-
This comprehensive guide analyzes the performance of general-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) against specialized AI modeling tools, specifically Visual Paradigm AI, using 2026 benchmarks for UML class diagram accuracy.

1. Executive Summary: The 2026 Accuracy Benchmark
In professional software architecture, the difference between a “creative sketch” and a “production-ready model” is measured by adherence to formal standards. As of 2026, benchmarks reveal a significant gap in reliability:
- General LLMs (PlantUML/Mermaid): Exhibit an error rate of 15–40%+ for complex prompts.
- Visual Paradigm AI: Maintains a low error rate, typically under 10%, with 80–90% first-draft completion for professional scenarios.
While general LLMs serve as creative generalists, Visual Paradigm AI operates as a “seasoned architect,” enforcing strict semantic rules based on UML 2.5+ standards.
2. Quantifying Common Hallucinations
A. Arrow Types and Relationship Semantics
One of the most persistent failures in LLM-generated PlantUML is the misapplication of relationship notation. Because general LLMs rely on text-prediction patterns rather than semantic logic, they frequently hallucinate relationship visuals:
- LLM Hallucinations: Confusing open vs. filled arrowheads (e.g., using a generalization arrow for an association) or failing to distinguish between composition (filled diamond) and aggregation (hollow diamond).
- Visual Paradigm AI: Enforces standard UML compliance, ensuring that “is-a” (inheritance) and “part-of” (composition) relationships are visually and logically distinct.
B. Multiplicity and Constraints
Multiplicity (e.g.,
0..*,1..1) requires a deep understanding of business logic, which general LLMs often lack or misinterpret in text syntax:- LLM Hallucinations: Frequently generates incorrect or missing multiplicity. It may misinterpret a “one-to-many” requirement, or produce syntax errors within the PlantUML code block that prevent rendering.
- Visual Paradigm AI: Uses a modeling-aware conversation engine to precisely apply multiplicity commands (e.g., “make it 1..*”) without side effects to the rest of the diagram.
C. Stereotypes and Non-Standard Elements
General LLMs often “invent” notation to bridge gaps in their training data, leading to fabrication:
- LLM Hallucinations: Fabrication of non-standard stereotypes or invalid UML constructs that do not exist in the formal specification.
- Visual Paradigm AI: Restricts output to established modeling standards (UML, SysML, ArchiMate), minimizing the risk of creative but incorrect fabrications.
D. Inheritance vs. Composition
Conceptual errors are common when LLMs translate natural language into structure:
- LLM Hallucinations: Logically inconsistent relationships, such as establishing bidirectional inheritance (which is impossible) or failing to recognize when an object should live and die with its parent (Composition).
- Visual Paradigm AI: Analyzes intent to suggest logical improvements, such as identifying when a class should extend an “Event” or suggesting inverse relationships to ensure structural integrity.
3. Workflow Stability: Static Text vs. Living Models
Feature LLM-Generated PlantUML Visual Paradigm AI Output Type Static text-based syntax requiring an external renderer. Native, editable visual diagrams that update live. Refinement Full regeneration often causes layout shifts and lost context. Conversational updates that preserve existing layout. Error Handling Moderate/high failure on complex prompts; code often breaks. High stability; automated checks catch design flaws early. Persistence Session-based; no shared model repository. Living model repository for reuse across different views. 4. Conclusion for Professionals
For architects and developers in high-stakes environments like healthcare or finance, the hallucination risk of general LLMs makes them better suited for casual brainstorming rather than final documentation. Visual Paradigm AI is the superior choice for production-grade modeling because it functions as an active participant in the design conversation, providing architectural critiques and quality reports that identify patterns and suggest structural improvements.
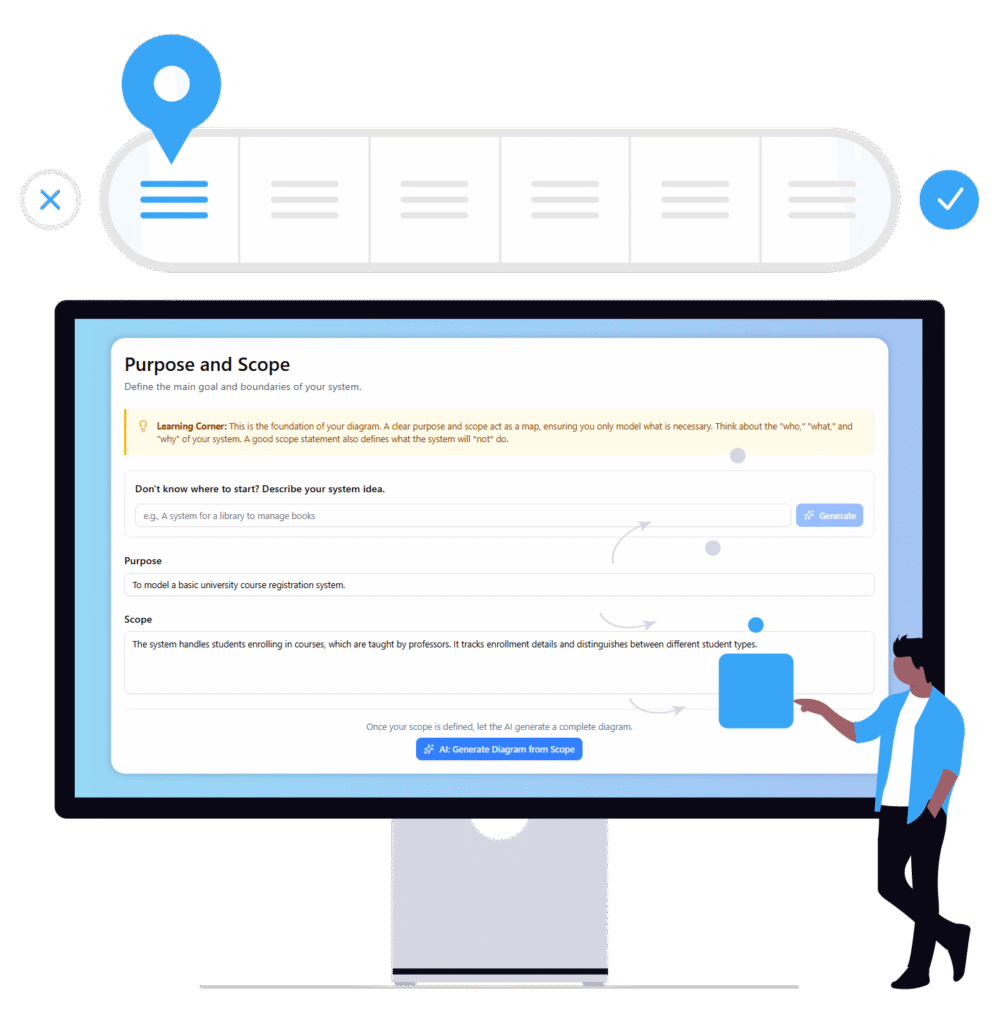
-
Visual Paradigm Chat – AI-Powered Interactive Design Assistant: An interactive AI interface for generating diagrams, writing code, and solving design challenges in real time.
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: AI analyzes text documents to automatically generate UML, BPMN, and ERD diagrams for faster modeling and documentation.
-
Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot Enhances Multi-Language Support …: AI chatbot supports multiple languages, enabling seamless diagram generation in Spanish, French, Chinese, and more.
-
AI -Powered BI Analytics by Visual Paradigm – ArchiMetric: Start using AI-powered BI analytics in under a minute—no installation or signup required for most features.
-
Discover the Power of Visual Paradigm ’s AI -Powered… – Visualize AI: Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered Image Translator leads the market with advanced capabilities beyond standard tools.
-
AI Chatbot for Diagramming: How It Works with Visual Paradigm: The AI chatbot converts natural language into diagrams, eliminating the need to learn modeling syntax or standards.
-
AI Brainstorming Features – Visual Paradigm: Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered brainstorming tools deliver intelligent idea generation and collaborative workflows to enhance creativity and productivity.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













