Introduction to Intelligent Modeling
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the distinction between general-purpose language models and specialized modeling engines is becoming increasingly critical for businesses. While general Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized text generation, they often struggle with the structural rigidity and logical interconnectedness required for technical diagramming. The primary difference between a general LLM chatbot and Visual Paradigm’s AI chatbot lies in modeling intelligence.
While a generic AI typically generates text or static images based on broad Internet data, Visual Paradigm’s AI is a specialized engine trained specifically on formal modeling standards like UML, ArchiMate, and C4. This guide explores the technical nuances, strategic purpose, and workflow advantages of using a dedicated domain expert for diagramming.
The Core Distinction: General LLMs vs. Specialized AI
Unlike generic AI tools that often treat diagrams as simple checklists or templates to fill, Visual Paradigm’s AI functions as a true domain expert. This distinction is rooted in how the underlying technology interprets user intent and structural logic.
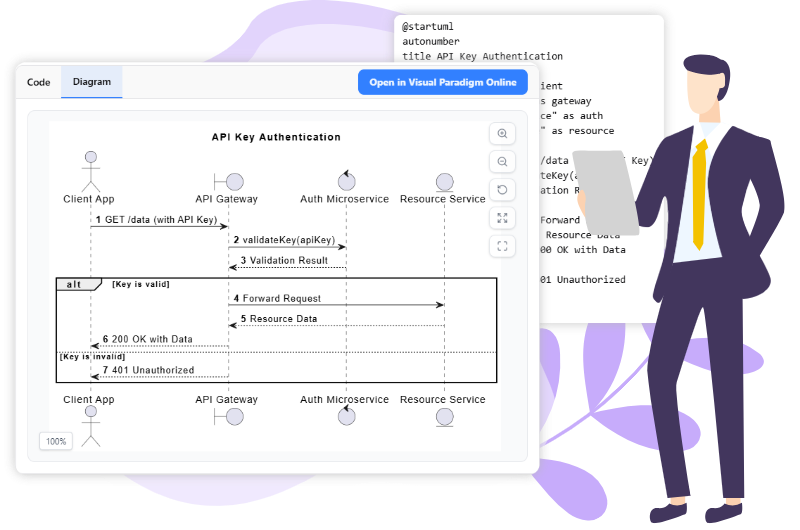
1. Semantic Understanding and Adherence to Standards
General LLMs often lack the ability to distinguish between complex technical relationships. They may generate a box labeled “User” without understanding the specific syntax required for an Actor in a Use Case diagram. In contrast, Visual Paradigm’s AI possesses deep semantic understanding. It discerns diagram semantics, such as the functional difference between a class and an attribute, or a process and a sub-process.
Furthermore, generic tools often produce visually “robotic” suggestions or inaccurate shapes that look correct superficially but fail technical review. Visual Paradigm’s AI is trained on formal industry standards, ensuring the output is not just a picture, but a technically accurate and logically meaningful model compliant with industry norms.
2. Interconnectivity and Logic Mapping
One of the most significant limitations of generic AI is the lack of context between data points. For example, in a SWOT analysis, a generic AI might list points in a vacuum. Visual Paradigm’s AI actively maps relationships, demonstrating how a specific “weakness” (such as inventory constraints) directly limits a specific “opportunity” (like market expansion). This logical mapping transforms a static diagram into a dynamic analysis tool.
3. Evolution vs. Static Generation
Most AI tools offer one-time generation: you input a prompt, and you receive an image or text. Visual Paradigm supports conversational diagram engineering. This allows users to evolve complex designs through an ongoing dialogue, refining the model iteratively rather than starting from scratch with every new prompt.
Comparative Overview
To better understand the operational differences, the following table contrasts the capabilities of general LLMs with Visual Paradigm’s specialized engine:
| Feature | General LLM Chatbot | Visual Paradigm AI |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Output | Text or static image generation | Technically accurate, standard-compliant models |
| Training Data | Broad, generalized internet data | Formal standards (UML, ArchiMate, C4) |
| Context Awareness | Isolated data points | Interconnected logic and relationship mapping |
| Workflow Style | One-off generation | Conversational diagram engineering (Iterative) |
The Strategic Purpose of the Platform
The Visual Paradigm AI platform is designed to act as an intelligent modeling partner that bridges the gap between abstract human ideas and technical precision. Its architecture serves three primary goals:
- Accessibility: It enables non-experts, such as startup founders or project managers, to participate in design conversations without needing to learn complex syntax or notation.
- Instant Visualization: It turns messy, vague requirements into presentation-ready diagrams in seconds. This capability facilitates faster alignment and creates fewer misunderstandings within agile teams.
- Active Documentation: It transforms static diagrams into a knowledge base. Users can interact with the model, asking questions such as “What are the security risks in this setup?” or “Explain the data flow,” turning the diagram into a living resource.
Value Proposition: Efficiency and Precision
Adopting specialized AI offers significant advantages over traditional manual drawing or generic text-based AI. The impact on workflow efficiency and accuracy is measurable.
Extreme Efficiency Gains
Case studies indicate that using this AI can reduce diagram creation time from 120 minutes to just 10 minutes—a 92% improvement. This massive reduction in time allows teams to focus on architectural decisions rather than the mechanics of drawing.
Refinement Without Friction
Users can modify diagrams with simple natural language commands like “Add a payment gateway” or “Make the activity loop tighter.” This avoids the manual “drag-and-drop” chore associated with traditional tools.
Professional Integration and Reduced Errors
Unlike standalone AI image generators, diagrams created here are not isolated. They can be imported directly into the Visual Paradigm desktop application, allowing professional modelers to apply advanced features like simulation, timing analysis, and team versioning. Furthermore, AI validation ensures that technical “happy paths” and “failure states” are correctly modeled, reducing missed logic branches by up to 75% compared to manual drafting.
Analogy for Understanding
To summarize the difference, think of a general LLM as a sketch artist who can draw a pretty picture of a building but doesn’t know how plumbing or electricity works. Visual Paradigm is an expert architect standing beside you. You describe your dream home, and they don’t just sketch it—they create a technically sound blueprint that follows all building codes. If you decide to “move a wall” later, the architect doesn’t just erase a line; they redraw the entire structural plan to ensure the house won’t collapse.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.












