When working with the AI Diagram Generator, such as AI Chatbot provided by Visual Paradigm Online, one of the first decisions you face is how much information you want to provide:
Should you enter a detailed prompt that fully describes your system or workflow?
Or should you start with a simple prompt and let the AI inspire you with ideas?
Both approaches are useful — they just serve different purposes. Understanding the difference helps you work faster and get diagrams that match your goal, whether you need precise visual documentation or early-stage creative direction.
This guide explains the differences, benefits, and ideal use cases for each prompt type, and also explores the commonly generated follow-up documents that teams create after receiving a diagram from the AI diagram generator.
1. What Is a Simple Prompt?
A simple prompt is a brief, high-level instruction that tells the VP AI Chatbot what type of diagram you want without going into specifics.
Examples include:
- “Create a UML Use Case Diagram for an online ticket system.”
- “Generate a C4 System Context model for a banking application.”
- “Show a SWOT Analysis for a travel company.”
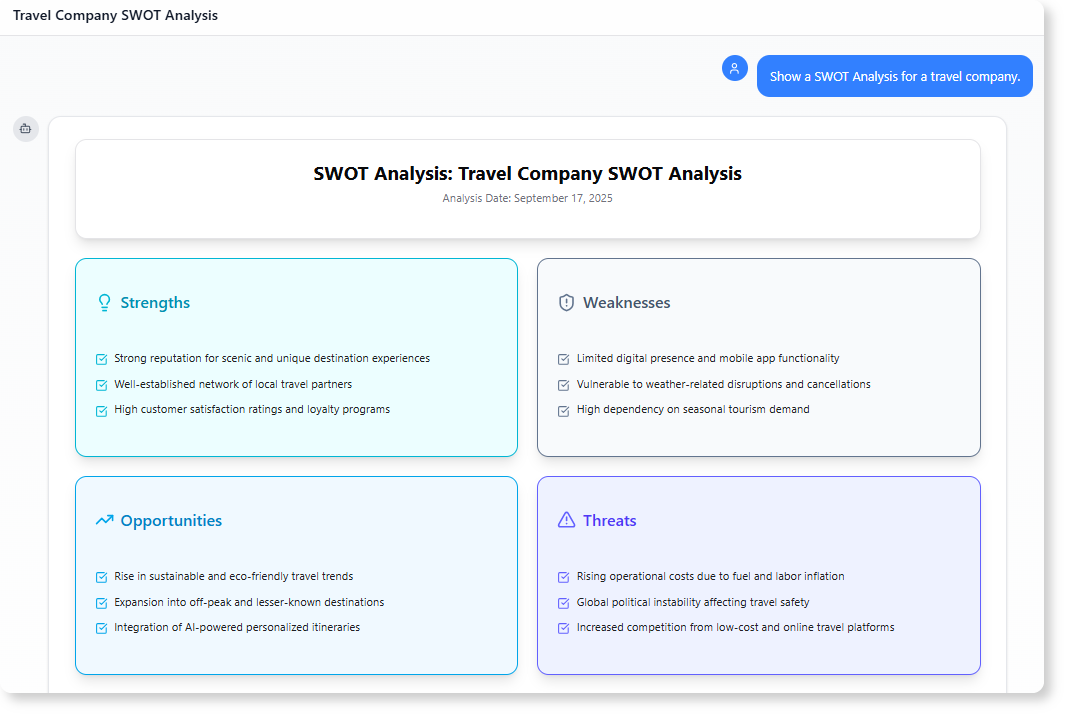
It gives the AI diagramming tool freedom to propose a structure, making it ideal for early exploration.
When to Use a Simple Prompt
(1) You want quick inspiration
If you do not yet know the details of your system or strategy, a simple prompt helps spark ideas. It is perfect when exploring frameworks like Ansoff Matrix, Eisenhower Matrix, or Blue Ocean Four Actions Framework.
(2) You are brainstorming or ideating
At early project stages, you may just want to see how a UML Activity Diagram, C4 Container diagram, or McKinsey 7S Model might look in general form.
(3) You need a fast starting point
During workshops or discussions, a simple prompt allows the AI diagram generator to produce a clean structure instantly.
What You Can Expect from a Simple Prompt
- General structure
- AI-suggested relationships
- Good as an initial draft
- Easy to refine with follow-up commands like “add login process” or “include a marketing channel”
2. What Is a Detailed Prompt?
A detailed prompt includes specific components, steps, rules, conditions, and naming conventions.
Examples include:
- “Create a UML Sequence Diagram with the steps: User selects product → System checks stock → Payment Gateway verifies card → Decision for success or failure.”
- “Generate a C4 Container model with a Web App, API Server, two external systems, and specific interactions.”
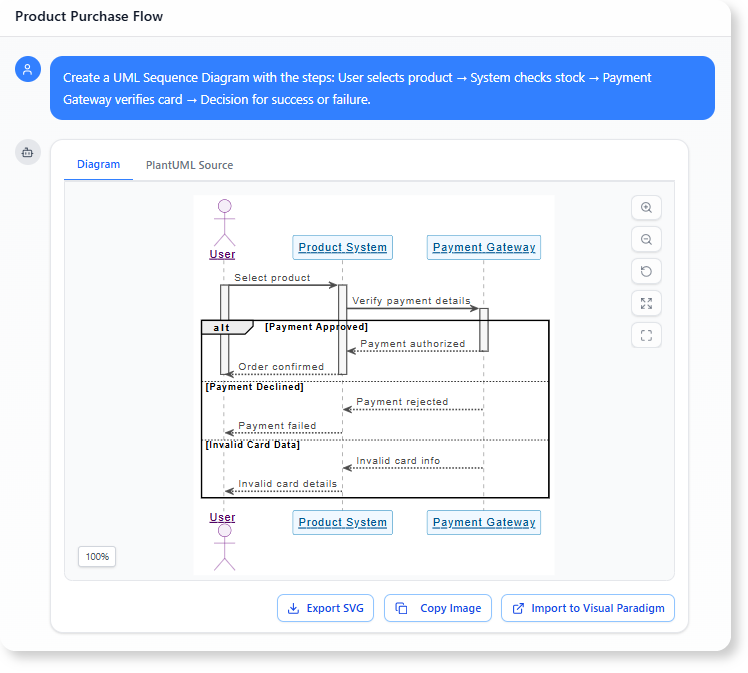
When to Use a Detailed Prompt
(1) You want a diagram that closely matches your requirements
A detailed prompt ensures the AI modeling assistant produces a diagram aligned to your exact system behavior or organizational needs.
This is essential for precise models like:
- UML Class Diagram
- UML Deployment Diagram
- UML Component Diagram
- C4 Deployment diagram
- ArchiMate Diagram
(2) You want to save editing time
Detailed prompts help produce diagrams that require little refinement, perfect for documentation and stakeholder approvals.
(3) You already have clear specifications
If you are working from requirements, user stories, PRDs, or system architecture descriptions, a detailed prompt will generate a highly accurate model.
What You Can Expect from a Detailed Prompt
- Highly specific structure
- Close alignment with business rules
- Models suitable for final documentation
- Minimal revisions required
3. Simple Prompt vs. Detailed Prompt: Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Simple Prompt | Detailed Prompt |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Inspiration / Draft | Precision / Documentation |
| Best For | Early-stage brainstorming | Mature project requirements |
| Speed | Very fast | Fast but requires effort |
| Output | Generalized diagram | Highly accurate diagram |
| Editing Needed | More | Very little |
4. Why Prompt Depth Matters in an AI Diagramming Tool
Choosing between simple and detailed prompts helps you:
(1) Get diagrams aligned to your real needs
A detailed prompt produces precise diagrams such as:
- UML State Machine Diagram
- UML Component Diagram
- C4 Component Diagram
- Requirement Diagram (SysML)
(2) Generate new ideas quickly
A simple prompt is perfect when exploring analytical models like:
- SWOT Analysis
- PEST Analysis
- SOAR Analysis
- Marketing Mix 4C’s Model
(3) Save time in planning 7and documentation
Instead of drawing manually, the AI diagram generator delivers a structured output that can be refined or extended instantly.
5. Common Follow-Up Documents Created After Using the VP AI Chatbot
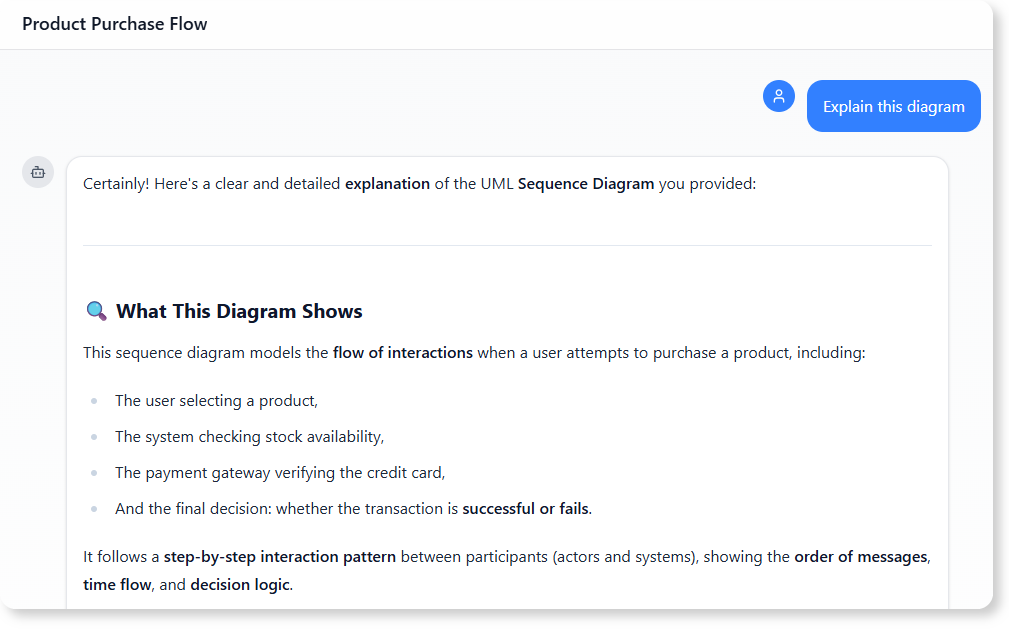
After generating a diagram, teams often ask the chatbot to produce related documentation. Below are the most common examples that align with your allowed diagram types:
(1) Process Narrative
For diagrams such as:
- UML Activity Diagram
- UML State Machine Diagram
(2) System Specification Document
Based on:
- UML Use Case Diagram
- UML Sequence Diagram
- UML Component Diagram
(3) Architecture Overview or Technical Design Document (TDD)
Created from:
- C4 System Context
- C4 Container
- C4 Component
- C4 Deployment
- UML Deployment Diagram
- UML Package Diagram
- ArchiMate Diagram
(4) Data Structure Summary
If creating structural diagrams like:
- UML Class Diagram
- UML Object Diagram
- UML Composite Structure Diagram
- Block Definition Diagram (SysML)
(5) Strategy or Analysis Summary
Useful when generating:
- SWOT Analysis
- PEST Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- SOAR Analysis
- Ansoff Matrix
- Blue Ocean Four Actions Framework
- McKinsey 7S Model
(6) Organization or Leadership Brief
Often created from:
- Organization Chart
- Marketing Mix 4C’s Model
Example follow-up prompts:
- “Write a system specification based on this UML Sequence Diagram.”
- “Explain the organizational impact of this McKinsey 7S Model.”
- “Create a strategy summary from the SWOT Analysis above.”
- “Write a component description based on this C4 Container diagram.”
6. When You Are Unsure — Start Simple, Then Refine with Detail
A practical workflow many teams use with the VP AI Chatbot:
- Start with a simple prompt to generate a high-level diagram.
- Review the structure to see if it captures the right concepts.
- Add details using commands like:
- “Add external systems to the C4 model.”
- “Add states for order processing in the UML State Machine Diagram.”
- “Include environmental factors in the PESTLE Analysis.”
- Generate follow-up documentation.
This allows flexibility while leading to highly accurate final outputs.
To learn more about UML and see how AI can help you visualize it, visit our UML resource hub.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













