The Comprehensive Guide to DBModeler AI: Transforming Database Design with Artificial Intelligence
In the traditional world of software engineering, database design has historically been a bottleneck. Translating business requirements into technical tables, defining keys, and painstakingly ensuring normalization rules are met is often a slow, error-prone process. Enter DBModeler AI by Visual Paradigm.
This comprehensive guide explores how DBModeler AI acts as an intelligent data design assistant, transforming plain English requirements into fully normalized, production-ready database schemas in a matter of minutes.
Key Concepts
Before diving into the workflow of DBModeler AI, it is essential to understand the foundational concepts that drive this tool. These definitions will help clarify the technical processes automated by the AI.
- ERD (Entity-Relationship Diagram): A flowchart that illustrates how “entities” (people, objects, or concepts) relate to each other within a system. It is the blueprint of a database.
- Normalization (1NF, 2NF, 3NF): The process of organizing data in a database. This involves creating tables and establishing relationships according to rules designed to protect the data and make the database more flexible by eliminating redundancy and inconsistent dependency.
- SQL DDL (Data Definition Language): A subset of SQL commands used to define data structures. For example, commands like
CREATE TABLEorALTER TABLE. - Domain Class Diagram: A visual representation of the conceptual classes in a system and their relationships, often used as a precursor to the detailed database design.
What is DBModeler AI?
DBModeler AI is a revolutionary, browser-based environment designed to bridge the gap between abstract concepts and executable code. It solves the complexity of manual schema creation by instantly translating plain English descriptions into robust, normalized database designs.
For teams seeking cloud agility, Visual Paradigm Online hosts this feature, serving as an accessible ERD tool and database modeling software. It functions not just as a drawing tool, but as an intelligent co-pilot that guides users from an initial idea to a fully-normalized, visualized, and tested schema.
How It Works: The 7-Step Workflow
DBModeler AI structures the complex task of database design into a seamless, interactive, AI-guided journey. Here is the step-by-step breakdown of how it transforms a problem description into an interactive SQL playground.
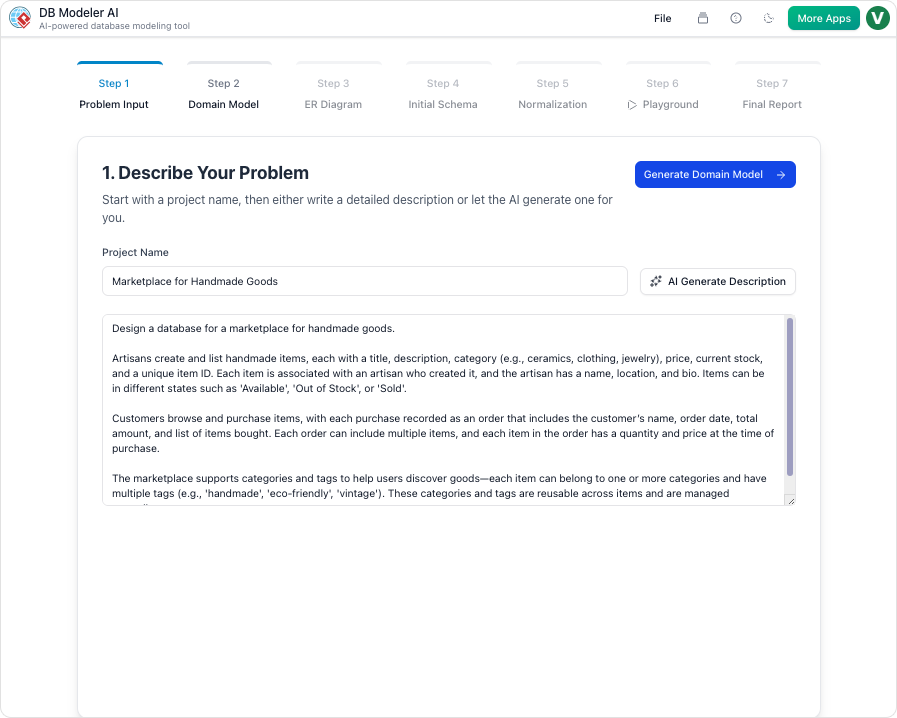
Step 1: Problem Input
The process begins with natural language. Users describe their application idea—for example, “A system to manage gym memberships and classes”—in plain English. The AI analyzes this input and expands the concept into detailed technical requirements, effectively acting as a business analyst.
Step 2: Domain Class Diagram
Before diving into tables, the tool visualizes high-level objects. It generates an editable PlantUML domain class diagram representing the entities and their attributes. This allows architects and developers to verify the conceptual model before technical implementation.
Step 3: ER Diagram
The AI converts the domain model into a database-specific Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD). At this stage, keys (primary and foreign) and specific relationships between entities are defined, providing a visual map of the database structure.
Step 4: Initial Schema Generation
Visual diagrams are translated into code. The system generates PostgreSQL-compatible SQL DDL statements based on the ERD. This automated translation ensures that the syntax is correct and ready for deployment.
Step 5: Intelligent Normalization
This is arguably the most powerful feature of DBModeler AI. The tool progressively optimizes the schema through 1NF (First Normal Form), 2NF, and 3NF. Unlike black-box automation, the AI provides educational explanations and rationales for every change it suggests. This stepwise normalization ensures redundancy is eliminated and data integrity is maintained.
Step 6: Interactive Playground
Historically, testing a schema required setting up a local database server. DBModeler AI removes this friction with an in-browser SQL client. The AI seeds the database with realistic, generated sample data, allowing users to run queries and test the design instantly without any installation.
Step 7: Final Report and Export
Once the design is validated, the final output—including all diagrams, documentation, and SQL scripts—can be exported as a polished PDF or JSON package. This facilitates easy handoff to development teams or integration into project documentation.
Use Cases and Benefits
DBModeler AI is versatile, catering to various roles within the software development lifecycle:
- Developers: Can bootstrap and validate the database layer for side projects or prototypes in minutes rather than hours.
- Students: The tool acts as an interactive tutor for learning relational modeling and normalization, providing instant feedback and explanations.
- Product Managers: Can turn loose business requirements into concrete technical specifications and ERDs for clearer communication with engineering teams.
- System Architects: Enables rapid prototyping and documentation of complex data relationships visually.
Getting Started
DBModeler AI is available for Visual Paradigm users with a Professional Edition license (or higher) and an active maintenance plan. Because it is browser-based, it can be accessed from anywhere via the Visual Paradigm Online platform.
Tips for Best Results
- Iterate on Requirements: Spend time refining your Step 1 input. A clearer problem description leads to a better initial schema.
- Leverage AI Explanations: Use the rationales provided during the normalization steps (Step 5) to understand why changes are being made, which is crucial for maintaining the database long-term.
- Test Thoroughly: Utilize the generated dummy data in the SQL playground to ensure your queries return expected results before exporting to a production environment.
Conclusion
Visual Paradigm’s DBModeler AI represents a significant leap forward in database design. By combining expert guidance, visual diagramming, and live SQL testing, it allows users to control every step of the design process with AI as a co-pilot. Whether you are building a complex enterprise system or learning the ropes of SQL, DBModeler AI ensures your foundation is solid, normalized, and ready for deployment.
Resources
- DB Modeler AI | AI-Powered Database Design Tool
- DBModeler AI
- DBModeler AI: Database Design Tool – Visual Paradigm Product …
- Data Modeling / Database Archives – Visual Paradigm Guides
- DBModeler AI – Interactive Database Design & Normalization Tool
- Visual Paradigm Database Designer Guides
- ERD Tool with AI | Visual Paradigm
- The Ultimate AI ERD Tool & Database Design Software
- Visual Paradigm AI: Advanced Software & Intelligent Apps
- How to Design Relational Database with ERD?
- How to Generating DB Specification from Database>
- Mastering Advanced ERD Modeling: A Comprehensive Tutorial with Examples
- AI Chatbot | Diagramming & Modeling with Visual Paradigm
- How to Model Relational Database Design with ERD?
- ERD / Database Generation Tool

