinement: “Make Book-Author many-to-many with junction table” or “Add weak entity for OrderItem” → instant updates.
- Maintain traceability — changes in class diagram can propagate suggestions to ERD (and vice versa via synchronization features).
Result: AI handles the conceptual-to-logical transition intelligently, reducing mapping errors and ensuring normalization basics are considered early.
3. From ERD to Database Modeling — AI Enables Rapid Physical Schema Creation
Traditional Challenge: Assigning DB-specific types, constraints, indexes; generating DDL; validating for production.
AI Acceleration:
- From the generated ERD, prompt: “Generate physical database model for MySQL/PostgreSQL from this ERD” or “Create SQL schema for bookstore database.”
- DB Modeler AI shines: Directly input business description or refine existing ERD → AI suggests:
- Appropriate column types (VARCHAR(255) for titles, DECIMAL for prices)
- Constraints (NOT NULL, UNIQUE on ISBN)
- Indexes on frequent query fields (e.g., book title, customer email)
- Even basic triggers or views
- Generate DDL scripts instantly via AI-assisted export.
- Iterative: “Add cascading delete on orders” or “Optimize for read-heavy queries” → AI proposes refinements.
- Reverse/forward engineering integration remains, but AI speeds initial prototyping.
Result: Move from conceptual ERD to near-production-ready physical model and DDL in minutes, with AI suggesting best practices.
Overall Benefits of Visual Paradigm AI in This Workflow
- Speed: Text-to-diagram in seconds; full pipeline (problem → class → ERD → DB) in minutes instead of hours/days.
- Quality & Intelligence: AI infers missing details, suggests relationships/keys, auto-applies layout standards, and provides analysis/feedback.
- Iterative & Collaborative: Chatbot enables natural-language refinement (“add loyalty points to Customer”); team members can describe changes verbally.
- Consistency & Traceability: Models stay linked; AI helps maintain synchronization across layers.
- Accessibility: Non-experts describe in plain English; experts get rapid prototyping + refinement power.
- Multiple Access Points: Desktop (Tools > AI Diagram Generation), Online, Chatbot (chat.visual-paradigm.com), specialized apps (DB Modeler AI, UML generators).
In summary, Visual Paradigm’s AI turns the traditional sequential, labor-intensive modeling process into an intelligent, conversational, and highly productive experience — ideal for agile teams, rapid prototyping, education, and enterprise architecture alike. For the latest interface details or examples, check Visual Paradigm’s official guides or try the free AI Chatbot at chat.visual-paradigm.com with your bookstore description.
- AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: This article explains how to use AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate diagrams such as UML and ERD for faster modeling and documentation.
- From Problem Description to Class Diagram: AI-Powered Textual Analysis: This guide explores how Visual Paradigm uses AI to convert natural language problem descriptions into accurate class diagrams for software modeling.
- AI-Powered UML Class Diagram Generator by Visual Paradigm: An overview of an advanced AI-assisted tool that automatically generates UML class diagrams from natural language descriptions, streamlining software design.
- AI Textual Analysis Tool by Visual Paradigm: This page features a powerful tool that transforms natural language input into structured diagrams, supporting software design and system modeling through NLP.
- AI-Powered Textual Analysis Tutorial for Software Design with Visual Paradigm: a comprehensive technical tutorial demonstrating how to leverage AI-driven analysis to extract key software design elements from requirements.
- Identifying Domain Classes Using AI Textual Analysis in Visual Paradigm: This resource teaches users how to automatically detect domain classes from textual inputs using integrated AI analysis tools.
- Case Study: AI-Powered Textual Analysis for UML Class Diagram Generation: An in-depth study on how AI-driven textual analysis enables the accurate and efficient generation of class diagrams from unstructured requirements.
- Visual Paradigm AI Toolbox: Textual Analysis Tool for Software Modeling: This page details an AI-driven tool that identifies entities, relationships, and key concepts within unstructured text to build structured software models.
- DBModeler AI: Intelligent Database Modeling Tool: An overview of an AI-powered database design tool that can generate ER diagrams and normalized schemas using an automated workflow.
- New Diagram Types Added to AI Diagram Generator: DFD & ERD: An official announcement regarding expanded AI support for the automatic generation of Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD).
- Advanced Textual Analysis Techniques in Visual Paradigm: This guide covers sophisticated methods for applying textual analysis, including sentiment analysis and keyword extraction, to modeling projects.
- Documenting Requirements Using Textual Analysis: This article explains how to use textual analysis to extract and organize requirements from documents to improve project clarity.
- How AI Enhances Class Diagram Creation in Visual Paradigm: This blog post explores how Visual Paradigm leverages AI to improve the creation of class diagrams, making software design faster and more accurate.
- AI-Powered Database Modeling with DBModeler AI: This feature highlight explores how AI enables intelligent database schema design and automated modeling within the platform.
- Real-Life Case Study: Generating UML Class Diagrams with Visual Paradigm AI: A practical case study showcasing the successful transformation of textual requirements into accurate UML class diagrams in a real-world project.