System design begins with an objective, but the path from a general idea to a formalized, secure specification is often slow and detailed. This case study demonstrates how a developer uses Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot in an iterative, conversational manner to bypass tedious manual work. We start with a high-level goal, allow the AI to generate a robust structure, and then refine that structure using simple natural language commands.
Our goal is to model a secure User Registration Process.
Phase 1: Idea to Inspiration – The Initial Simple Prompt
The developer started with the most basic statement of intent, using a high-level goal as the prompt, intending only to get a basic structure for inspiration.
The Initial AI Prompt:
“Generate a UML Activity Diagram for a ‘User Registration Process’.”
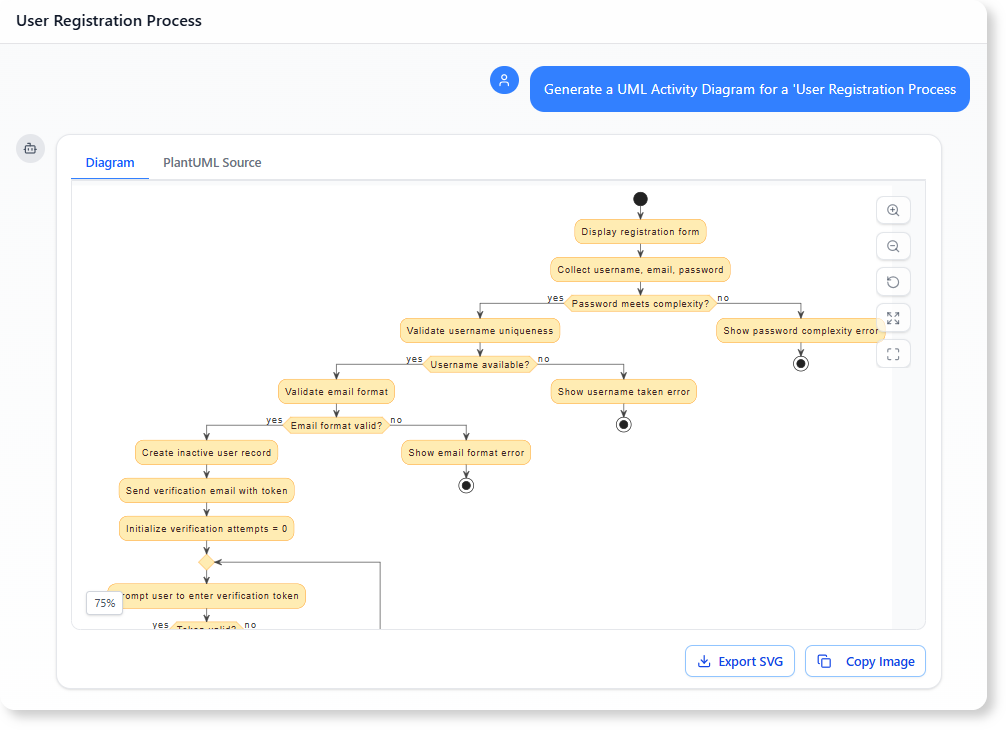
The AI Chatbot immediately responded with a highly detailed PlantUML structure, going far beyond a simple linear flow by incorporating crucial, real-world complexity:
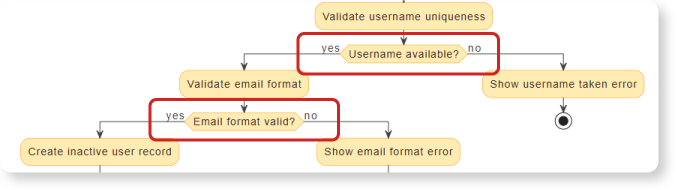
- Layered Pre-Checks: Sequential validation of Password Complexity, Username Uniqueness, and Email Format.
- Security Looping: A
repeat whileloop allowing token verification retries but limited to< 3attempts.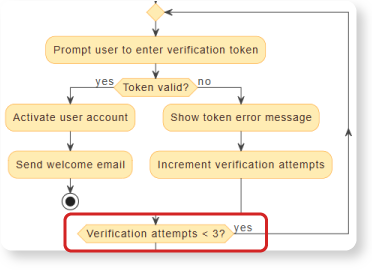
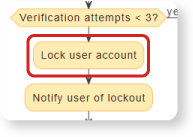
- Lockout Logic: A defined path leading to Lock user account upon failure of the verification loop.
This complex, production-ready structure saved hours of manual effort, transforming the basic idea into a strong design foundation instantly.
Phase 2: Conversational Refinement – Updating the Diagram with Natural Language
The powerful initial output provided a perfect foundation, but the developer needed two small, final adjustments for clarity and compliance. In a conversational modeling environment, this means simple text commands, not dragging shapes.
The Refinement Prompts:
- Adding a Mandatory Security Step: For compliance, the password processing must be explicitly modeled early in the flow.
“Add a new action immediately after ‘Collect username, email, password’ named ‘Securely Hash and Salt Password’.”
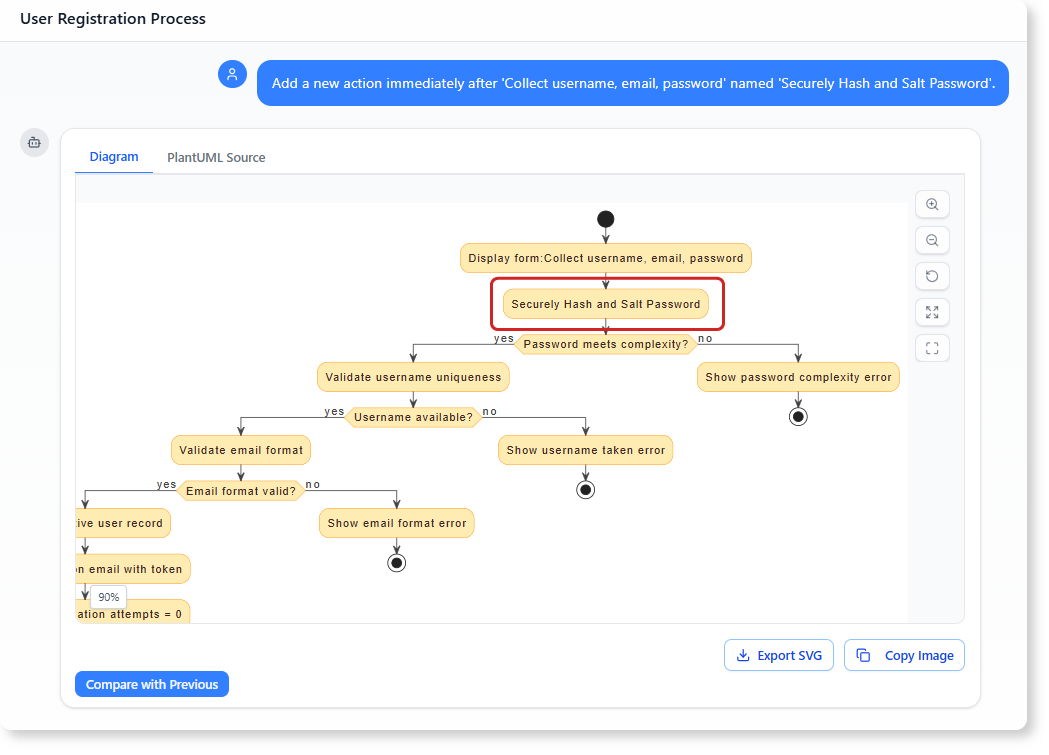
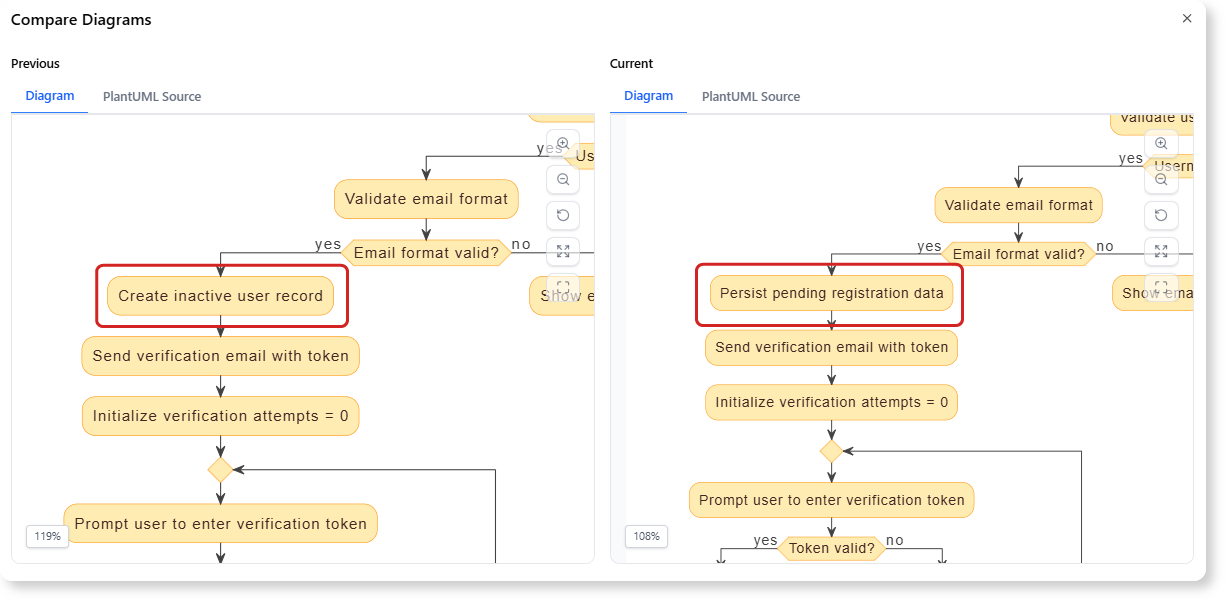
- Renaming an Action: The current action for saving the data, ‘Create inactive user record’, is too specific for a high-level process model.
“Rename the action ‘Create inactive user record’ to ‘Persist pending registration data’.”
Benefit: This conversational, iterative process is the hallmark of modern AI diagramming. Instead of wrestling with connectors and notation, the developer issues simple commands. The AI understands the context, adjusts the complex PlantUML code, and delivers a finalized, accurate model ready for the next phase of analysis.
Phase 3: Analysis and Documentation – Leveraging the Finalized Diagram
With the high-fidelity Activity Diagram finalized through conversational commands, the next step is to leverage the AI again to generate critical project documentation based on the visual model.
A. Formal Security Path Identification for Auditing
The diagram’s detailed logic, particularly the security loop, is essential for compliance and testing. The AI is asked to formally trace the intended failure path.
The Analysis Prompt:
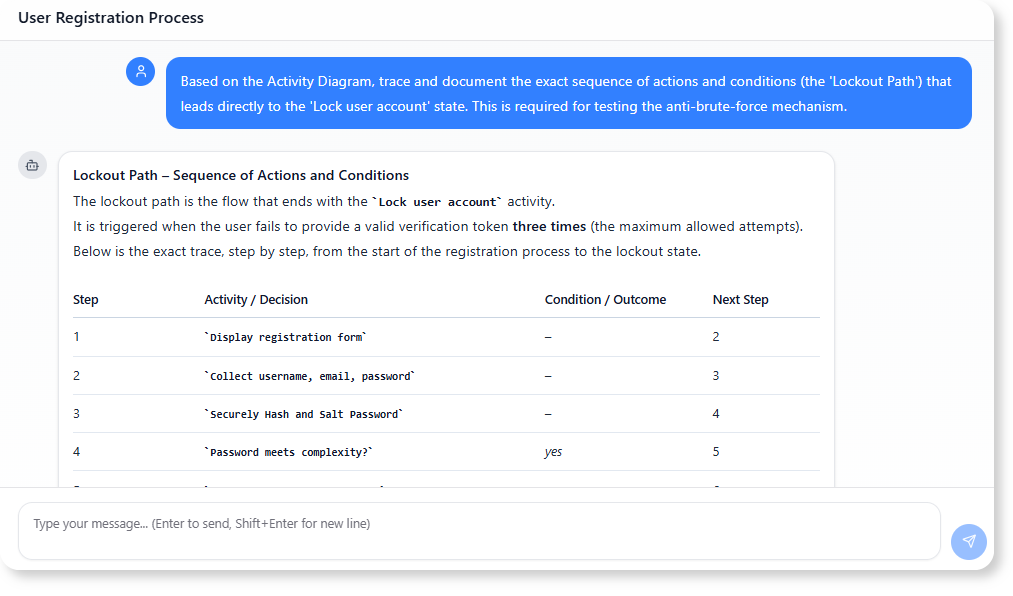
“Based on the Activity Diagram, trace and document the exact sequence of actions and conditions (the ‘Lockout Path’) that leads directly to the ‘Lock user account’ state. This is required for testing the anti-brute-force mechanism.”
Benefit: The AI automatically extracts the precise sequence of events for security testing: Three iterations of (Token invalid → Show error → Increment attempts) leads to the final conditional exit [Verification attempts < 3? is (no)] → Lock user account.
B. Generating State Transition Documentation for the Backend
The registration process is defined by its state changes (e.g., Inactive, Active, Locked). The diagram makes these transitions clear, allowing the AI to generate technical specifications for the database.
The Analysis Prompt:
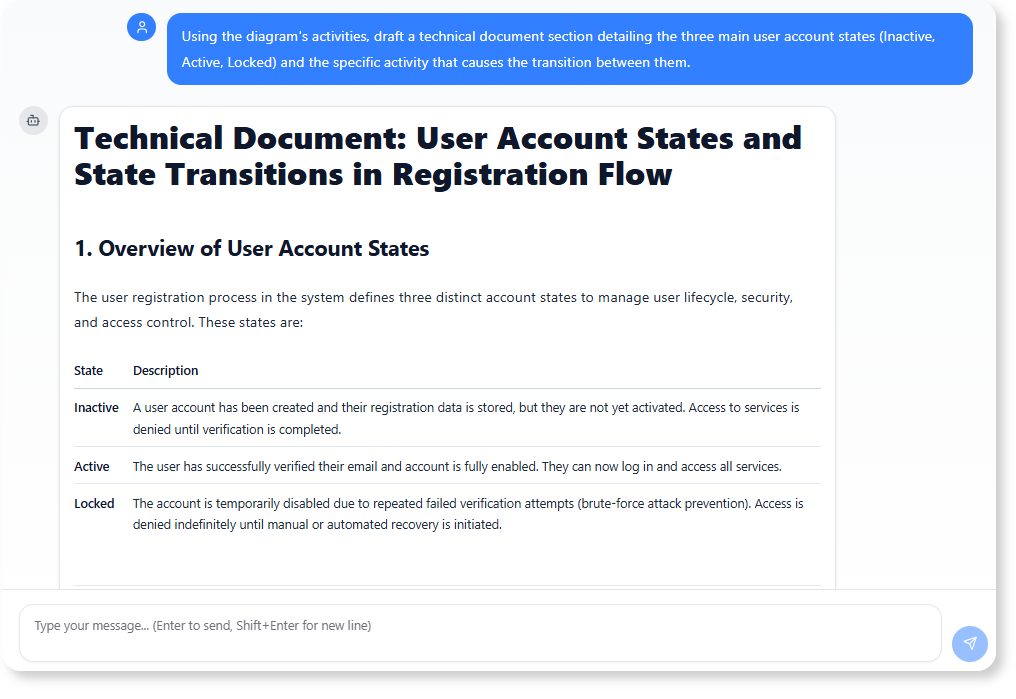
“Using the diagram’s activities, draft a technical document section detailing the three main user account states (Inactive, Active, Locked) and the specific activity that causes the transition between them.”
Benefit: This uses the formal model to automatically generate a State Transition Specification, which is essential for backend developers to ensure they implement the correct database status updates (Create inactive user record, Activate user account, Lock user account) at the exact points defined in the approved flow. This minimizes translation errors between the design and the implemented code.
For more information on UML and AI-powered visualization, visit our UML resource hub.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













