Introduction Communication diagrams, also known as collaboration diagrams in UML 1.x, are a type of interaction diagram that emphasizes the
Continue reading
Learning one new thing everyday


Introduction Communication diagrams, also known as collaboration diagrams in UML 1.x, are a type of interaction diagram that emphasizes the
Continue reading
Introduction Unified Modeling Language (UML) sequence diagrams are essential tools in software engineering for visualizing how objects interact in a
Continue reading
Introduction Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standardized modeling language used in software engineering to visualize the design of a
Continue reading
1. Introduction 1.1 Overview of Sequence Diagrams Sequence diagrams are a crucial component of the Unified Modeling Language (UML), providing
Continue reading
1. Introduction 1.1 Background and Motivation The Unified Modeling Language (UML) has become a cornerstone in the field of software
Continue reading
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) was developed with several primary goals in mind, which have been refined over time to
Continue reading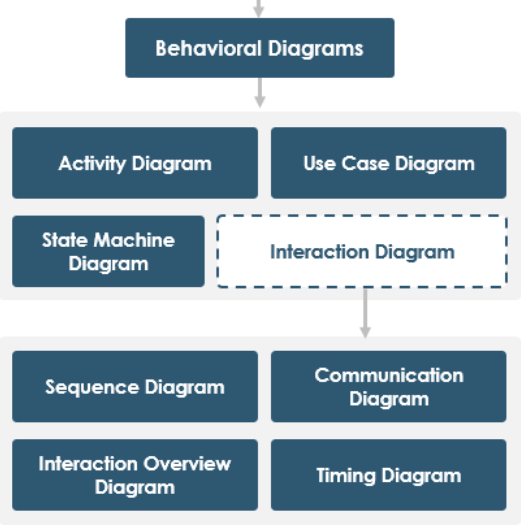
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a powerful tool for modeling the dynamic behavior of systems. It provides a rich
Continue reading
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) was developed with several key goals in mind, which are reflected in its design and
Continue reading
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a versatile and powerful tool for modeling a wide variety of systems, not limited to
Continue reading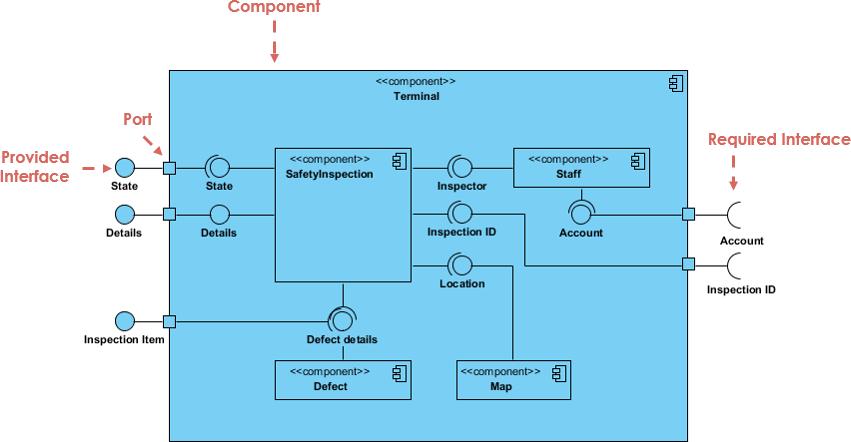
Introduction In this case study, we will explore the component diagram for an e-commerce system. The component diagram is a
Continue reading