“The best way to learn object-oriented design is not by memorizing patterns — it’s by playing the roles.”
In this article, we’ll walk through a step-by-step introduction to CRC cards (Class–Responsibility–Collaborator) using a real-world, beginner-friendly example: a Library Book Borrowing System. Whether you’re just starting your journey into software design or leading a team workshop, CRC cards offer a simple, powerful, and collaborative way to model object-oriented systems.
🎯 What Are CRC Cards?
CRC cards are a lightweight, physical (or digital) modeling technique used in object-oriented design. Each card represents a class and contains three key elements:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Class | The name of the class (e.g., Book) |
| Responsibilities | What the class knows or does |
| Collaborators | Other classes this class needs to work with |
They’re especially effective for brainstorming, designing, and validating class structures early in development — before writing a single line of code.
📚 Case Study: Library Book Borrowing System
Let’s imagine a small public library where members can:
-
Search for books by title
-
Borrow available books (up to a limit)
-
Return books when done
The system must track:
-
Which books are borrowed
-
By whom
-
When they are due
We’ll use the CRC card method to discover and refine the classes in this system — step by step.
✅ Step 1: Find Candidate Classes (Brainstorm Nouns)
Start by reading the scenario and pulling out nouns — these are potential classes.
From the description, we identify:
-
Library
-
Member (or Patron)
-
Book
-
Loan (or Borrowing)
-
DueDate (possibly too small)
-
LibraryCard (might be part of Member)
We filter and keep only the most meaningful ones:
✅ Member, Book, Loan
⚠️ Note: Don’t worry about getting all classes right at first — that’s the beauty of CRC cards. You’ll discover missing ones through role-play!
✏️ Step 2: Create Initial CRC Cards
Now, we assign responsibilities and collaborators to each class.
📘 Class: Book
| Responsibilities | Collaborators |
|---|---|
| Know its title | — |
| Know its author | — |
| Know its ISBN | — |
| Know if it is currently available | Loan |
| Be borrowed | Loan |
| Be returned | Loan |
💬 The Book doesn’t “know” who borrowed it — it only knows whether it has an active loan.
👤 Class: Member
| Responsibilities | Collaborators |
|---|---|
| Know name | — |
| Know member ID | — |
| Know how many books are currently borrowed | Loan |
| Borrow a book (if allowed) | Book, Loan |
| Return a book | Book, Loan |
| Check if borrowing limit is reached | Loan |
💬 The Member manages its own borrowing behavior and checks limits via the Loan class.
📅 Class: Loan
| Responsibilities | Collaborators |
|---|---|
| Record which book was borrowed | Book |
| Record which member borrowed it | Member |
| Record borrow date | — |
| Calculate due date | — |
| Know if it is overdue | — |
| Mark as returned | Book |
💬 The Loan class holds the relationship between a Member and a Book, including timing details.
🎭 Step 3: Role-Play a Scenario — “Borrow a Book”
Now comes the fun part: role-playing the scenario as if the cards were real objects.
📖 Scenario: Curtis wants to borrow “Clean Code”, which is available.
Let’s walk through it step by step:
-
Member (Curtis) says: “I want to borrow ‘Clean Code’.”
→ First checks: “Do I have fewer than 3 books already?”
→ Asks Loan: “How many active loans do I have?” -
Loan responds: “You have 1 active loan → you can borrow.”
-
Member searches for the book: “Where is ‘Clean Code’?”
→ Asks Book: “Are you available?” -
Book checks: “Do I have an active (not returned) Loan?”
→ Asks Loan: “Is there an active loan for me?” -
Loan replies: “No — you’re available!”
-
Member creates a new Loan object:
-
Links to this Book and Member
-
Sets borrow date = today
-
Calculates due date = today + 14 days
-
-
Book is updated: “Now I have an active loan → I’m no longer available.”
✅ Result: The borrowing process feels natural, distributed, and logical.
🔄 Step 4: Another Scenario — “Return a Book”
📖 Scenario: Curtis returns “Clean Code”
-
Member (Curtis) says: “I want to return ‘Clean Code’.”
-
Member finds the matching Loan (likely by querying Loan with the book and member).
-
Loan marks itself as returned.
-
Loan tells Book: “You are now available again.”
✅ Clean, clear, and cohesive — no class is doing work outside its responsibility.
🔍 Step 5: Refine & Add Missing Classes
After role-playing, we notice a gap:
❓ Who finds the book by title?
Currently, Member is asking Book directly — but Book doesn’t know how to search!
We need a central coordinator.
➕ New Class: Library
| Responsibilities | Collaborators |
|---|---|
| Add a new book to the collection | Book |
| Find book by title | Book |
| Register a new member | Member |
| Process book borrowing request | Member, Book, Loan |
| Process book return | Member, Book, Loan |
| Know all current loans | Loan |
💬 The Library acts as the central hub — it knows all books, all members, and all loans.
✨ Updated Flow: “Borrow a Book” with Library
-
Member → Library: “Find book titled ‘Clean Code’.”
-
Library searches its collection and returns the Book (or
nullif not found). -
Member now knows the book exists → asks Library: “Can I borrow this book?”
-
Library checks:
-
Is the book available? (via
Book.isAvailable()) -
Is the member under the borrowing limit? (via
Loan.countActiveLoans(member))
-
-
If yes → Library creates a new Loan and updates both Book and Loan.
-
Book becomes unavailable; Loan tracks the relationship.
✅ Now the flow makes sense — the Library handles discovery and coordination.
🧩 Final CRC Cards Summary (Simplified for Beginners)
| Class | Key Responsibilities | Key Collaborators |
|---|---|---|
| Library | Manages books, members, loans; handles borrowing/returning | Book, Member, Loan |
| Member | Knows personal info; initiates borrow/return | Library, Loan |
| Book | Stores metadata; tracks availability | Library, Loan |
| Loan | Tracks borrowing history; calculates due dates; manages return status | Member, Book, Library |
✅ Design Principle: Each class has one clear purpose, and responsibilities are cohesive and well-distributed.
🌟 Why CRC Cards Work So Well (Beginner Takeaways)
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Responsibility-Driven Design | Forces you to think: “What does this class know or do?” instead of just storing data. |
| Natural Discovery of Missing Classes | Role-playing reveals gaps (like the missing Library) — no guesswork needed. |
| Immediate Feedback via Role-Play | If a flow feels awkward, you know the responsibility is in the wrong place. |
| Low-Ceremony & Collaborative | No complex tools — just index cards, sticky notes, or a whiteboard. Great for teams. |
| Bridges Requirements to Code | Turns user stories into real class interactions. |
🛠️ Quick Tips for Your First CRC Session
-
Use physical cards (3×5 index cards or sticky notes) — it’s more engaging.
-
One class per card — keep it simple.
-
Write large and legible — others should read it easily.
-
Role-play out loud — pass cards around like real objects.
-
Start with 3–6 core scenarios (e.g., borrow, return, search).
-
Don’t aim for perfection — the goal is iteration, not a final design. Refine as you go.
-
Use simple, domain-specific names — avoid technical jargon. Use “Member” instead of “Patron” if your team agrees.
-
Invite everyone to participate — even non-programmers can help spot missing responsibilities.
-
Sketch a simple class diagram afterward — to visualize relationships and confirm consistency.
-
Keep it fun — treat it like a game. The more engaged your team, the better the results.
🔄 Try It Yourself: Next Domains to Explore
Once you’ve mastered the library system, try applying CRC cards to other beginner-friendly domains:
☕ Coffee Shop Order System
-
Classes:
Customer,Order,MenuItem,Barista,CashRegister -
Scenarios: Place order → Add drink → Apply discount → Pay → Print receipt
🪙 Vending Machine
-
Classes:
VendingMachine,Product,Coin,Dispenser,ChangeCalculator -
Scenarios: Insert coin → Select item → Dispense product → Return change
🎮 Quiz Game
-
Classes:
Quiz,Question,Player,ScoreTracker,GameSession -
Scenarios: Start quiz → Answer question → Check correctness → Show final score
🚗 Parking Garage
-
Classes:
Garage,Car,ParkingSpot,Ticket,Gate -
Scenarios: Enter garage → Park car → Exit → Pay fee → Get ticket
Each of these systems builds on the same principles:
-
Identify nouns → assign responsibilities → role-play → refine → repeat.
📌 Final Thoughts: CRC Cards Are More Than a Technique — They’re a Mindset
The real power of CRC cards isn’t in the cards themselves — it’s in the conversation they spark.
When you write a card and say, “Who does this?” or “Who does it need to talk to?”, you’re already thinking like an object-oriented designer.
🔥 Pro Tip: Use CRC cards during sprint planning, tech spikes, or even in interviews to demonstrate your design thinking.
They’re not just for developers — they’re for anyone involved in building software: product managers, designers, testers, and students.
📎 Want More?
👉 Download a printable CRC card template (PDF or digital) to use in your next workshop.
👉 Try a live CRC session with a teammate — assign roles: “You’re the Member,” “You’re the Book,” etc.
👉 Share your results — post your cards on social media with #CRCcards or #OODesignJourney.
🏁 Conclusion
The Library Book Borrowing System is one of the most classic and effective CRC card examples — not because it’s complex, but because it’s simple, relatable, and revealing.
By following just five steps — brainstorming, card creation, role-playing, refining, and iterating — you can:
-
Discover classes naturally
-
Assign responsibilities clearly
-
Spot design flaws early
-
Build a shared mental model as a team
And best of all? You don’t need to be a senior developer to do it.
You just need curiosity, a few cards, and a willingness to play.
🚀 How Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered CRC Tool Streamlines the Design Process
Creating effective CRC (Class–Responsibility–Collaborator) cards is a cornerstone of object-oriented design — but it’s often time-consuming, especially during early brainstorming or team workshops. That’s where Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered CRC card generator transforms the experience from tedious to transformative.
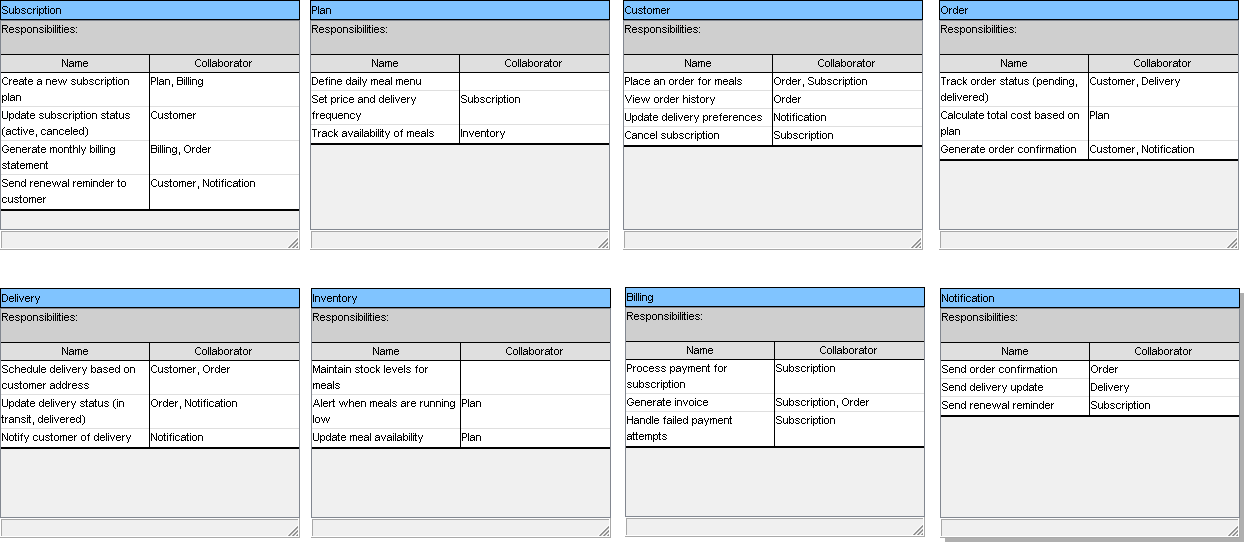
Instead of starting from scratch — listing classes, guessing responsibilities, and mapping collaborators — Visual Paradigm’s AI does the heavy lifting intelligently, giving you a smart, structured foundation to build upon. Here’s how it supercharges every step of the CRC design process:
✅ 1. Instant Brainstorming with Natural Language Input
No more blank cards or endless debate about “what should the class be?”
Just describe your system in plain English — like:
“I’m building a library system where members can borrow books, return them, and search by title. Each book has a title, author, and ISBN. There’s a borrowing limit of 3 books.”
Visual Paradigm’s AI instantly analyzes your input and suggests:
-
Candidate classes:
Member,Book,Loan,Library -
Responsibilities: e.g., “Check if book is available”, “Calculate due date”
-
Collaborators: e.g.,
Bookcollaborates withLoan,Membertalks toLibrary
👉 Result: Within seconds, you have a fully populated initial CRC card diagram — no guesswork, no wasted time.
✅ 2. Smart Suggestions That Match Real-World Design Principles
Unlike generic AI tools that spit out random class names, Visual Paradigm’s AI understands object-oriented design patterns and responsibility-driven thinking.
For example, when you mention “borrowing,” the AI:
-
Suggests a
Loanclass (not just aBorrowingorTransaction) -
Assigns meaningful responsibilities like “Record borrow date”, “Mark as returned”
-
Proposes correct collaborators:
Book,Member, andLibrary
This isn’t just automation — it’s AI-guided design wisdom that helps beginners learn best practices while experts save time.
✅ 3. Seamless Transition from Sketch to Professional Model
The AI doesn’t just generate a rough sketch. It creates a fully editable, native Visual Paradigm diagram — meaning you can:
-
Drag and drop cards to reorganize the layout
-
Edit responsibilities and collaborators in real time
-
Add icons, colors, or notes for clarity
-
Link cards to use cases, requirements, or code
💡 Pro Tip: Use the “Refine with AI” feature to ask:
“Suggest better responsibilities for the Member class based on borrowing rules.”
The AI will re-suggest more accurate or complete actions — like “Check if borrowing limit is reached” — helping you avoid common design flaws.
✅ 4. Role-Play Simulation Built-In (Yes, Really!)
One of the most powerful features? Visual Paradigm allows you to simulate scenarios directly in the diagram.
After generating the CRC cards, you can:
-
Click on a scenario (e.g., “Borrow a book”)
-
Use the AI to walk through the flow step-by-step
-
See which classes interact, in what order, and what responsibilities are triggered
This turns abstract cards into living design stories, making it easy to spot:
-
Misplaced responsibilities
-
Missing classes (like
Library) -
Broken collaboration chains
🔍 Example: The AI flags: “The Member class is trying to find a book — but no class handles search. Suggest adding a Library class.”
→ Instant insight. No guesswork.
✅ 5. Traceability & Integration with Full Development Workflows
The real power of Visual Paradigm’s AI CRC tool isn’t just in creating diagrams — it’s in connecting them to real development.
Once your CRC diagram is refined:
-
Generate UML Class Diagrams with one click
-
Export code skeletons (Java, C#, Python, etc.)
-
Link to requirements or user stories in your project
-
Share with team members via real-time collaboration
This means your CRC cards aren’t just a brainstorming artifact — they’re the starting point of your actual software design.
✅ 6. Perfect for Teams, Workshops, and Learning
Whether you’re:
-
A student learning OOP for the first time
-
A team lead running a design sprint
-
A developer prototyping a new feature
Visual Paradigm’s AI CRC tool adapts to your needs:
-
Use it in VP Desktop for deep editing and integration
-
Try it in VP Online for quick collaboration
-
Use the AI chat interface to ask questions like:
“What should the Loan class know?”
“Who should handle book availability checks?”
It’s like having a senior designer in your pocket — always ready to help you think clearly, organize responsibilities, and avoid design anti-patterns.
🎯 Summary: Why Visual Paradigm’s AI CRC Tool Is a Game-Changer
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Natural language input | Start with a story — get a design |
| Smart, context-aware suggestions | Avoid common design mistakes |
| Fully editable native diagram | Refine, organize, and polish |
| Scenario simulation & role-play | Test logic before coding |
| Traceability to code & requirements | Design → Implementation in one flow |
| Team collaboration & sharing | Work together in real time |
📌 Final Thought
“Good design isn’t about speed — it’s about clarity. And Visual Paradigm’s AI CRC tool gives you both.”
Instead of spending hours debating “who should do what,” you spend time thinking, refining, and validating your design — with confidence.
With Visual Paradigm, you’re not just using AI to draw diagrams.
You’re using AI to think better.
👉 Ready to experience the future of CRC design?
Start your free trial of Visual Paradigm today and turn your next idea into a smart, professional, AI-assisted CRC card diagram — in minutes.
🌟 No more blank cards. No more guesswork. Just clear, powerful design — powered by AI.
✅ Now it’s your turn: Grab some sticky notes, pick a simple system (like a coffee shop or vending machine), and try the CRC method.
📌 Remember: Good design isn’t about writing perfect code — it’s about asking the right questions.
And with CRC cards, you’re already asking them.
📌 Bonus: Printable CRC Card Template (Text Version)
┌────────────────────┐
│ [CLASS NAME] │
├────────────────────┤
│ Responsibilities: │
│ - │
│ - │
│ - │
├────────────────────┤
│ Collaborators: │
│ - │
│ - │
└────────────────────┘
Print this on 3×5 cards or use it in a digital tool like Miro, Figma, or Google Slides.
📚 Next Step?
Want a full walkthrough of the Coffee Shop Order System using the same CRC style?
👉 Just say the word — I’ll send you the next case study, step by step, with cards, scenarios, and role-play!
Happy designing! 🎮🧩💻
- How to Draw CRC Cards in Visual Paradigm: This step-by-step guide provides instructions on creating CRC cards using the software’s dedicated diagramming tools.
- Understanding CRC Card Diagrams in Visual Paradigm: An overview that explains how these diagrams are used to model object-oriented systems and their interactions.
- How to Create a CRC Card Diagram in Visual Paradigm: A detailed tutorial found on the Community Circle covering the creation and customization of CRC diagrams.
- Introduction to CRC Diagrams in Visual Paradigm: A comprehensive guide focused on utilizing CRC diagrams for object-oriented design and broader system modeling.
- Generating CRC Cards from Class Diagrams: This community discussion explores methods for leveraging existing class diagrams to automatically generate cards through reverse engineering.
- Synchronizing CRC Cards with Class Diagrams: A technical resource discussing bidirectional modeling to ensure design consistency between cards and class models.
- Introduction to CRC Card Diagrams (PDF Guide): A downloadable technical resource that explains the core concepts and applications of CRC cards in system analysis.
- Establishing Links Between CRC Cards and Class Diagrams: This article highlights techniques for maintaining traceability and linkage between different modeling levels.
- CRC Card Template in Visual Paradigm Gallery: A resource featuring a downloadable template designed to support early-stage object-oriented design.
- Moving CRC Cards Between Diagrams: A guide detailing how to transfer cards across different diagrams while maintaining data consistency.
