From messy problem statements to clean, actionable class diagrams—in minutes.
🎯 What Is AI-Powered Textual Analysis?
Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered Textual Analysis is an intelligent modeling assistant that helps product managers, software architects, and developers translate unstructured natural language (e.g., user stories, requirements, or system descriptions) into a structured domain model — specifically, a UML Class Diagram.
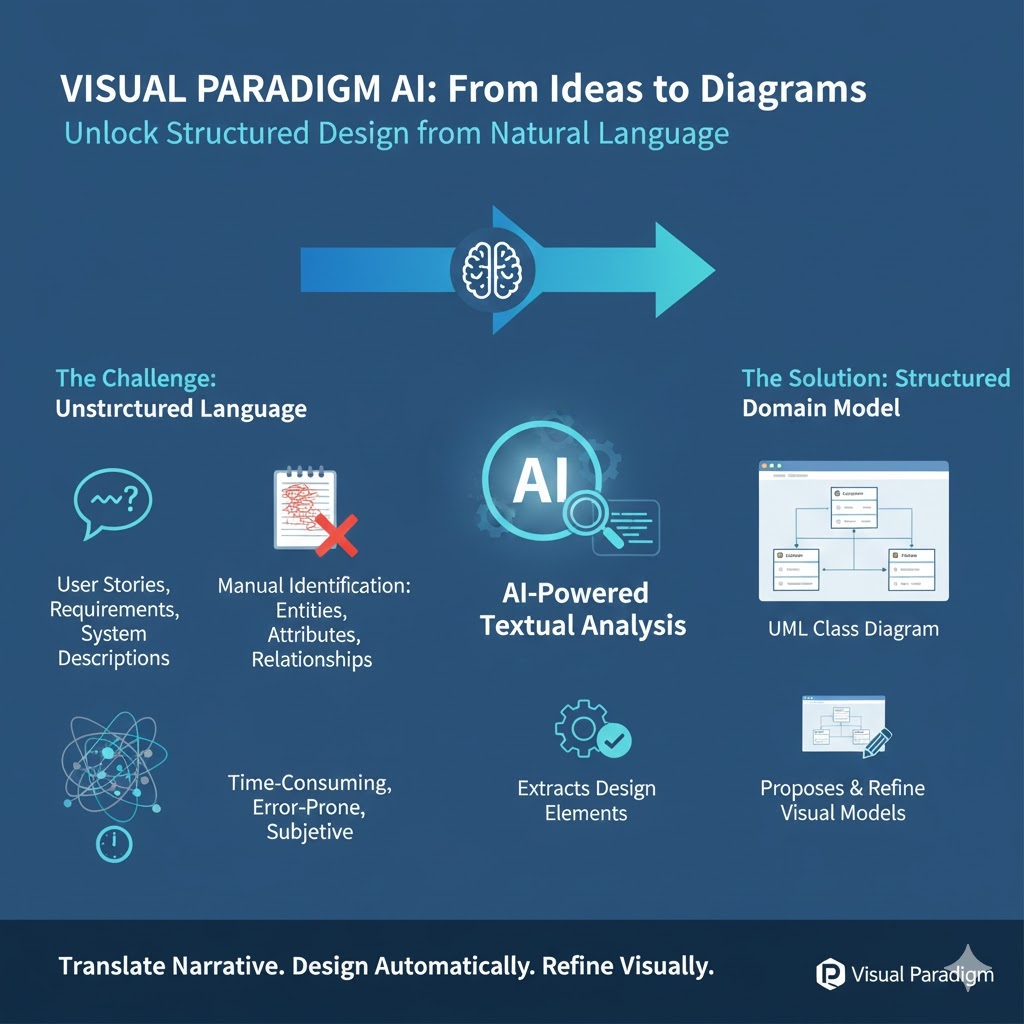
Instead of manually identifying entities, attributes, and relationships, the AI parses the text, extracts relevant design elements, and proposes a visual model you can refine.
🔍 Core Idea: Turn narrative → nouns → classes → relationships → diagram — automatically.
✅ Key Advantages
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed & Efficiency | Reduces initial modeling time from hours to minutes. |
| Consistency | Minimizes subjective interpretation across teams. |
| Learning Aid | Great for junior developers learning object-oriented design. |
| Traceability | Every suggestion includes a reason — transparent and auditable. |
| Iterative Refinement | Start with AI → edit freely in VP Online → export to code or docs. |
| Domain Discovery | Surfaces hidden concepts (e.g., Transaction, AuditLog) you might overlook. |
🛠️ Step-by-Step Tutorial (With Real Examples)
Let’s walk through three progressively complex examples, from simple to enterprise-grade.
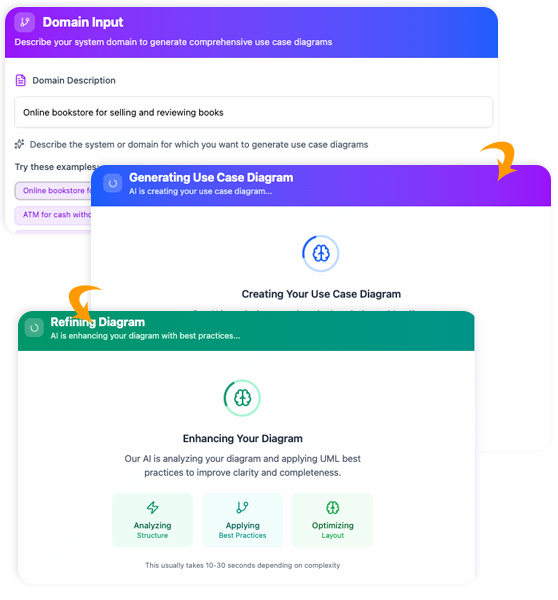
📘 Example 1: Library Management System (Starter)
📝 Step 1: Provide Problem Description
- Go to Tools > Apps > Textual Analysis > Start Now
- Enter:
Library Management System - Click [Generate Problem Description]
👉 AI generates:
“A library management system allows librarians to manage books, members, and loans. Members can search for books, borrow up to 5 items at a time, and return them. Overdue books incur fines. Each book has a title, author, ISBN, and availability status. Librarians can add/remove books and view loan history.”
✅ Edit if needed — e.g., add: “Supports digital e-books and reservation queues.”
👥 Step 2: Identify Candidate Classes
Click [Identify Candidate Classes]
| Class Name | Reason | Description |
|---|---|---|
Book |
Core entity mentioned repeatedly | Represents physical/digital books |
Member |
Subject of actions (borrows, returns) | Library user with contact info |
Loan |
Action noun → key transaction | Records borrowing of a book by a member |
Librarian |
Actor performing admin tasks | Staff managing the system |
Fine |
Consequence of overdue loans | Monetary penalty incurred |
🔁 Also see: “Nouns Not Qualified” (e.g., status, history → too vague or attribute-like).
✅ Accept all, or remove Librarian if roles are handled via permissions (e.g., using User + role flag).
📋 Step 3: Identify Class Details
Click [Identify Class Details]
Sample output for Book:
- Attributes:
isbn: String
title: String
author: String
isAvailable: Boolean
format: Enum {Physical, Digital} - Operations:
checkAvailability(): Boolean
markAsBorrowed()
markAsReturned()
For Loan:
- Attributes:
loanDate: Date
dueDate: Date
returnDate: Date? - Operations:
calculateOverdueDays(): Int
applyFine()
💡 Pro Tip: Rename isAvailable → status: BookStatus (enum: Available, Borrowed, Reserved) for extensibility.
🔗 Step 4: Identify Class Relationships
Click [Identify Class Relationships]
| From → To | Type | Multiplicity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Member — Loan |
Composition | 1 → * | A member owns their loans |
Loan — Book |
Association | 1 → 1 | Each loan involves one book |
Loan — Fine |
Optional Composition | 1 → 0…1 | A loan may generate a fine if overdue |
⚠️ Watch out: AI may miss aggregation vs composition. Edit manually if Loan should reference (not own) Book.
🖼️ Step 5: Generate Diagram
Click [Generate Diagram] → A full UML Class Diagram appears!
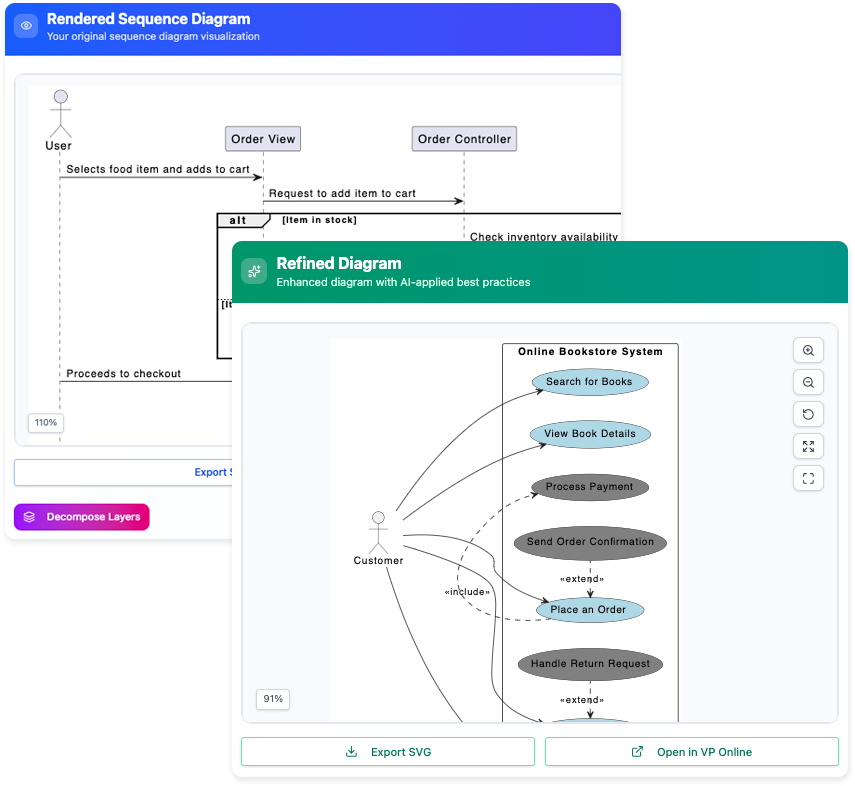
✅ Then click [Open in Visual Paradigm Online] to:
- Rearrange layout
- Add stereotypes (
«entity»,«boundary») - Link to use cases or sequence diagrams
- Export as PNG, PDF, or generate Java/Python stubs
🛒 Example 2: E-Commerce Shopping Cart (Intermediate)
Input Prompt:
“Online store where users browse products, add items to cart, apply promo codes, checkout with credit card or PayPal, and track orders. Admins manage inventory and view sales reports.”
AI-Identified Classes:
User,Product,ShoppingCart,CartItem,Order,Payment,PromoCode,Inventory,Admin
Notable Relationships:
ShoppingCart◇——CartItem(aggregation; cart has items, but items aren’t destroyed with cart)Order◆——Payment(composition; payment is part of order lifecycle)PromoCode——Order(0…1 → 1; optional at checkout)
Insight Gained:
AI suggests CartItem as separate from Product — good! Because:
CartItemhasquantity,addedAt, and snapshot of price (to handle price changes).ProducthascurrentPrice,stockLevel.
➡️ Prevents common modeling mistake: conflating catalog item with cart line item.
🏥 Example 3: Hospital Appointment System (Advanced)
Input Prompt (edited for realism):
“Patients schedule appointments with doctors. Each appointment has a date/time, type (e.g., consultation, follow-up), and status (scheduled, completed, canceled). Doctors have specialties and work schedules. The system sends reminders 24h prior. Nurses can check patients in. Lab results are attached post-visit.”
AI Highlights:
| Class | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
Appointment |
Central workflow object |
DoctorSchedule |
Separated from Doctor → respects SRP (Single Responsibility) |
Reminder |
External behavior → may become event-driven service later |
LabResult |
Attached to appointment, not patient — traceability! |
Smart Relationship:
Appointment◆——LabResult(1 → 0…*)
→ Enforces: Results only exist for completed appointments.
Hidden Gem:
AI flags "type" and "status" in appointment → suggests enums:
enum AppointmentType { CONSULTATION, FOLLOW_UP, VACCINATION }
enum AppointmentStatus { SCHEDULED, CHECKED_IN, COMPLETED, CANCELED }
✅ Developer saves time defining domain enums + validation logic.
🚀 Pro Tips for Maximizing Value
| Tip | How to Apply |
|---|---|
| Start vague, then refine | First prompt: "Food delivery app". Then edit generated description to add: “Supports restaurant onboarding, driver dispatch, real-time tracking, and rating system.” |
| Use user stories as input | Paste: “As a customer, I want to filter restaurants by cuisine and delivery time so I can choose quickly.” → AI extracts Cuisine, DeliveryTimeEstimate, FilterCriteria. |
| Combine with Use Case Modeling | Run Textual Analysis first to get classes → then derive actors & use cases (e.g., Customer → Place Order, Driver → Update Location). |
| Validate with CRC Cards | After AI suggests classes, do a quick CRC (Class-Responsibility-Collaborator) session with your team to sanity-check. |
| Export to Code | In VP Online: Right-click diagram → Tools > Code > Generate Code (Java, C#, Python supported). |
⚠️ Limitations & How to Mitigate
| Limitation | Mitigation |
|---|---|
May over-generate (e.g., Date, Time as classes) |
Review “Nouns Not Qualified” table → merge into attributes or use built-in types. |
| Can’t infer business rules (e.g., “max 3 loans”) | Add constraints as OCL (Object Constraint Language) or notes: { maxLoans = 3 } |
| Struggles with ambiguous nouns | Clarify in input: “‘User’ refers to customer, not admin” or “‘Session’ means therapy session, not login session.” |
| No inheritance detection by default | Manually add Patient, Doctor, Nurse → generalize to Person if needed. |
📊 When to Use It (Best Fit Scenarios)
| Scenario | Why It Shines |
|---|---|
| Early discovery workshops | Rapidly whiteboard domain model from raw notes |
| Agile sprint 0 / backlog refinement | Turn epics into candidate classes before grooming |
| Academic projects / capstones | Students focus on design logic, not notation |
| Legacy system modernization | Feed old BRDs (Business Requirement Docs) to extract domain model |
| Cross-functional alignment | Business + tech teams validate shared vocabulary |
🌐 Next Steps: Beyond the Diagram
Your AI-generated class diagram is just the beginning. In Visual Paradigm, you can:
- Generate Database Schema → ERD → SQL DDL
- Derive Sequence Diagrams from operations (e.g.,
Order.checkout()) - Link to Requirements (e.g., tie
applyPromoCode()to BRD section 4.2) - Simulate with VP Model Simulation
- Publish as Web Portal for stakeholder review
📬 Final Thought
“The AI doesn’t replace the designer — it replaces the tedium.”
Use Textual Analysis to get 80% of the model right in 20% of the time, then invest your expertise in the critical 20%: edge cases, scalability, and domain nuance.
📎 Ready to Try?
→ Launch: Visual Paradigm Online
→ App: Tools > Apps > Textual Analysis
Let me know if you’d like:
- A downloadable cheat sheet (PDF)
- Template prompts for fintech, SaaS, IoT, or healthcare domains
- Comparison with manual CRC/Domain Modeling
Happy modeling! 🧩
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













