The UML Class Diagram is the essential blueprint for a system’s structure. It defines the core data entities (classes), their attributes, and the precise relationships (associations, inheritance, multiplicity) between them. For any data-intensive application, like a Library Management System, accurately modeling these relationships is critical for building a robust and scalable database and codebase.
This case study demonstrates how a system architect uses the Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot to rapidly move from a high-level concept to a complex, object-oriented model, leveraging conversational commands to refine structural details.
Phase 1: Idea to Foundation – The Initial Prompt
The architect begins with the fundamental entities of the library system.
The Initial AI Prompt:
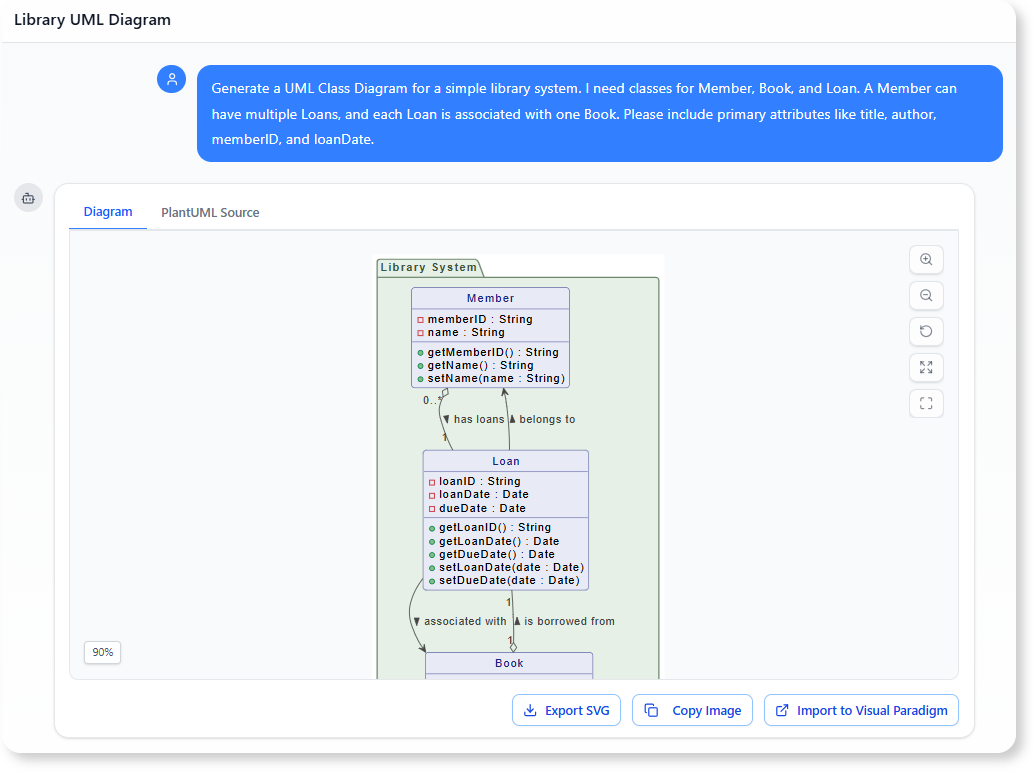
“Generate a UML Class Diagram for a simple library system. I need classes for Member, Book, and Loan. A Member can have multiple Loans, and each Loan is associated with one Book. Please include primary attributes like
title,author,memberID, andloanDate.”
The AI Chatbot responds by creating the three classes with their basic associations (e.g., 1..* between Member and Loan), instantly defining the core data relationships. Notably, the AI proactively added isbn to Book and dueDate to Loan, delivering a more robust and complete model than initially requested.
Phase 2: Conversational Refinement – Adding Complexity and Inheritance
The initial diagram is functional, but the architect recognizes two major necessary refinements: adding inheritance for media types and explicitly defining multiplicity constraints for business rules.
The Refinement Prompts:
- Introducing Inheritance: To handle future media types (DVDs, magazines), the design needs an abstract, reusable structure.
“Create an abstract class called
LibraryItem. Make bothBookand a new class,DVD, inherit from it. Move the common attributeisReserved: Booleanto the parentLibraryItem.”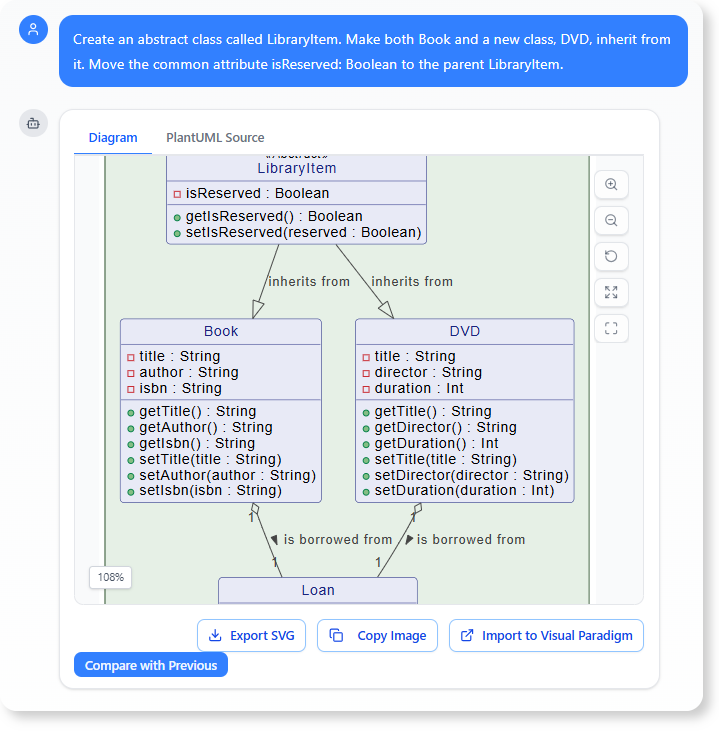
- Defining Multiplicity Constraints (Business Rules): The library imposes a clear borrowing limit.
“Update the association between
MemberandLoanto reflect a maximum borrowing limit of 5 items. The multiplicity should be updated to $0..5$ loans per member.”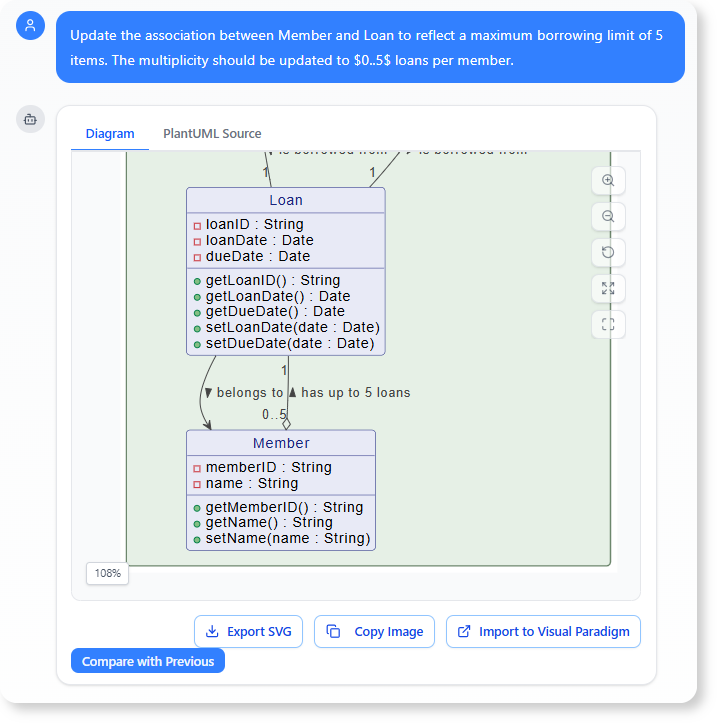
Benefit: This demonstrates the AI’s ability to handle advanced object-oriented concepts like inheritance and accurately modify the critical multiplicity notation based on a simple, spoken business rule. The model becomes a precise, compliant structural blueprint without requiring manual diagram manipulation.
Phase 3: Analysis and Implementation – Leveraging the Finalized Diagram
With the structural model finalized, the Class Diagram serves as the single source of truth for downstream documentation tasks. The AI is used to directly convert the model into essential project documentation.
A. Generating the Functional Requirements Document (FRD) Section
The classes, attributes, and associations define the scope and capabilities of the system.
The Analysis Prompt:
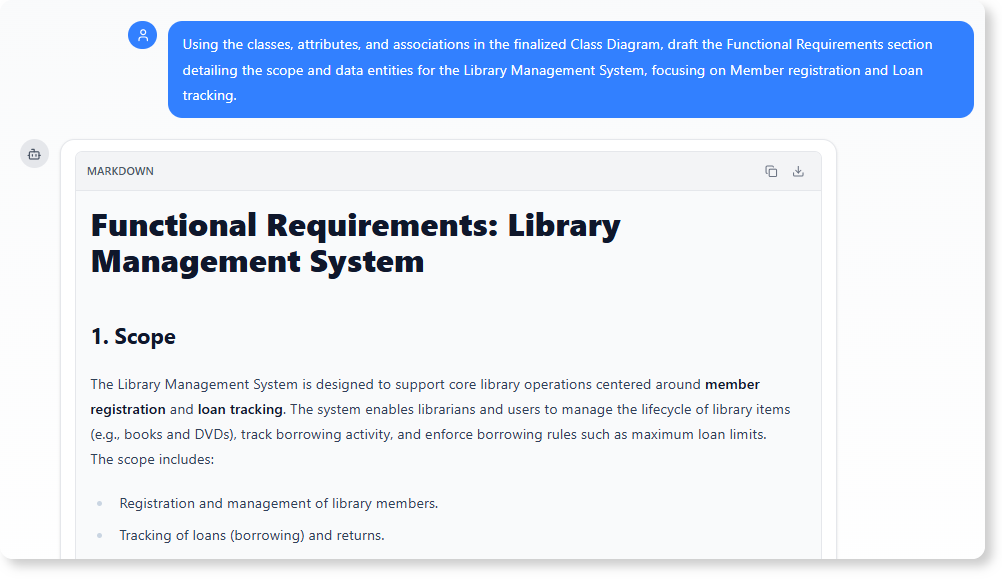
“Using the classes, attributes, and associations in the finalized Class Diagram, draft the Functional Requirements section detailing the scope and data entities for the Library Management System, focusing on Member registration and Loan tracking.”
Benefit: This task instantly translates the visual structural model into a formal section of the FRD, ensuring the project documentation is consistent with the approved design blueprint.
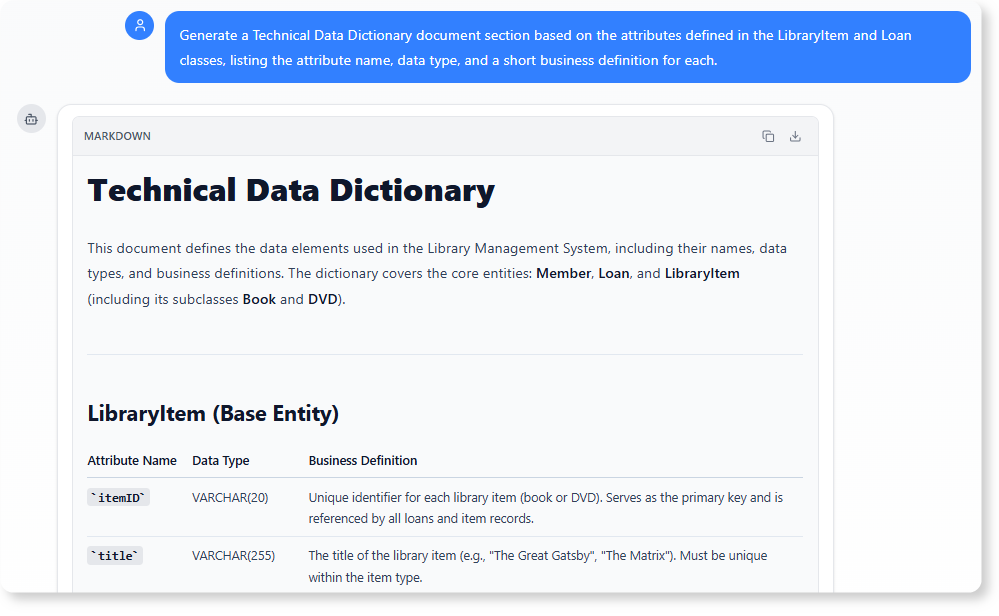
B. Generating the Technical Data Dictionary
The specific attributes, data types, and constraints defined in the diagram form the basis of the system’s technical specification.
The Analysis Prompt:
“Generate a Technical Data Dictionary document section based on the attributes defined in the
LibraryItemandLoanclasses, listing the attribute name, data type, and a short business definition for each.”
Benefit: The AI provides the exact technical specifications necessary for developers and database administrators, leveraging the data types and names defined directly in the UML model to create clear, implementation-ready documentation.
To get more information about UML and its AI-driven visualization methods, visit our UML resource hub.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













