In the fast-paced world of modern software development, the journey from an abstract concept to a production-ready database is a defining challenge. At the core of this transition lies the concept of architectural maturity—a state where data structures are not just functional, but scalable, efficient, and robust. Central to achieving this maturity is database normalization, a critical process ensuring long-term data health.
Traditionally, bridging the gap between object-oriented concepts and relational database schemas has been a manual, error-prone task. However, new advancements in generative AI, specifically Visual Paradigm’s AI DB Modeler, are revolutionizing this workflow. This guide explores the principles of normalization, the transition from class diagrams to Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs), and how AI acts as an intelligent co-pilot to streamline these complex architectural phases.
The Pillars of Data Integrity: Understanding Normalization
Database normalization is the systematic process of organizing data to ensure data integrity and eliminate redundancy. Without proper normalization, databases often suffer from anomalies—unexpected errors during insertion, updates, or deletion—that can cripple an application as it scales.
To achieve architectural maturity, a database typically progresses through three primary stages of optimization, known as Normal Forms:
- First Normal Form (1NF): This is the foundational level. It ensures that every table cell contains a single, atomic value and that every record is unique. It eliminates repeating groups and establishes a basic structure.
- Second Normal Form (2NF): Building upon 1NF, this stage focuses on relationships. It ensures that all non-key attributes are fully functional and dependent on the primary key, removing partial dependencies in composite key scenarios.
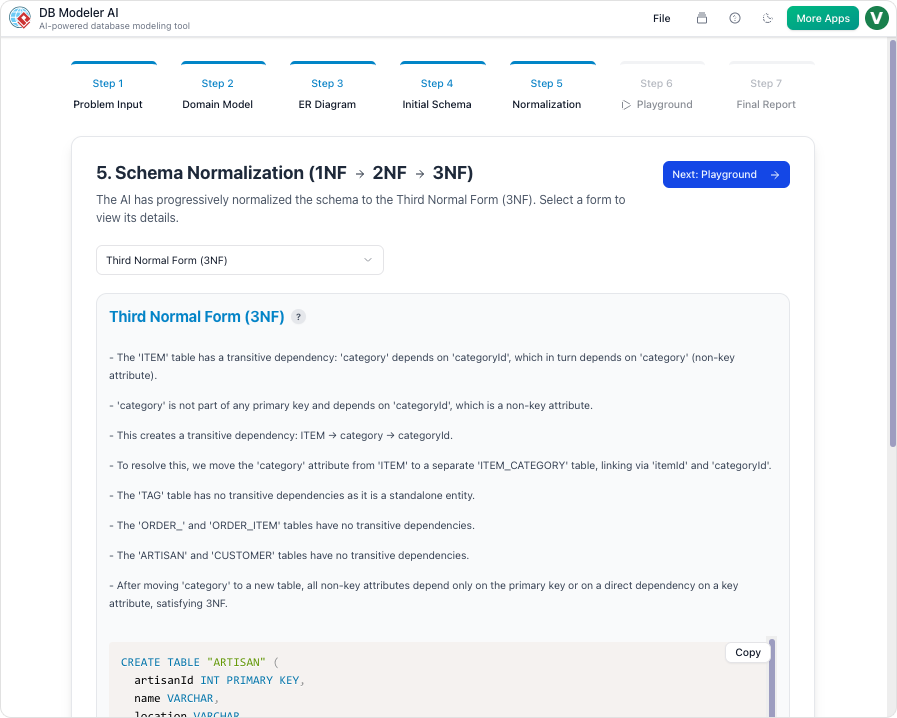
- Third Normal Form (3NF): This is often considered the standard level for production databases. It ensures that all attributes are dependent only on the primary key, effectively removing transitive dependencies where non-key columns rely on other non-key columns.
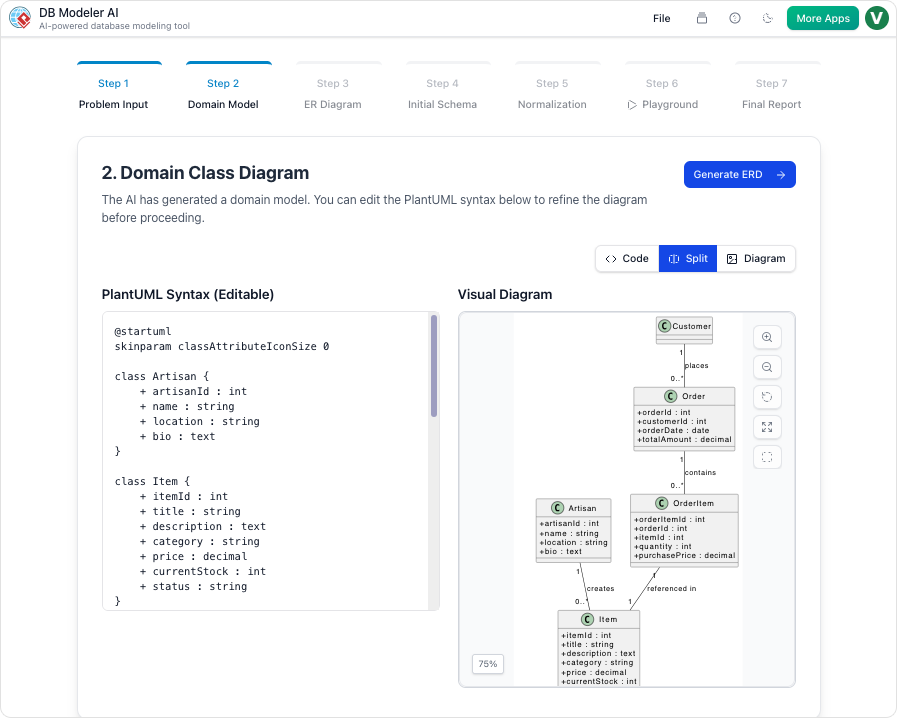
The Architectural Bridge: From Class Diagrams to ERDs
Database design is rarely an isolated task; it is part of a broader modeling lifecycle that translates business logic into technical implementation. Understanding the distinction between conceptual and technical models is vital.
The Modeling Lifecycle
The evolution of a database design generally follows three steps:
- Class Diagrams (Conceptual View): These diagrams describe a system’s objects and behaviors. They map out the ‘what’ and ‘how’ of the business logic without being constrained by the rigid rules of relational databases.
- Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs): This stage moves the design into the technical realm. It defines tables, columns, primary keys, and foreign key constraints, acting as the blueprint for the physical database.
- Normalization (Optimization View): The final phase where the ERD is streamlined to ensure efficiency, reducing data duplication and enforcing integrity constraints.
To understand this transition, consider the analogy of manufacturing a car. The Class Diagram is the initial artistic sketch of how the car looks and functions. The ERD represents the detailed mechanical blueprints showing how every part connects. finally, Normalization is the engineering process of streamlining those parts to ensure there is no unnecessary weight or loose bolts.
Accelerating Development with Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler
While the theory of normalization is well-established, the manual execution is time-consuming. Visual Paradigm’s AI DB Modeler addresses this by serving as an intelligent co-pilot that automates the heavy lifting of database architecture.
1. The Automated 7-Step Workflow
The platform replaces manual drafting with a guided 7-step AI workflow designed to transform plain English requirements into tested, optimized schemas:
- Instant Generation: Users describe their system needs in natural language. The AI parses this input to expand it into detailed technical requirements.
- Multi-Level Modeling: The tool automatically generates a Domain Class Diagram to capture business logic and then converts it into a database-specific ER Diagram.
- Intelligent Normalization: Perhaps the most critical feature, the AI progressively optimizes the schema toward 3NF. It provides educational rationales for every structural change, helping designers understand the ‘why’ behind the architectural shifts.
2. Conversational Refinement and Global Reach
Productivity is further enhanced through an AI Chatbot that enables conversational editing. Instead of manually dragging shapes or re-routing connectors, designers can issue commands such as “Add payment gateway” or “Rename Customer to Buyer.” The AI updates the diagram instantly, allowing architects to focus on high-level strategy rather than formatting.
Furthermore, the tool supports over 40 languages, including Spanish, Chinese, Japanese, and German. This breaks down communication barriers in multinational teams, ensuring that generated content and explanations feel native to every stakeholder.
Validation and Lifecycle Management
A diagram is only as good as the database it produces. To reduce architectural debt, the AI DB Modeler includes an Interactive SQL Playground. This feature generates PostgreSQL-compatible SQL DDL statements and seeds the environment with realistic, AI-generated sample data.
This allows developers to:
- Test complex queries against the proposed schema.
- Validate relationships and constraints instantly.
- Avoid the need for local database installation during the design phase.
Finally, the tool ensures synchronization across the entire project lifecycle. Whether performing Forward Engineering to generate production scripts or Reverse Engineering to modernize legacy databases, the AI ensures the design models and the physical database remain in perfect alignment.
Conclusion
Achieving architectural maturity requires more than just knowing SQL; it requires a disciplined approach to structure and optimization. By integrating generative AI into the database design process, Visual Paradigm transforms what was once a manual chore into an automated, error-free workflow. From conceptualizing class diagrams to finalizing 3NF schemas, AI-powered modeling empowers developers to build software that is robust, scalable, and ready for the future.

