The landscape of data architecture is undergoing a significant transformation. Traditional methods of database design, which often involve manual shape dragging, tedious normalization calculations, and raw SQL coding, are being revolutionized by artificial intelligence. By integrating tools like DB Modeler AI and advanced AI Chatbots, modern platforms are automating the entire lifecycle of database creation. This guide explores how these technologies transform natural language requirements into technical, production-ready schemas through a seamless, automated workflow.
1. Transforming Natural Language into Technical Models
The foundation of AI-driven database design lies in its ability to process and understand human language. The integration begins with Text-to-Model generation, a feature that allows architects and developers to describe their application or business needs using plain English rather than complex syntax.
Intent Interpretation and Expansion
Advanced AI algorithms go beyond simple keyword matching. They perform deep intent interpretation to suggest relationships and fill in missing details. This ensures that a vague concept is expanded into a structured diagram, capturing the nuance of the user’s requirements.
Conversational Modeling
Through an integrated AI Chatbot, the design process becomes interactive. Users can modify their schemas using simple commands. For example, typing “Add payment gateway” or “Rename Customer to Buyer” executes immediate structural changes. This eliminates the manual friction of dragging shapes and connecting lines, allowing designers to move at the speed of thought.
Multi-Language Capabilities
To support global development teams, these AI tools detect and respond to prompts in various languages, including Spanish, Chinese, Japanese, and German. This ensures that generated diagrams and their accompanying explanations are localized, reducing communication barriers in international projects.
2. Automated Diagram Generation Mechanics
Once the natural language input is processed, the AI automates the creation of foundational database models. This automation covers several types of diagrams necessary for a robust architecture.
- AI ERD Generation: The tool automatically defines tables, columns, and foreign key constraints based on textual descriptions. It infers relationships that might not be explicitly stated but are contextually necessary.
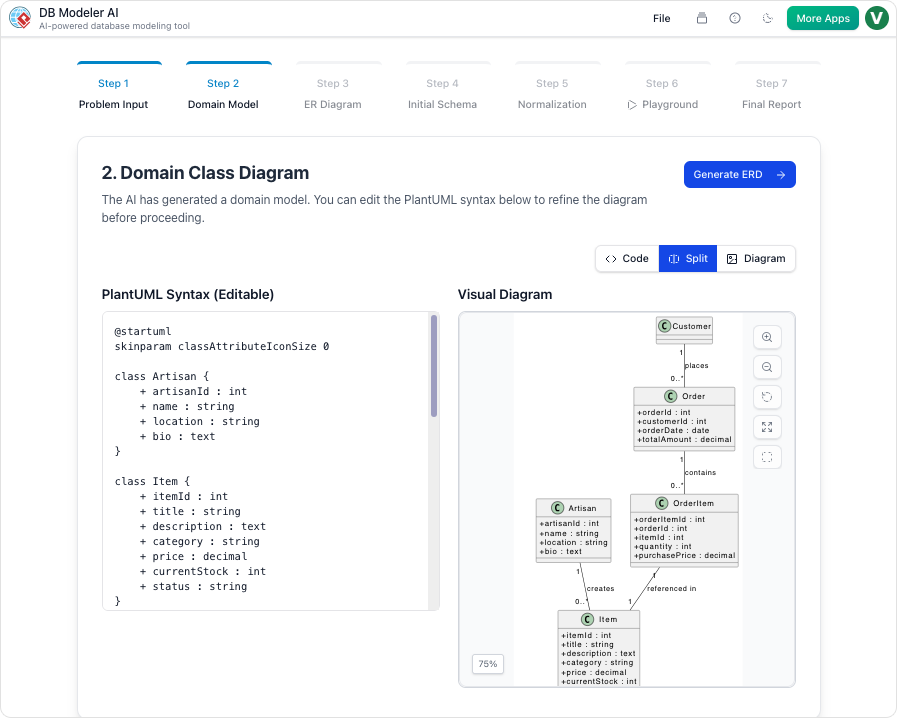
- Domain Class Diagrams: Before committing to a physical database structure, the AI generates PlantUML domain class diagrams. This visualizes high-level objects and attributes, providing a conceptual overview of the system.
- Instant Entity Suggestions: Even within a desktop environment, the AI provides real-time assistance. Typing a phrase like “Design a Hospital Management System” prompts the generation of relevant entities, attributes, and relationships immediately.
3. The Guided 7-Step AI Workflow
For complex database designs, simple automation is not enough. The DB Modeler AI employs a specialized, sequential workflow to bridge the gap between abstract ideas and concrete implementation. This 7-step process ensures data integrity and structural soundness.
| Step | Process Phase | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Problem Input | The AI converts natural language descriptions into a detailed set of technical requirements. |
| 2 | Domain Class Diagram | High-level objects are visualized in an editable format to establish the conceptual framework. |
| 3 | ER Diagram | The conceptual model is converted into a database-specific Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) with defined primary and foreign keys. |
| 4 | Initial Schema Generation | The ERD is translated into PostgreSQL-compatible SQL DDL statements, preparing the structure for deployment. |
| 5 | Intelligent Normalization | A critical automated step where the AI optimizes the schema progressively from 1NF to 3NF. It provides rationales for every change to eliminate data redundancy. |
| 6 | Interactive Playground | Users can test the schema in a browser-based SQL client seeded with realistic AI-generated sample data to verify logic before deployment. |
| 7 | Final Report and Export | The AI packages all diagrams, SQL scripts, and technical documentation into PDF or JSON formats for easy sharing and implementation. |
4. Synchronization and Optimization
Maintenance and consistency are often the most challenging aspects of database management. AI platforms address this through model-driven synchronization and intelligent analysis.
Model-Driven Synchronization
For existing models, users can synchronize ERDs to Class Diagrams. The AI assists in mapping entities to classes and columns to attributes, ensuring that different technical views of the system remain consistent without manual updates.
Intelligent Analysis and Layout
Designers can query the AI Chatbot regarding their specific diagrams to receive suggestions for design improvements and best practices. Furthermore, a Smart Layout feature utilizes AI to ensure diagrams are generated with perfect spacing, alignment, and balance. This allows the architect to focus on the structural integrity of the data rather than the aesthetics of the diagram.
Conclusion
To understand the magnitude of this technology, think of the platform’s AI as an expert architect and contractor combined. You describe the kind of house you want in plain words; the architect (AI) instantly draws the blueprints, the engineer (AI) automatically ensures the plumbing and wiring (normalization and constraints) meet code, and the contractor (AI) builds a “model home” with furniture (sample data) so you can walk through it before the real construction begins. This comprehensive automation shifts the focus from manual drafting to high-level architectural strategy.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













